Question: Item 1 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by

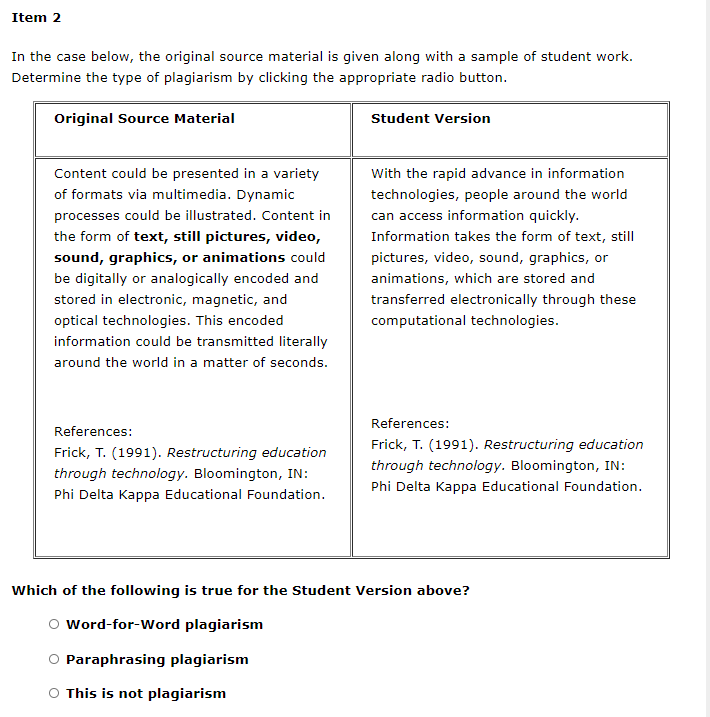


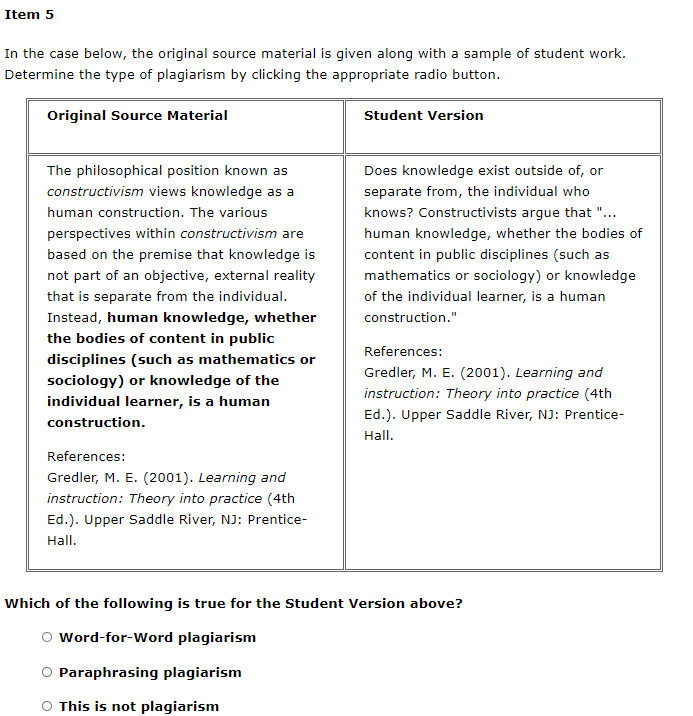
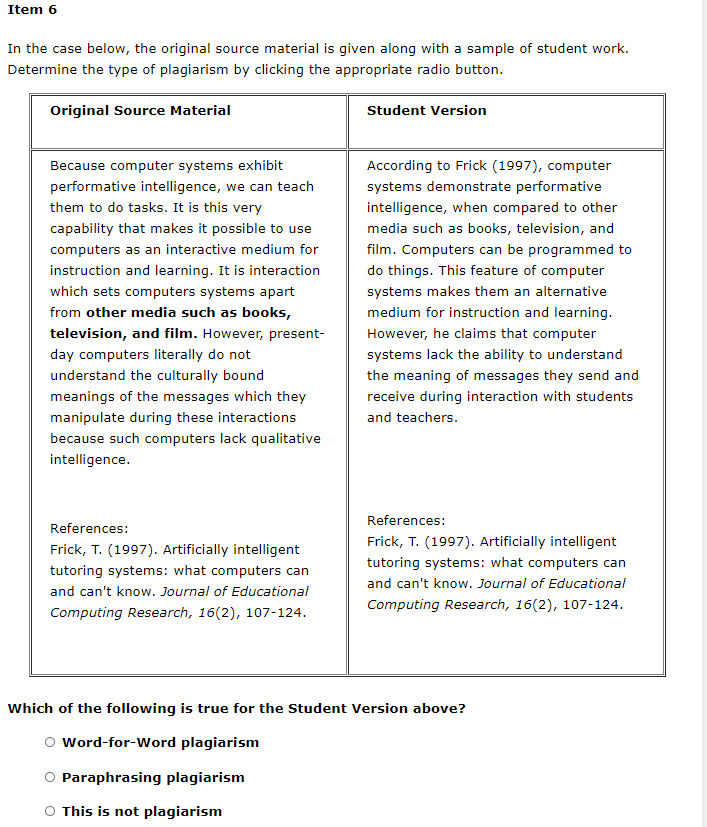


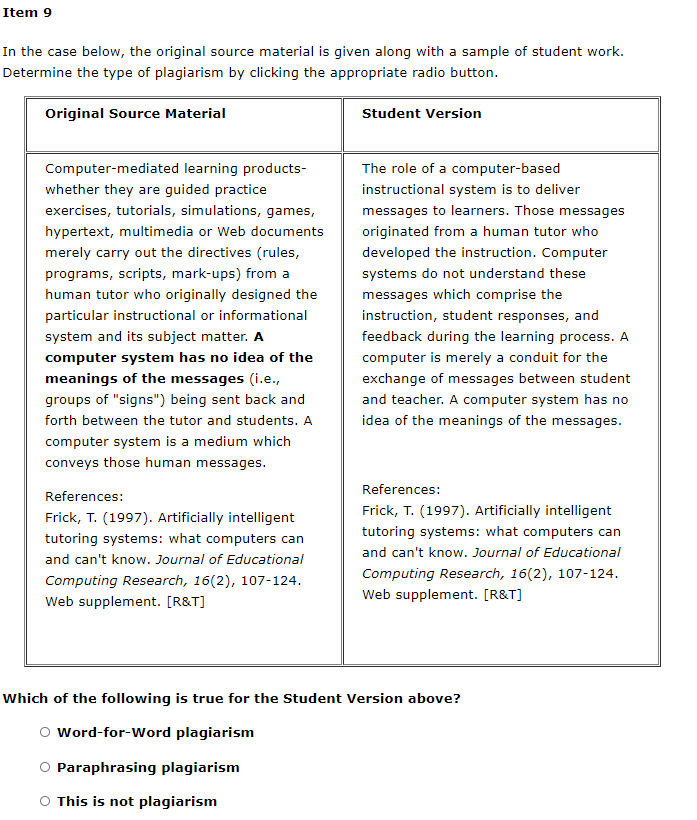

Item 1 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version The philosophical position known as constructivism views knowledge as a human construction. The various perspectives within constructivism are based on the premise that knowledge is not part of an objective, external reality that is separate from the individual. Instead, human knowledge, whether the bodies of content in public disciplines (such as mathematics or sociology) or knowledge of the individual learner; is a human construction. "The philosophical position known as constructivism views knowledge as a human construction. The various perspectives within constructivism are based on the premise that knowledge is not part of an objective, external reality that is separate from the individual. Instead, human knowledge is a human construction" (p. 29). References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? O Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism O This is not plagiarism Item 2 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version Content could be presented in a variety of formats via multimedia. Dynamic processes could be illustrated. Content in the form of text, still pictures, video, sound, graphics, or animations could be digitally or analogically encoded and stored in electronic, magnetic, and optical technologies. This encoded information could be transmitted literally around the world in a matter of seconds. With the rapid advance in information technologies, people around the world can access information quickly. Information takes the form of text, still pictures, video, sound, graphics, or animations, which are stored and transferred electronically through these computational technologies. References: Frick, T. (1991). Restructuring education through technology. Bloomington, IN: Phi Delta Kappa Educational Foundation. References: Frick, T. (1991). Restructuring education through technology. Bloomington, IN: Phi Delta Kappa Educational Foundation. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 3 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version There is a design methodology called rapid prototyping, which has been used successfully in software engineering. Given similarities between software design and instructional design, we argue that rapid prototyping is a viable method for instructional design, especially for computer-based instruction. Tripp and Bichelmeyer (1990) suggested that rapid prototyping could be an advantageous methodology for developing innovative computer-based instruction. They noted that this approach has been used successfully in software engineering; hence, rapid prototyping could also be a viable method for instructional design due to many parallels between software design and instructional design. References: Tripp, S. D., & Bichelmeyer, B. A. (1990). Rapid prototyping: An alternative instructional design strategy. Educational Technology Research and Development, 38(1), 31-44. References: Tripp, S. D., & Bichelmeyer, B. A. (1990). Rapid prototyping: An alternative instructional design strategy. Educational Technology Research and Development, 38(1), 31-44. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? o Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 4 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version Learning is a complex set of processes that may vary according to the developmental level of the learner, the nature of the task, and the context in which the learning is to occur. As already indicated, no one theory can capture all the variables involved in learning. References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle, NJ: Prentice-Hall. A learning theory is made up of a set of constructs linking observed changes in performance with whatever is thought to bring about those changes. Therefore since "learning is a complex set of processes that may vary according to the developmental level of the learner, the nature of the task, and the context in which the learning is to occur," it is apparent that no