Question: INSTRUCTIONS: EXAMPLE OF A CRASHING PROJECT FOR REFERENCE: Problem 3. (Chapter 5 Project Management) Table below contains information about an environmental clean-up project. Shorten the
INSTRUCTIONS: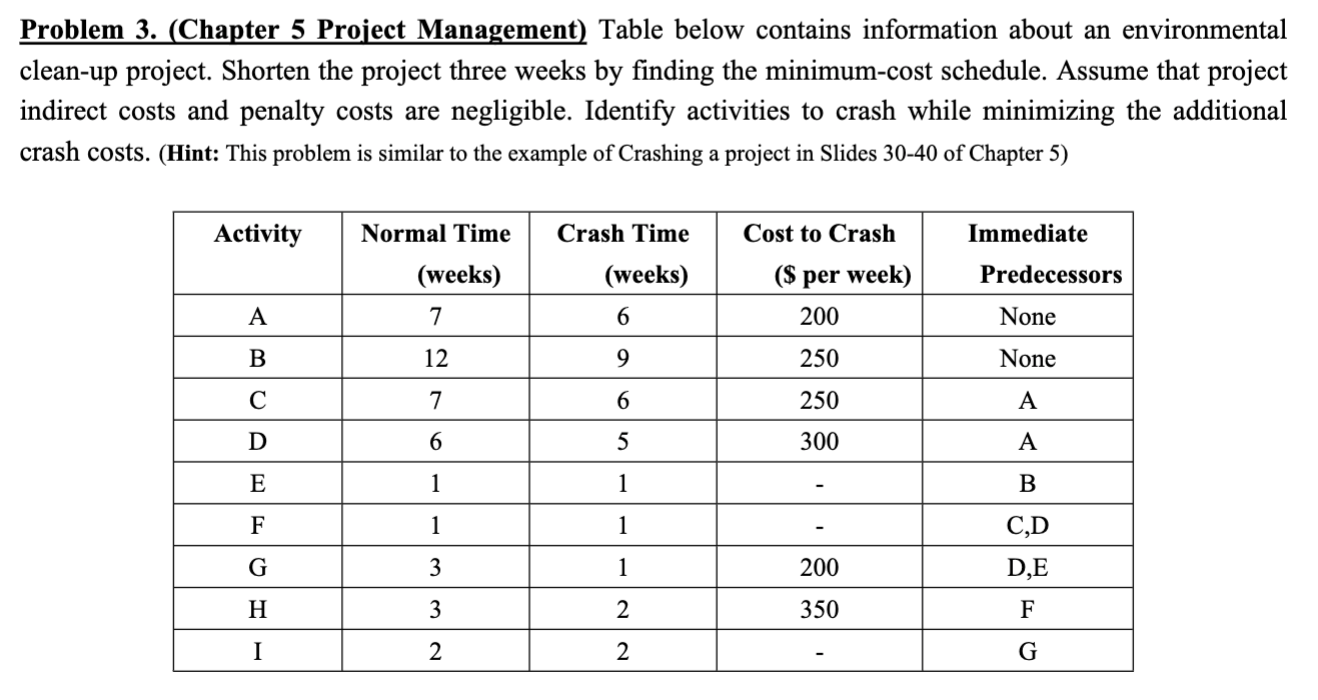
EXAMPLE OF A CRASHING PROJECT FOR REFERENCE:

