Question: Inventory Model As a distributor for PC Tech, you sell XP computers to retailers. The monthly demand for XP computers is Poisson with a mean

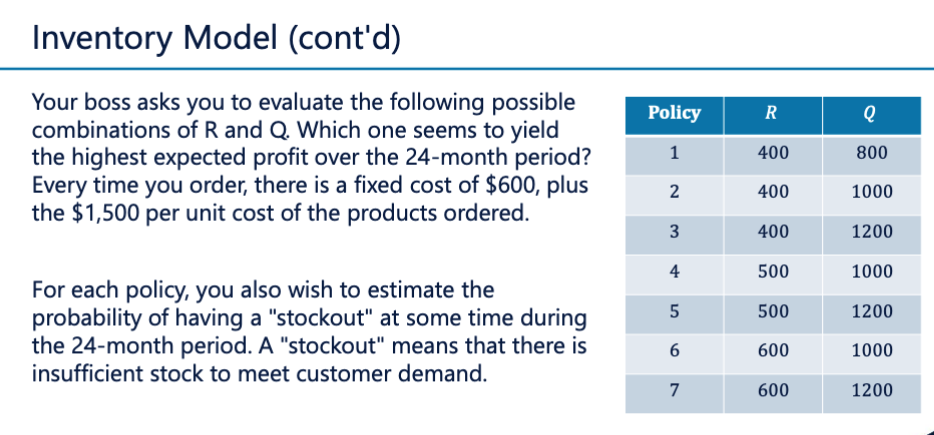
Inventory Model As a distributor for PC Tech, you sell XP computers to retailers. The monthly demand for XP computers is Poisson with a mean of 400. The units cost you $1,500 each, and you sell them for $2,800. You can carry inventory from month-to-month, and estimate your inventory holding cost as $10 per unit left in inventory at the end of a month. Every time you order from PC Tech, there is a fixed cost of $600, plus the $1,500 per unit cost of the products ordered. You want to simulate a 24-month period, at the outset of which you have 700 units in stock. For every unit in stock at the end of this period, you assess a "salvage" credit of $1,500. You are considering ordering policies of the following form: if the ending inventory for a given month is less than or equal to some "threshold" value R, immediately order another Q units. For simplicity, assume that these units become available immediately at the beginning of the next month. Inventory Model (cont'd) Policy R Q Your boss asks you to evaluate the following possible combinations of R and Q. Which one seems to yield the highest expected profit over the 24-month period? Every time you order, there is a fixed cost of $600, plus the $1,500 per unit cost of the products ordered. 1 400 800 2 400 1000 3 400 1200 4 500 1000 5 500 1200 For each policy, you also wish to estimate the probability of having a "stockout" at some time during the 24-month period. A "stockout" means that there is insufficient stock to meet customer demand. 6 600 1000 7 600 1200 Inventory Model Simulation approach >What is the decision variable? Range of values? >What are the input random variables? Distributions? >What is the output random variable? Metrics of interest? Inventory Model As a distributor for PC Tech, you sell XP computers to retailers. The monthly demand for XP computers is Poisson with a mean of 400. The units cost you $1,500 each, and you sell them for $2,800. You can carry inventory from month-to-month, and estimate your inventory holding cost as $10 per unit left in inventory at the end of a month. Every time you order from PC Tech, there is a fixed cost of $600, plus the $1,500 per unit cost of the products ordered. You want to simulate a 24-month period, at the outset of which you have 700 units in stock. For every unit in stock at the end of this period, you assess a "salvage" credit of $1,500. You are considering ordering policies of the following form: if the ending inventory for a given month is less than or equal to some "threshold" value R, immediately order another Q units. For simplicity, assume that these units become available immediately at the beginning of the next month. Inventory Model (cont'd) Policy R Q Your boss asks you to evaluate the following possible combinations of R and Q. Which one seems to yield the highest expected profit over the 24-month period? Every time you order, there is a fixed cost of $600, plus the $1,500 per unit cost of the products ordered. 1 400 800 2 400 1000 3 400 1200 4 500 1000 5 500 1200 For each policy, you also wish to estimate the probability of having a "stockout" at some time during the 24-month period. A "stockout" means that there is insufficient stock to meet customer demand. 6 600 1000 7 600 1200 Inventory Model Simulation approach >What is the decision variable? Range of values? >What are the input random variables? Distributions? >What is the output random variable? Metrics of interest
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


