Question: Instructions: This exercise should be done by hand, that is, not using Python. All necessary calculations should be included in the submission, as well as
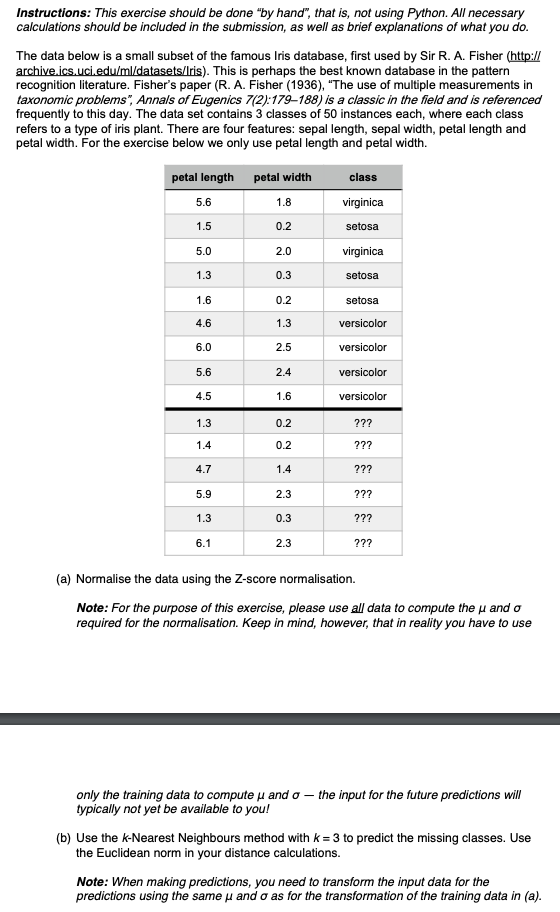
Instructions: This exercise should be done by hand", that is, not using Python. All necessary calculations should be included in the submission, as well as brief explanations of what you do. The data below is a small subset of the famous Iris database, first used by Sir R. A. Fisher (http:// archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Iris). This is perhaps the best known database in the pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper (R. A. Fisher (1936), "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems", Annals of Eugenics 7(2):179-188) is a classic in the field and is referenced frequently to this day. The data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a type of iris plant. There are four features: sepal length, sepal width, petal length and petal width. For the exercise below we only use petal length and petal width petal width petal length 5.6 1.8 class virginica setosa 1.5 0.2 5.0 2.0 virginica 1.3 0.3 setosa 1.6 0.2 setosa versicolor 4.6 1.3 6.0 2.5 5.6 2.4 versicolor versicolor versicolor 4.5 1.6 1.3 0.2 ??? 1.4 0.2 ??? 4.7 1.4 ??? 5.9 2.3 ??? 1.3 0.3 ??? 6.1 2.3 ??? (a) Normalise the data using the Z-score normalisation. Note: For the purpose of this exercise, please use all data to compute the u and o required for the normalisation. Keep in mind, however, that in reality you have to use only the training data to compute and o the input for the future predictions will typically not yet be available to you! (b) Use the k-Nearest Neighbours method with k = 3 to predict the missing classes. Use the Euclidean norm in your distance calculations. Note: When making predictions, you need to transform the input data for the predictions using the same u and o as for the transformation of the training data in (a). Instructions: This exercise should be done by hand", that is, not using Python. All necessary calculations should be included in the submission, as well as brief explanations of what you do. The data below is a small subset of the famous Iris database, first used by Sir R. A. Fisher (http:// archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Iris). This is perhaps the best known database in the pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper (R. A. Fisher (1936), "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems", Annals of Eugenics 7(2):179-188) is a classic in the field and is referenced frequently to this day. The data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a type of iris plant. There are four features: sepal length, sepal width, petal length and petal width. For the exercise below we only use petal length and petal width petal width petal length 5.6 1.8 class virginica setosa 1.5 0.2 5.0 2.0 virginica 1.3 0.3 setosa 1.6 0.2 setosa versicolor 4.6 1.3 6.0 2.5 5.6 2.4 versicolor versicolor versicolor 4.5 1.6 1.3 0.2 ??? 1.4 0.2 ??? 4.7 1.4 ??? 5.9 2.3 ??? 1.3 0.3 ??? 6.1 2.3 ??? (a) Normalise the data using the Z-score normalisation. Note: For the purpose of this exercise, please use all data to compute the u and o required for the normalisation. Keep in mind, however, that in reality you have to use only the training data to compute and o the input for the future predictions will typically not yet be available to you! (b) Use the k-Nearest Neighbours method with k = 3 to predict the missing classes. Use the Euclidean norm in your distance calculations. Note: When making predictions, you need to transform the input data for the predictions using the same u and o as for the transformation of the training data in (a)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


