Question: Java's implementation of LinkedList stores two references in each node: one for the previous, and one for the next. In addition, both the head and
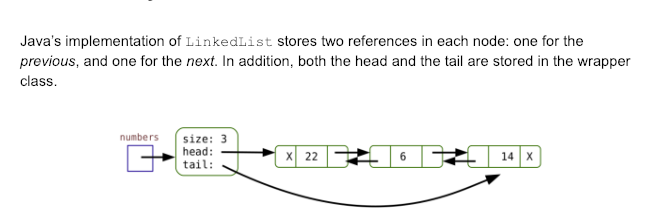


Java's implementation of LinkedList stores two references in each node: one for the previous, and one for the next. In addition, both the head and the tail are stored in the wrapper class. numbers size: 3 head tail: x 22 14 X 19. How many operations are required to add an element at the start of this list? 20. How many operations are required to add an element at the end of this list? 21. How much memory is required for each node? How does that amount compare with using an ArrayList? 22. What problems of singly-linked lists do doubly-linked lists solve? (In other words, what do the previous and tail make possible?) use? (ArrayList Vs LinkedList) 12. Discuss why ArrayList is a poor choice of List in the program below import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 4 public class ArraysAr eBad public static void main (String[] args) 6 ArrayList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


