Question: JAVA: I'm having trouble with the following DNA and Protein Synthesis program, mainly with Task 3 and Task 4. I have completed Task 0, 1
JAVA: I'm having trouble with the following DNA and Protein Synthesis program, mainly with Task 3 and Task 4. I have completed Task 0, 1 and 2 and they are working fine. I am stuck on Tasks 3 and 4. My code is attached at the end. 





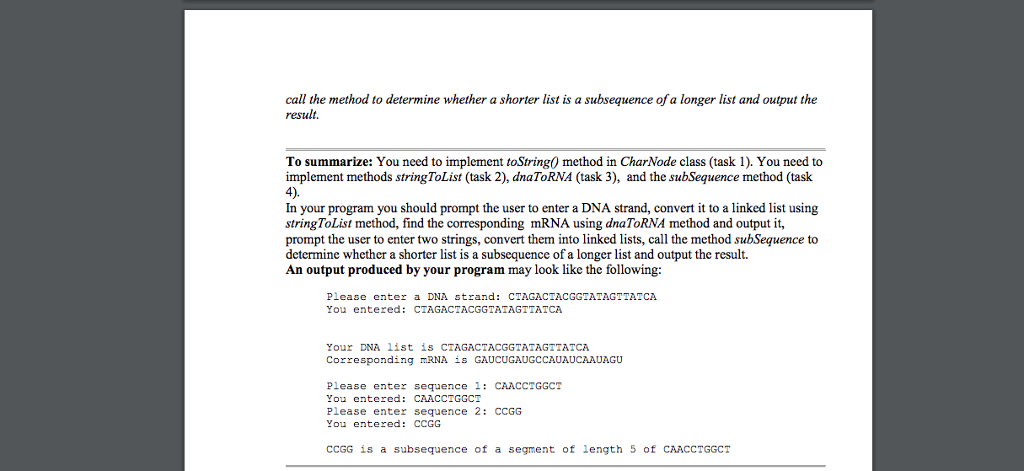
CharNode.java and my Tasks 1 and 2 are as follows:
// File: CharNode.java from the package edu.colorado.nodes // Complete documentation is available from the CharNode link in: // http://www.cs.colorado.edu/~main/docs //package edu.colorado.nodes; /****************************************************************************** * A CharNode provides a node for a linked list with * char data in each node. * * @note * Lists of nodes can be made of any length, limited only by the amount of * free memory in the heap. But beyond Integer.MAX_VALUE (2,147,483,647), * the answer from listLength is incorrect because of arithmetic * overflow. * * @see * * Java Source Code for this class * (www.cs.colorado.edu/~main/edu/coloradoodes/CharNode.java) * * @author Michael Main * (main@colorado.edu) * * @version * March 6, 2002 * * @see Node * @see BooleanNode * @see ByteNode * @see DoubleNode * @see FloatNode * @see IntNode * @see LongNode * @see ShortNode ******************************************************************************/ public class CharNode { // Invariant of the CharNode class: // 1. The node's char data is in the instance variable data. // 2. For the final node of a list, the link part is null. // Otherwise, the link part is a reference to the // next node of the list. private char data; private CharNode link; /** * Initialize a node with a specified initial data and link to the next * node. Note that the initialLink may be the null reference, * which indicates that the new node has nothing after it. * @param initialData * the initial data of this new node * @param initialLink * a reference to the node after this new node--this reference may be null * to indicate that there is no node after this new node. * @postcondition * This node contains the specified data and link to the next node. **/ public CharNode(char initialData, CharNode initialLink) { data = initialData; link = initialLink; } /** * Modification method to add a new node after this node. * @param item * the data to place in the new node * @postcondition * A new node has been created and placed after this node. * The data for the new node is item. Any other nodes * that used to be after this node are now after the new node. * @exception OutOfMemoryError * Indicates that there is insufficient memory for a new * CharNode. **/ public void addNodeAfter(char item) { link = new CharNode(item, link); } /** * Accessor method to get the data from this node. * @param - none * @return * the data from this node **/ public char getData( ) { return data; } /** * Accessor method to get a reference to the next node after this node. * @param - none * @return * a reference to the node after this node (or the null reference if there * is nothing after this node) **/ public CharNode getLink( ) { return link; } /** * Copy a list. * @param source * the head of a linked list that will be copied (which may be * an empty list in where source is null) * @return * The method has made a copy of the linked list starting at * source. The return value is the head reference for the * copy. * @exception OutOfMemoryError * Indicates that there is insufficient memory for the new list. **/ public static CharNode listCopy(CharNode source) { CharNode copyHead; CharNode copyTail; // Handle the special case of the empty list. if (source == null) return null; // Make the first node for the newly created list. copyHead = new CharNode(source.data, null); copyTail = copyHead; // Make the rest of the nodes for the newly created list. while (source.link != null) { source = source.link; copyTail.addNodeAfter(source.data); copyTail = copyTail.link; } // Return the head reference for the new list. return copyHead; } /** * Copy a list, returning both a head and tail reference for the copy. * @param source * the head of a linked list that will be copied (which may be * an empty list in where source is null) * @return * The method has made a copy of the linked list starting at * source. The return value is an * array where the [0] element is a head reference for the copy and the [1] * element is a tail reference for the copy. * @exception OutOfMemoryError * Indicates that there is insufficient memory for the new list. **/ public static CharNode[ ] listCopyWithTail(CharNode source) { CharNode copyHead; CharNode copyTail; CharNode[ ] answer = new CharNode[2]; // Handle the special case of the empty list. if (source == null) return answer; // The answer has two null references . // Make the first node for the newly created list. copyHead = new CharNode(source.data, null); copyTail = copyHead; // Make the rest of the nodes for the newly