Question: Introduction For this program, let's explore some of the ways we can use C to perform numerical integration. We'll restrict our attention to definite integrals
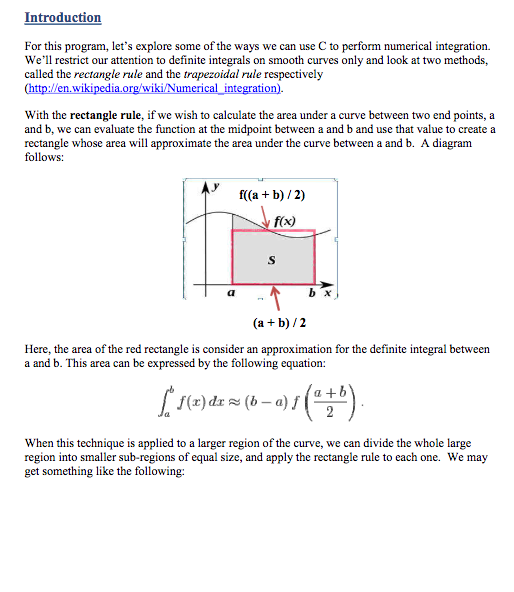
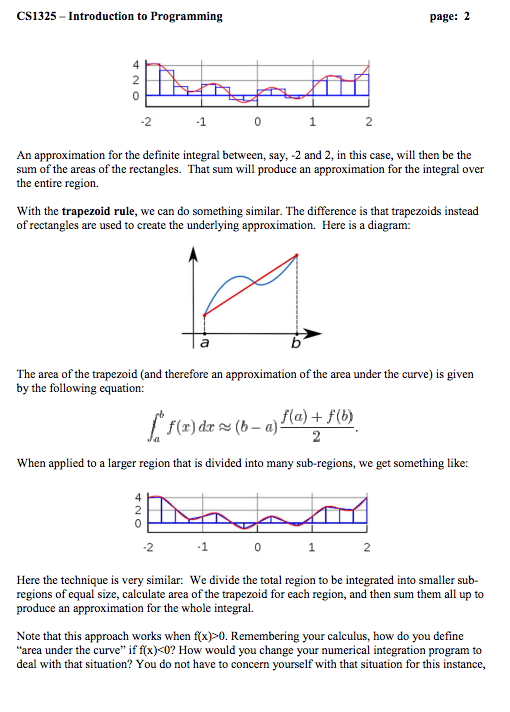

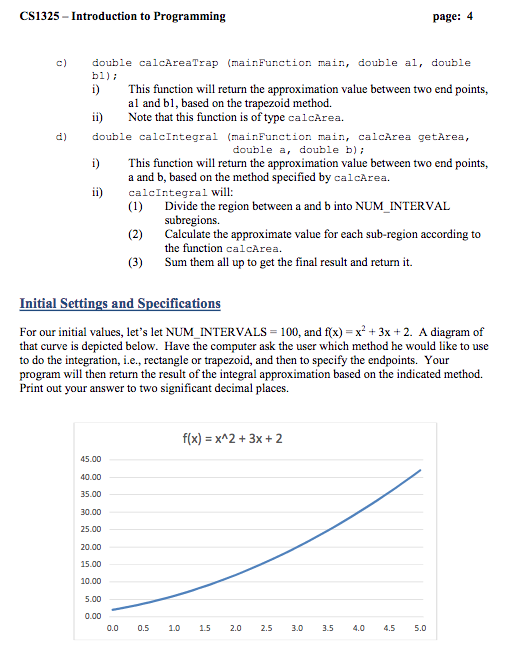

Introduction For this program, let's explore some of the ways we can use C to perform numerical integration. We'll restrict our attention to definite integrals on smooth curves only and look at two methods, called the rectangle rule and the trapezoidal rule respectively With the rectangle rule, if we wish to calculate the area under a curve between two end points,a and b, we can evaluate the function at the midpoint between a and b and use that value to create a rectangle whose area will approximate the area under the curve between a and b. A diagram follows: f((a +b) 2) f(a) b x (a +b)/2 Here, the area of the red rectangle is consider an approximation for the definite integral between a and b. This area can be expressed by the following equation: [1(r) dz ~ (b-a) ,() When this technique is applied to a larger region of the curve, we can divide the whole large region into smaller sub-regions of equal size, and apply the rectangle rule to each one. We may get something like the following
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


