Question: Input: A nondeterministic finite automaton (NFA) is a 5-tuple (Q, y, qa, A, 5), where Q is a finite set of states, is a finite
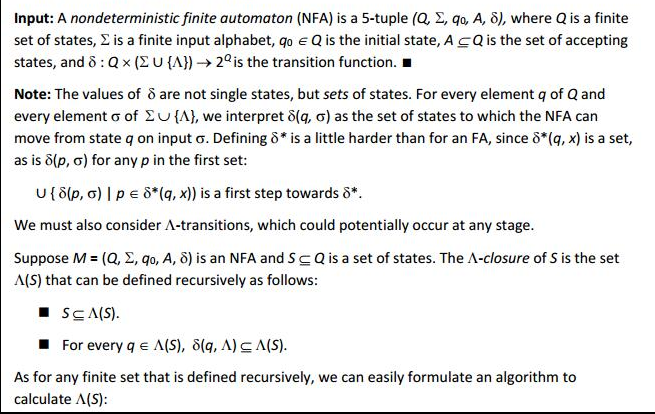

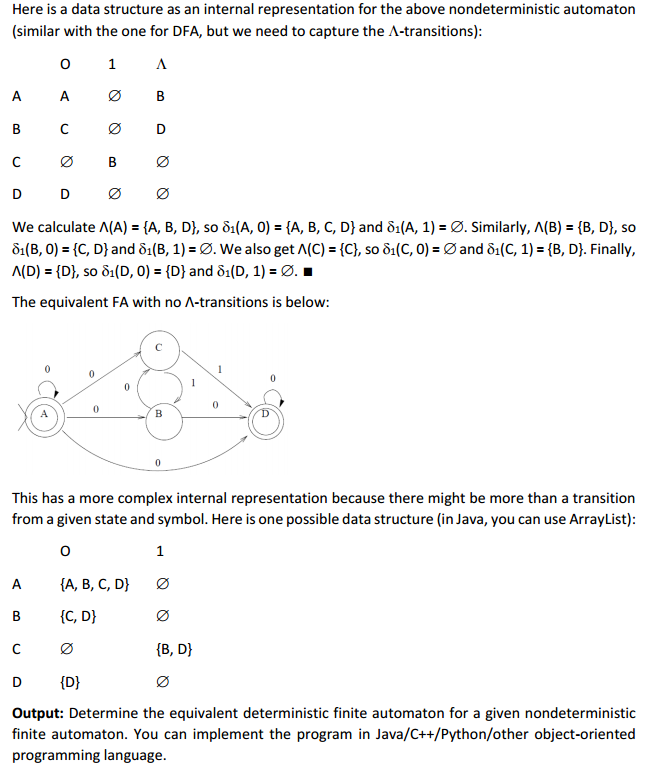
Input: A nondeterministic finite automaton (NFA) is a 5-tuple (Q, y, qa, A, 5), where Q is a finite set of states, is a finite input alphabet, qo E Q is the initial state, A c Q is the set of accepting states, and Q x U{A) 2 is the transition function. Note: The values of are not single states, but sets of states. For every element q of Q and every element of NU A), we interpret o(q, G) as the set of states to which the NFA can move from state q on input o. Defining is a little harder than for an FA, since (q, x) is a set, as is 5(p, o) for any p in the first set: u{6(p, o) l p E (q, x)) is a first step towards o*. We must also consider A-transitions, which could potentially occur at any stage. Suppose M (Q, y, qo, A, o) is an NFA and Sg Q is a set of states. The A-closure of S is the set A(S) that can be defined recursively as follows: SgA (S) For every q E A(S), (q, A) cA(S). As for any finite set that is defined recursively, we can easily formulate an algorithm to calculate A(S)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