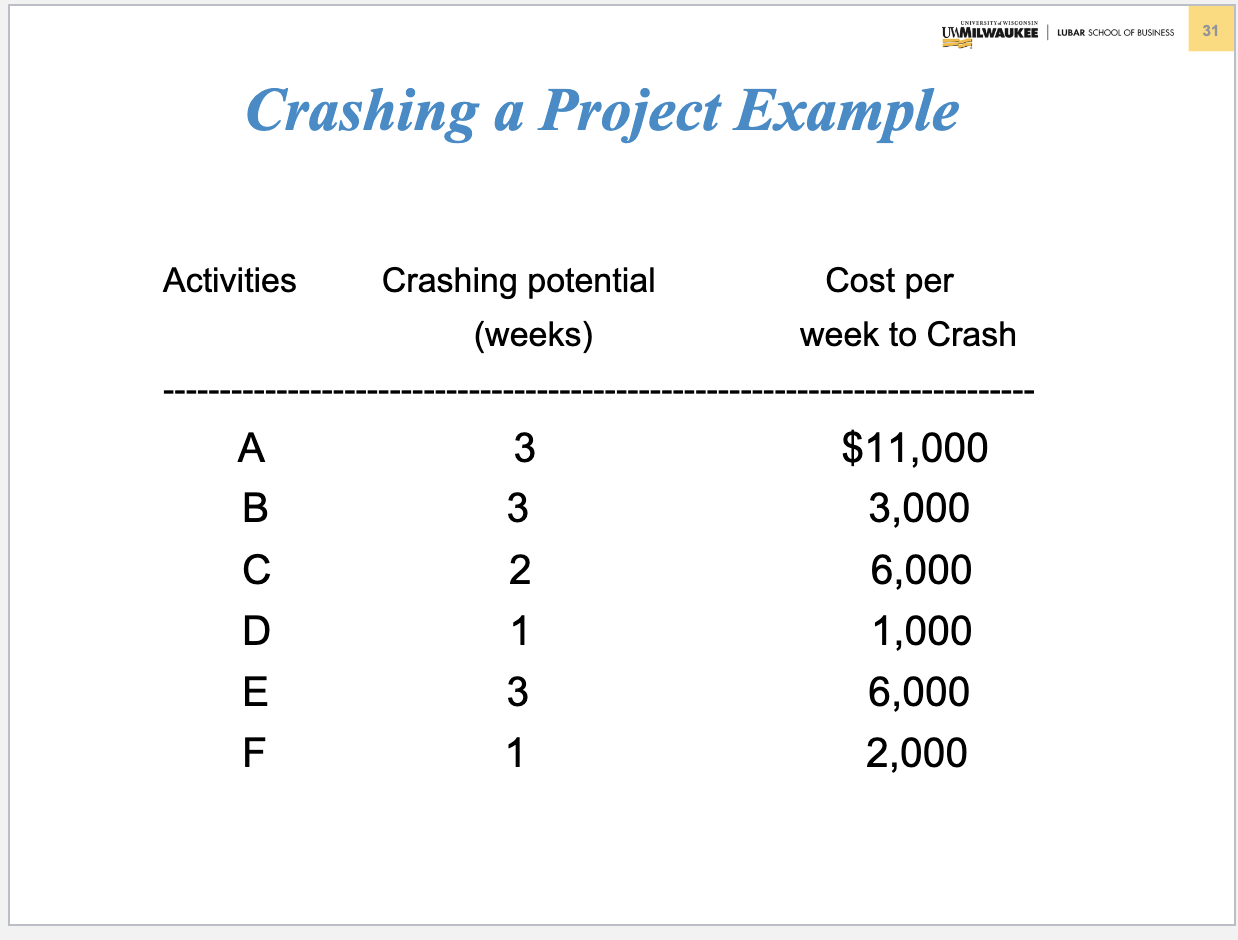
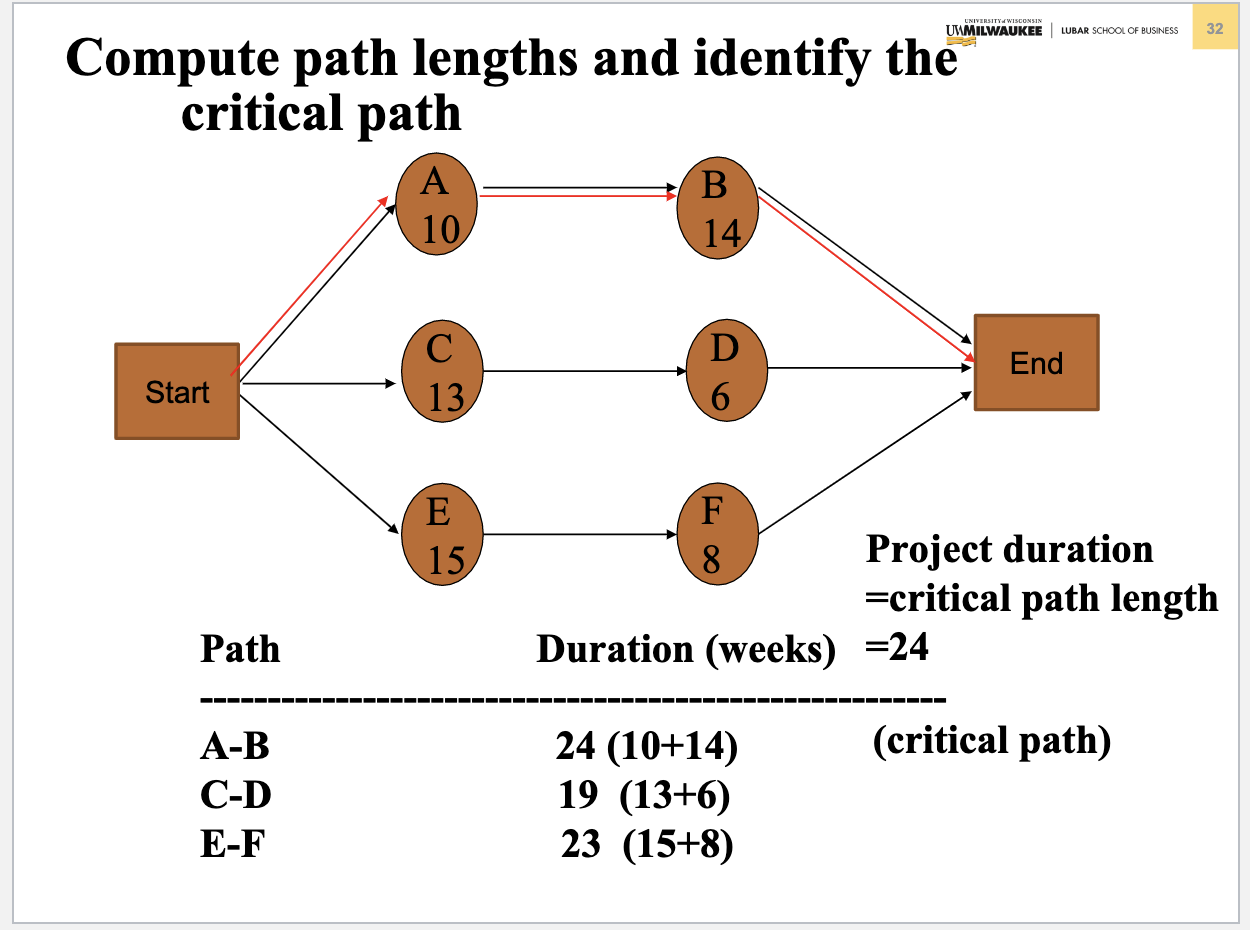

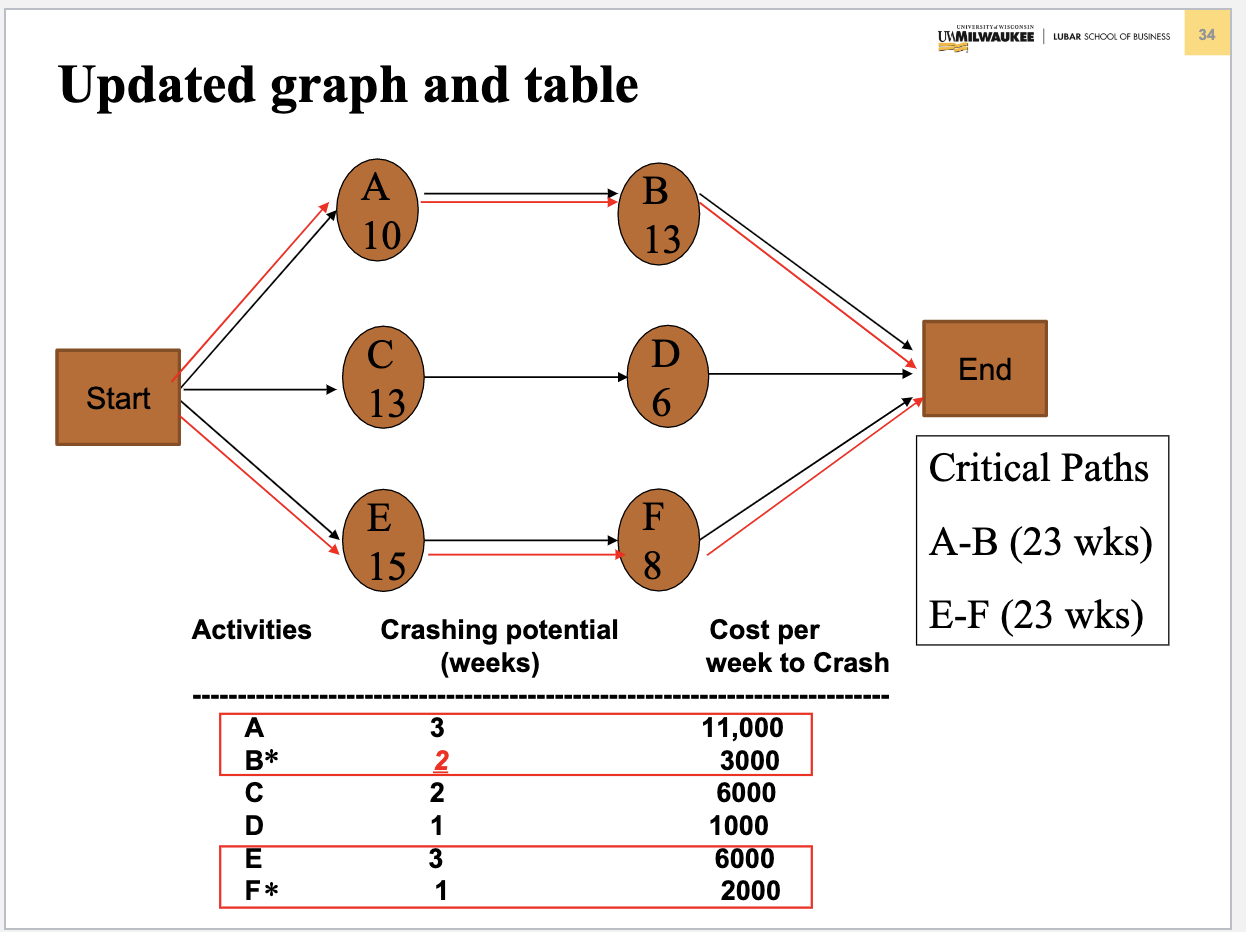

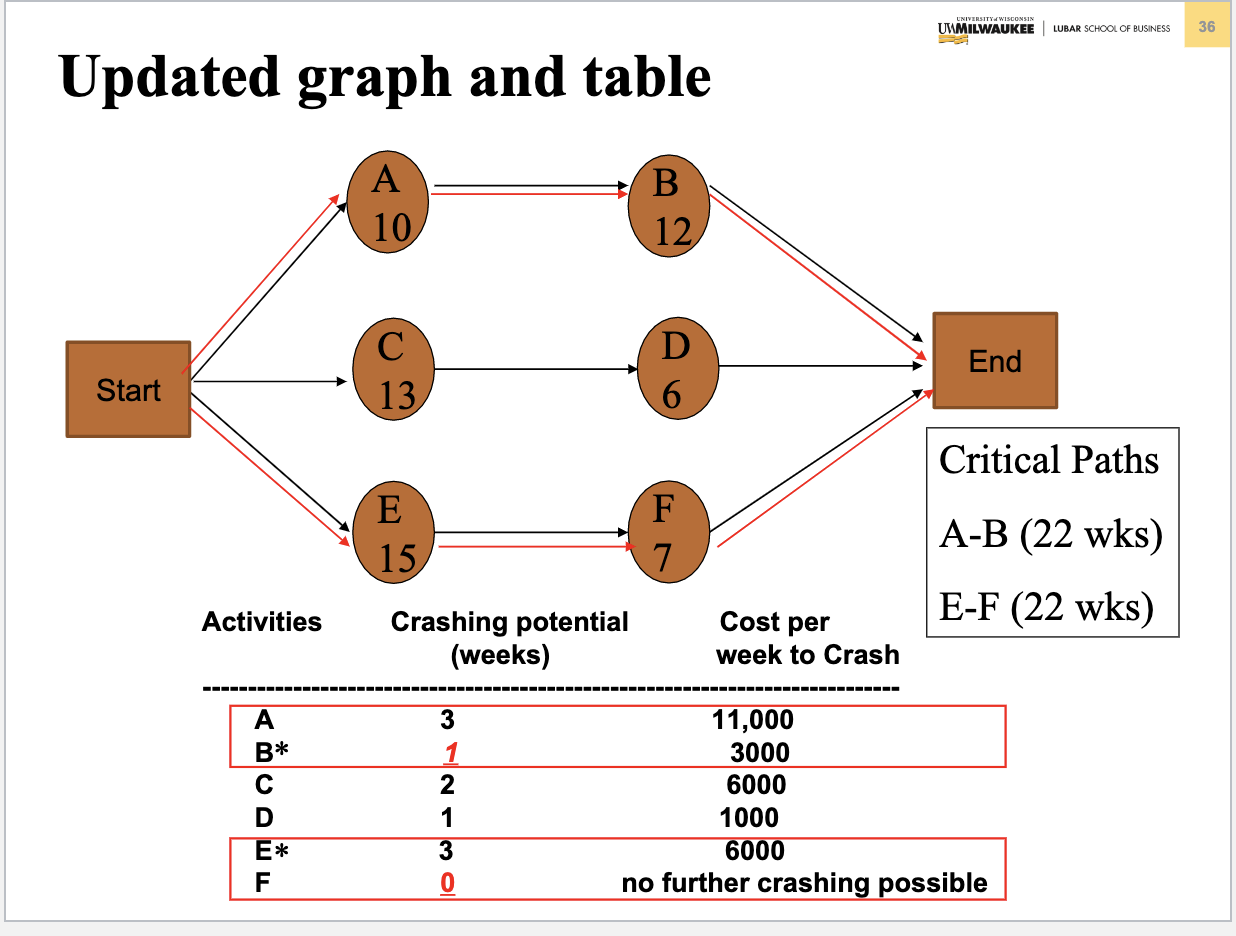
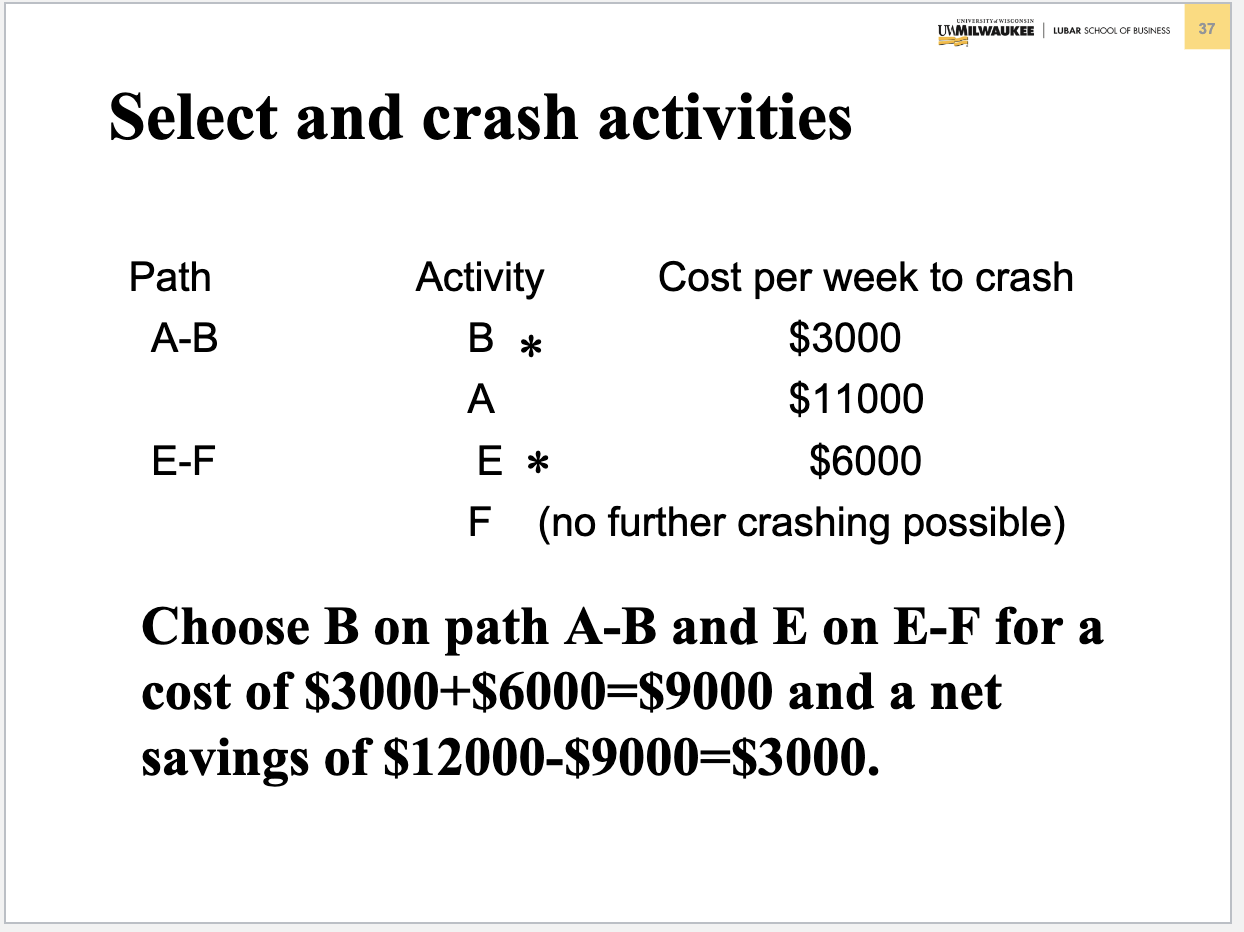
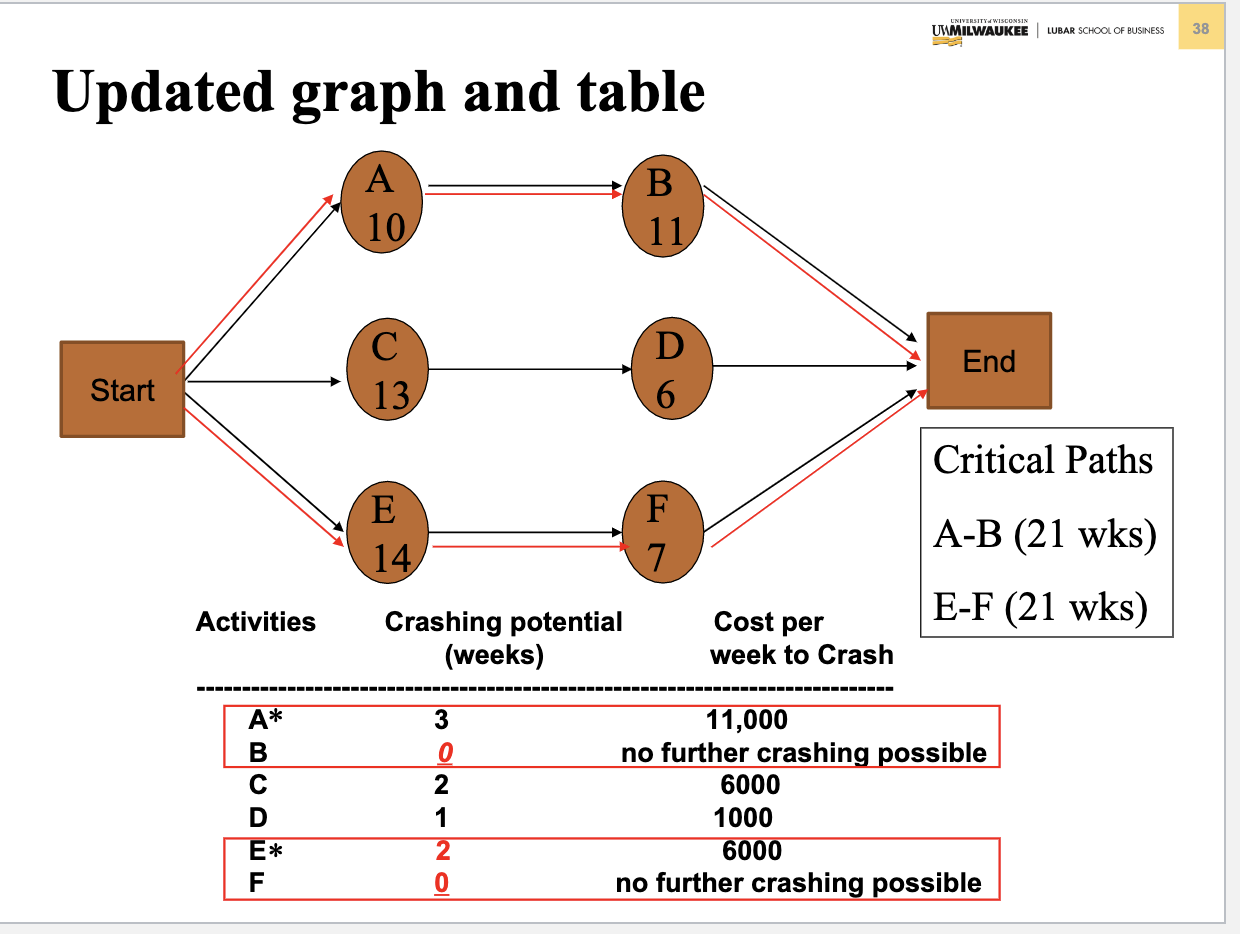
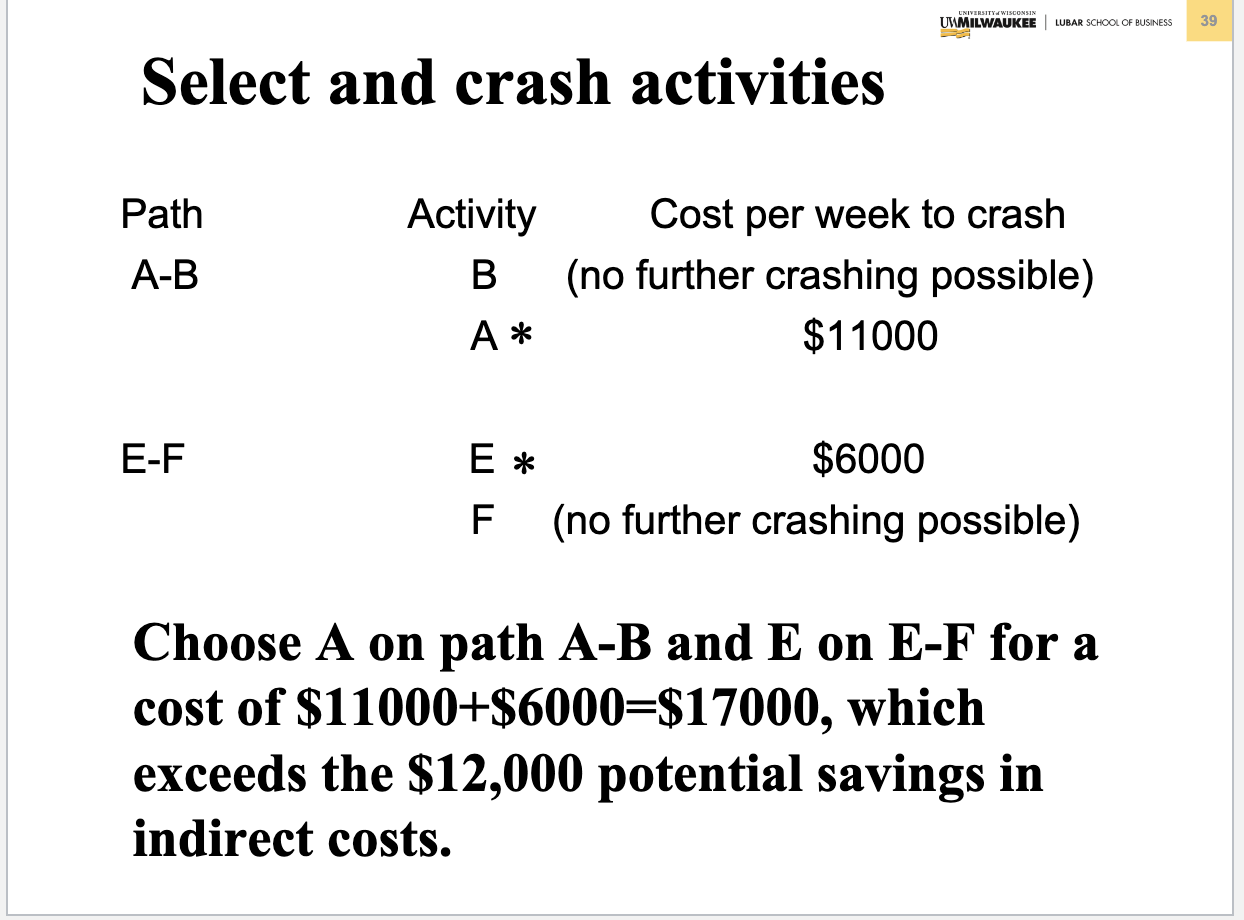
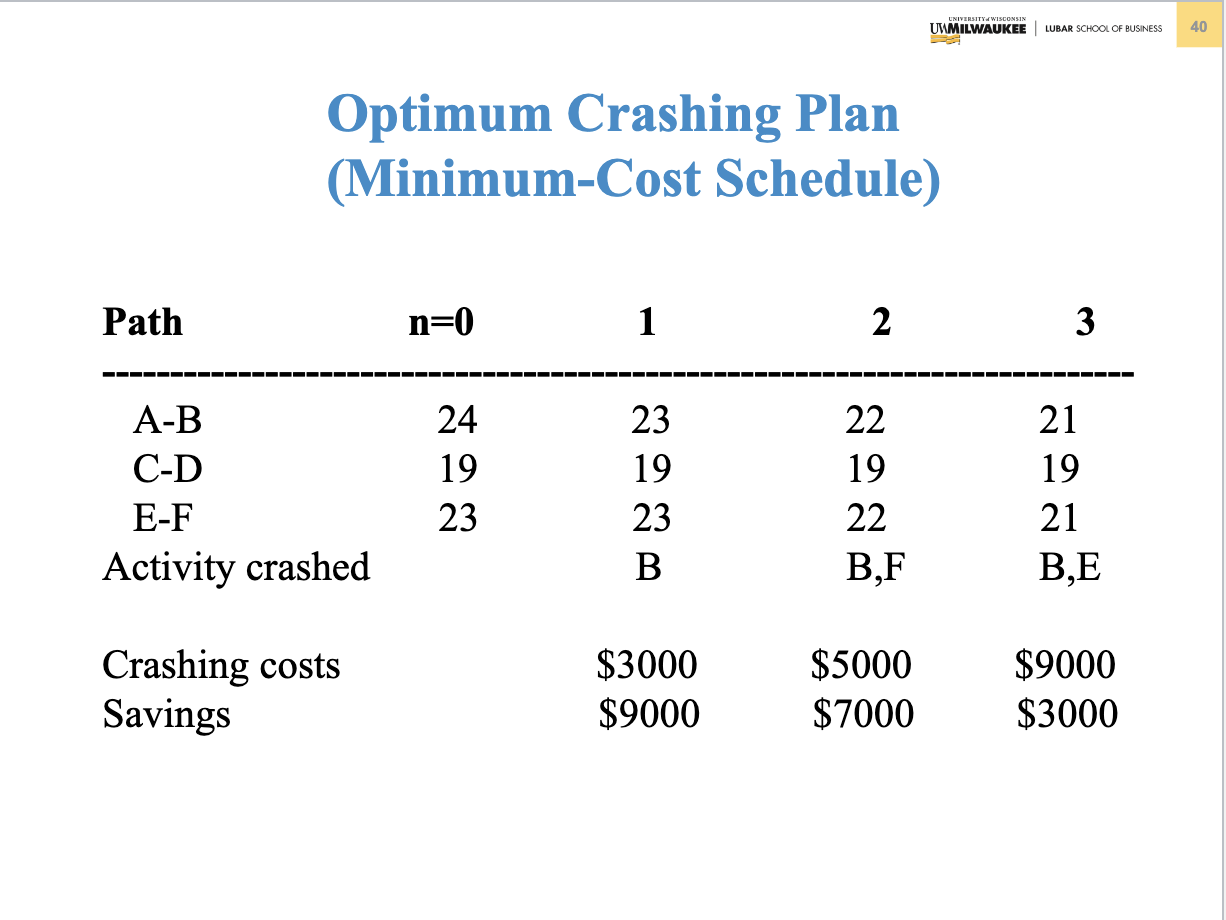