one theory can capture all the variables involved in learning (Driscoll, 2000, p.10). A learning theory, there, comprises a set of constructs linking observed changes in performance with what is thought to bring about those changes. References: Driscoll, M. P. (2000). Psychology of learning for instruction (2nd Ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon. References: Driscoll, M. P. (2000). Psychology of learning for instruction (2nd Ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 5 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version The philosophical position known as constructivism views knowledge as a human construction. The various perspectives within constructivism are based on the premise that knowledge is not part of an objective, external reality that is separate from the individual. Instead, human knowledge, whether the bodies of content in public disciplines (such as mathematics or sociology) or knowledge of the individual learner, is a human construction. Does knowledge exist outside of, or separate from, the individual who knows? Constructivists argue that "... human knowledge, whether the bodies of content in public disciplines (such as mathematics or sociology) or knowledge of the individual learner, is a human construction." References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice- Hall. References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice- Hall. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? O Word-for-Word plagiarism O Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 6 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version Because computer systems exhibit performative intelligence, we can teach them to do tasks. It is this very capability that makes it possible to use computers as an interactive medium for instruction and learning. It is interaction which sets computers systems apart from other media such as books, television, and film. However, present- day computers literally do not understand the culturally bound meanings of the messages which they manipulate during these interactions because such computers lack qualitative intelligence. According to Frick (1997), computer systems demonstrate performative intelligence, when compared to other media such as books, television, and film. Computers can be programmed to do things. This feature of computer systems makes them an alternative medium for instruction and learning. However, he claims that computer systems lack the ability to understand the meaning of messages they send and receive during interaction with students and teachers. References: Frick, T. (1997). Artificially intelligent tutoring systems: what computers can and can't know. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 16(2), 107-124. References: Frick, T. (1997). Artificially intelligent tutoring systems: what computers can and can't know. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 16(2), 107-124. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? o Word-for-Word plagiarism O Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 7 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version The philosophical position known as constructivism views knowledge as a human construction. The various perspectives within constructivism are based on the premise that knowledge is not part of an objective, external reality that is separate from the individual. Instead, human knowledge, whether the bodies of content in public disciplines (such as mathematics or sociology) or knowledge of the individual learner, is a human construction. Does knowledge exist outside of, or separate from, the individual who knows? Constructivists hold that human knowledge, whether the bodies of content in public disciplines (such as mathematics or sociology) or knowledge of the individual learner, is a human construction (Gredler, 2001). References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice- Hall. References: Gredler, M. E. (2001). Learning and instruction: Theory into practice (4th Ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice- Hall. