Question: I've created Matlab code for this question, everything works fine for both rk4 and rk3 but separately. How can I include RK3 and RK4 in
I've created Matlab code for this question, everything works fine for both rk4 and rk3 but separately. How can I include RK3 and RK4 in one program, and if you find any requirements not present, please complete them. This is my program. For RK3 and %% rk4 %%. Thank you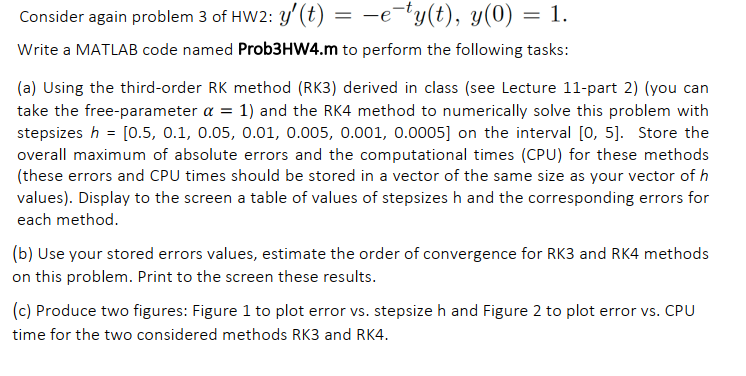
--------------
close all; clc; clf format short % time interval and initial value: a=0; b=5; y0=1;
% righ-hand-side function f(t,y) f = @(t,y) -expm(-t)*y; % The set of chosen step sizes h:
h_vals=[0.5,0.1,0.05,0.01,0.005,0.001,0.0005];
% an array to store errors corresponding to chosen h values err = zeros(1,size(h_vals,1));
% matrices to store times, numerical solutions, and absolute errors every one unit time % corresponding to different values of h t_h =[]; Y = []; abs_error = [];
% Do a loop over h values: for i= 1:length(h_vals) h = h_vals(i); t = a:h:b; N = length(t); zero = zeros(size(t));
% compute the exact solution: yexact = zero; yexact(1) = y0; for n=1:N-1 yexact(n+1)= expm(expm(-t(n+1))-1); end
% compute the numerical solution using RK4 method: [t_RK4, yRK4] = RK4(f, t, y0);
% (a) a vector contain absolute errors every one unit time: abs_error{i} = abs(yRK4 - yexact);
% b) compute the global errors (the overall maximum of the absolute errors) % stored them in a vector of the same size as the vector h_vals err(i) = max(abs_error{i});
% store time values corresponding to each stepsize h t_h{i}= t; Y{i} = yRK4; end
% (c) Verify the convergence order of RK4 method: disp('Estimate the order of RK4 method:')
p = log(err(1:end-1)./err(2:end))./log(h_vals(1:end-1)./h_vals(2:end))
disp('Results for global errors:')
fprintf(' h error_RK4 '); fprintf(' ----------------------------------- '); fprintf(' %.4f %.3e ',h_vals(1),err(1)); fprintf(' %.4f %.3e ',h_vals(2),err(2)); fprintf(' %.4f %.3e ',h_vals(3),err(3)); fprintf(' %.4f %.3e ',h_vals(4),err(4)); fprintf(' %.4f %.3e ',h_vals(5),err(5)); fprintf(' ---------------------------------------- ');
% (d) plot the numerical solutions (corresponding to h values) and the true % solution in the same figure
set(0,'DefaultTextFontSize',14) set(0,'DefaultAxesFontSize',14) LW = 'linewidth';
plot(t, yexact,'b', LW, 2) legend('true solution') hold on for i= 1:length(h_vals) h = ['h = ',num2str(h_vals(i))]; plot(t_h{i}, Y{i},'DisplayName',h, LW, 2) end hold off title('RK4') xlabel('t') ylabel('y')
figure(1) semilogy(h_vals,err) xlabel('h') ylabel('error') legend('RK4')
function [t,y] = RK4(f, tvals, y0)
% initialize output arrays y = zeros(size(tvals)); t = tvals; y(1) = y0;
% iterate over time steps for n = 1:length(t)-1 % RK4 h = t(n+1)-t(n); k1 = f(t(n),y(n)); k2 = f(t(n)+(0.5)*h,y(n)+(0.5)*k1*h); k3 = f((t(n)+(0.5)*h),(y(n)+(0.5)*k2*h)); k4 = f(t(n)+h,y(n)+k3*h); y(n+1) = y(n)+((k1+2*k2+2*k3+k4)/6)*h; %% % RK3 h = t(n+1)-t(n); k1 = f(t(n),y(n)); k2 = f(t(n)+(2/3)*h,y(n)+(2/3)*h*k1); k3 = f((t(n)+(2/3)*h),(y(n)+(5/12)*h*k1+(1/4)*h*k2)); y(n+1) = y(n) + (1/4)*(k1-k2+4*k3)*h; %% end
end
Consider again problem 3 of HW2: Y'(t) = -e-ty(t), y(0) = 1. Write a MATLAB code named Prob3HW4.m to perform the following tasks: (a) Using the third-order RK method (RK3) derived in class (see Lecture 11-part 2) (you can take the free-parameter a = 1) and the RK4 method to numerically solve this problem with stepsizes h = [0.5, 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, 0.005, 0.001, 0.0005] on the interval [0, 5]. Store the overall maximum of absolute errors and the computational times (CPU) for these methods (these errors and CPU times should be stored in a vector of the same size as your vector of h values). Display to the screen a table of values of stepsizes h and the corresponding errors for each method. (b) Use your stored errors values, estimate the order of convergence for RK3 and RK4 methods on this problem. Print to the screen these results. (c) Produce two figures: Figure 1 to plot error vs. stepsize h and Figure 2 to plot error vs. CPU time for the two considered methods RK3 and RK4. Consider again problem 3 of HW2: Y'(t) = -e-ty(t), y(0) = 1. Write a MATLAB code named Prob3HW4.m to perform the following tasks: (a) Using the third-order RK method (RK3) derived in class (see Lecture 11-part 2) (you can take the free-parameter a = 1) and the RK4 method to numerically solve this problem with stepsizes h = [0.5, 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, 0.005, 0.001, 0.0005] on the interval [0, 5]. Store the overall maximum of absolute errors and the computational times (CPU) for these methods (these errors and CPU times should be stored in a vector of the same size as your vector of h values). Display to the screen a table of values of stepsizes h and the corresponding errors for each method. (b) Use your stored errors values, estimate the order of convergence for RK3 and RK4 methods on this problem. Print to the screen these results. (c) Produce two figures: Figure 1 to plot error vs. stepsize h and Figure 2 to plot error vs. CPU time for the two considered methods RK3 and RK4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