created list. while (source.link != null) { source = source.link; copyTail.addNodeAfter(source.data); copyTail = copyTail.link; } // Return the head and tail references. answer[0] = copyHead; answer[1] = copyTail; return answer; } /** * Compute the number of nodes in a linked list. * @param head * the head reference for a linked list (which may be an empty list * with a null head) * @return * the number of nodes in the list with the given head * @note * A wrong answer occurs for lists longer than Int.MAX_VALUE. **/ public static int listLength(CharNode head) { CharNode cursor; int answer; answer = 0; for (cursor = head; cursor != null; cursor = cursor.link) answer++; return answer; } /** * Copy part of a list, providing a head and tail reference for the new copy. * @param start/end * references to two nodes of a linked list * @param copyHead/copyTail * the method sets these to refer to the head and tail node of the new * list that is created * @precondition * start and end are non-null references to nodes * on the same linked list, * with the start node at or before the end node. * @return * The method has made a copy of the part of a linked list, from the * specified start node to the specified end node. The return value is an * array where the [0] component is a head reference for the copy and the * [1] component is a tail reference for the copy. * @exception IllegalArgumentException * Indicates that start and end are not references * to nodes on the same list. * @exception NullPointerException * Indicates that start is null. * @exception OutOfMemoryError * Indicates that there is insufficient memory for the new list. **/ public static CharNode[ ] listPart(CharNode start, CharNode end) { CharNode copyHead; CharNode copyTail; CharNode cursor; CharNode[ ] answer = new CharNode[2]; // Make the first node for the newly created list. Notice that this will // cause a NullPointerException if start is null. copyHead = new CharNode(start.data, null); copyTail = copyHead; cursor = start; // Make the rest of the nodes for the newly created list. while (cursor != end) { cursor = cursor.link; if (cursor == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("end node was not found on the list"); copyTail.addNodeAfter(cursor.data); copyTail = copyTail.link; } // Return the head and tail references answer[0] = copyHead; answer[1] = copyTail; return answer; } /** * Find a node at a specified position in a linked list. * @param head * the head reference for a linked list (which may be an empty list in * which case the head is null) * @param position * a node number * @precondition * position > 0. * @return * The return value is a reference to the node at the specified position in * the list. (The head node is position 1, the next node is position 2, and * so on.) If there is no such position (because the list is too short), * then the null reference is returned. * @exception IllegalArgumentException * Indicates that position is not positive. **/ public static CharNode listPosition(CharNode head, int position) { CharNode cursor; int i; if (position public String toString () {
CharNode cursor;
String result = "";
for (cursor = this; cursor != null; cursor = cursor.link) {
result = result + cursor.data;
} // end for loop
return result;
} // end toString method
// Task 2: stringToList method
public static CharNode stringToList (String userDNA) {
if (userDNA == null) {
return null;
} // end if
char head;
head = userDNA.charAt(0);
CharNode temp = new CharNode (head, null);
CharNode tail = temp;
for (int i = 1; i
char b = userDNA.charAt(i);
tail.addNodeAfter(b);
tail = tail.getLink();
} // end for
return temp;
} // end stringToList method
}
For this assignment you will need to use file CharNode.java, CharNode provides a node for a linked list with char data in each node. (CharNode is like IntNode, only elements are of type char instead of int.) DNA and Protein Synthesis DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is in the family of molecules referred to as nucleic acids. One strand of DNA has a backbone consisting of a polymer of the simple sugar deoxyribose bonded to something called a phosphate unit. Very unimpressively then, the backbone of a strand of DNA resembles this: sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate- What is impressive about DNA is that each sugar molecule in the strand also binds to one of four different nucleotide bases. These bases: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T), are the beginnings of what we will soon see is a molecular alphabet. Each sugar molecule in the DNA strand will bind to one nucleotide base. Thus, as our description of DNA unfolds, we see that a single strand of the molecule looks more like this: sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate- Each strand of DNA contains millions or even billions (in the case of human DNA) of nucleotide bases. These bases are arranged in a specific order according to our genetic ancestry. The order of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