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? O Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism O This is not plagiarism Item 8 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version While solitary negative reactions or unjustified suggestions for change have the potential to dissipate discourse rather than build it, the pattern analysis shows that the anonymous condition seemed to provide a safe explorative space for learners to try out more reasons for their multiple solutions. Teachers will rarely give anonymous feedback, but the experience of giving anonymous feedback may open a social space where learners can try out the reasons for their suggestions. Teachers don't often provide feedback anonymously, but the ability to provide feedback anonymously may create a context where the rationale associated with specific suggestions can be more safely explored (Howard, Barrett, & Frick, 2010). However, we cannot assume that all anonymous online spaces will serve as safe social spaces. References: Howard, C. D., Barrett, A. F., & Frick, T. W. (2010). Anonymity to promote peer feedback: Pre-service teachers' comments in asynchronous computer- mediated communication. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 43(1), 89-112. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 9 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version Computer-mediated learning products- whether they are guided practice exercises, tutorials, simulations, games, hypertext, multimedia or Web documents merely carry out the directives (rules, programs, scripts, mark-ups) from a human tutor who originally designed the particular instructional or informational system and its subject matter. A computer system has no idea of the meanings of the messages (i.e., groups of "signs") being sent back and forth between the tutor and students. A computer system is a medium which conveys those human messages. The role of a computer-based instructional system is to deliver messages to learners. Those messages originated from a human tut who developed the instruction. Computer systems do not understand these messages which comprise the instruction, student responses, and feedback during the learning process. A computer is merely a conduit for the exchange of messages between student and teacher. A computer system has no idea of the meanings of the messages. References: Frick, T. (1997). Artificially intelligent tutoring systems: what computers can and can't know. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 16(2), 107-124. Web supplement. [R&T] References: Frick, T. (1997). Artificially intelligent tutoring systems: what computers can and can't know. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 16(2), 107-124. Web supplement. [R&T] Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism Item 10 In the case below, the original source material is given along with a sample of student work. Determine the type of plagiarism by clicking the appropriate radio button. Original Source Material Student Version Instructional designers typically employ models to guide their day-to- day work. Due to the increased practice of the systematic design of instruction in a growing number of settings, available models become more and more proliferated, focusing on particular types and contexts of learning, particular groups of learners or designers, or particular instructional units (either whole curricula or individual modules or lessons.) "The main goal of any instructional design process is to construct a learning environment in order to provide learners with the conditions that support desired learning processes" (van Merrinboer, 1997, p. 2). Process models proliferate because more and more designers generate models that focus on specific contexts, learners, or even units of instruction, according to van Merrinboer. The main goal of any instructional design process is to construct a learning environment in order to provide learners with the conditions that support desired learning processes. References: Merrinboer, J. J. van. (1997). Training complex cognitive skills. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications. References: Merrinboer, J. J. van. (1997). Training complex cognitive skills. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications. Which of the following is true for the Student Version above? O Word-for-Word plagiarism Paraphrasing plagiarism This is not plagiarism