Problem 3. (Chapter 5 Project Management) Table below contains information about an environmental clean-up project. Shorten the project three weeks by finding the minimum-cost schedule. Assume that project indirect costs and penalty costs are negligible. Identify activities to crash while minimizing the additional crash costs. (Hint: This problem is similar to the example of Crashing a project in Slides 3040 of Chapter 5) Step 1. Find the critical path and identify the critical activitie Step 2 If there is only one critical path, select and crash the activity by one unit on the critical path with the smallest crash cost per unit. If there are more than one critical path (e.g. two or three), select and crash one activity by one unit with the smallest crash cost per unit on each critical path. Step 3. Return to step 1. Crashing should continue as long as the cost to crash is less than the benefit derived from crashing. Crashing a Project Example Comnitta noth lannths ond idnntifor thon Select and crash activities B is selected since it has the lower crashing cost. This would reduce indirect cost by $12,000 at a cost of $3,000, for a net saving of $9,000. Updated graph and table Select and crash activities Choose one activity (the least costly) on each path to crash: B on AB and F on E F, for a total cost of $3000+$2000=$5000 and a net savings of $12000$5000=$7000. Updated graph and table Select and crash activities Choose B on path AB and E on E-F for a cost of $3000+$6000=$9000 and a net savings of $12000$9000=$3000. Updated graph and table Select and crash activities Choose A on path A-B and E on E-F for a cost of $11000+$6000=$17000, which exceeds the $12,000 potential savings in indirect costs. Optimum Crashing Plan (Minimum-Cost Schedule)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


