Question: Just for which has a question mark 1. Obtain a piece of magnesium ribbon approximately 3 cm long. Clean it until it is shiny (free
Just for which has a question mark 
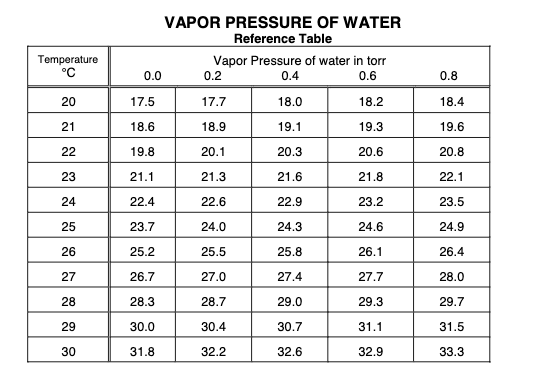
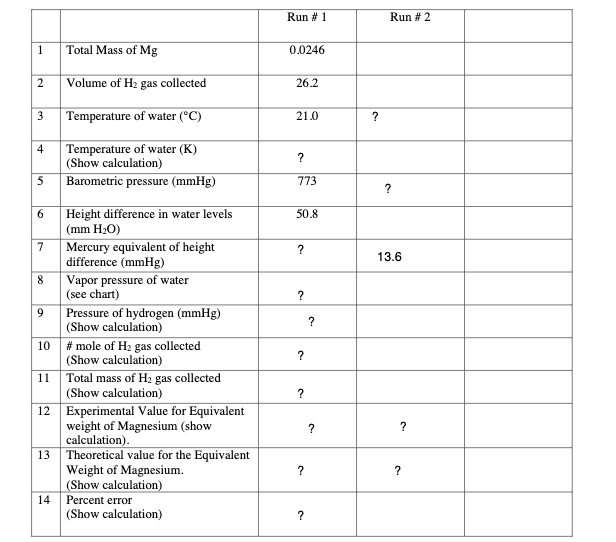
1. Obtain a piece of magnesium ribbon approximately 3 cm long. Clean it until it is shiny (free of oxide). 2. Measure the mass of the magnesium. Record this on the data sheet. 3. Cut a piece of copper wire about 6 inches long. Fold the magnesium ribbon and wrap the copper around it as completely as possible. Leave at least 2 inches of the wire straight. 4. Clean a gas buret. Carefully pour approximately 5 mL of concentrated HCl into the buret. Do this in the hood so as not to breathe in the fumes. Hold the buret at an angle and slowly add water so as not to allow too much mixing of the acid and water. Fill the buret in this way completely to the top with water. 5. Fill a 250 mL beaker about 1/2 with water. 6. Saturate a piece of cotton with water squeezing out as much air as possible. Place the magnesium ribbon into the buret. Hook the straight end of the copper wire around the outside of the buret and hold it in place with the cotton. The magnesium should be about 2 inches from the top of the buret and there should be no air in the buret. 7. Invert the buret and place it into the beaker of water. Clamp it to a ring stand. 8. After the reaction is complete and bubbles of hydrogen gas stop rising to the surface, allow the system to stand for approximately 5 minutes. 9. At this point gently tap the sides of the buret to free as many bubbles of gas as possible. 10. Measure and record the following: a. The volume of gas in the buret. b. The temperature of the liquid in the beaker. This should also be the temperature of the hydrogen gas. c. The difference in height between the top of the water in the buret and the top of the water in the beaker. Use a meter stick. VAPOR PRESSURE OF WATER Reference Table Vapor Pressure of water in torr 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Temperature C 0.8 20 17.5 17.7 18.0 18.2 18.4 21 18.6 18.9 19.1 19.3 19.6 22 19.8 20.1 20.3 20.6 20.8 23 21.1 21.3 21.6 21.8 22.1 24 22.4 22.6 22.9 23.2 23.5 25 23.7 24.0 24.3 24.6 24.9 26 25.2 25.5 25.8 26.1 26.4 27 26.7 27.0 27.4 27.7 28.0 28 28.3 28.7 29.0 29.3 29.7 29 30.0 30.4 30.7 31.1 31.5 30 31.8 32.2 32.6 32.9 33.3 Run # 1 Run #2 1 Total Mass of Mg 0.0246 2 Volume of H2 gas collected 26.2 3 Temperature of water (C) 21.0 ? 4 ? Temperature of water (K) (Show calculation) Barometric pressure (mmHg) 5 773 ? 50.8 ? 13.6 ? ? ? 6 Height difference in water levels (mm H2O) 7 Mercury equivalent of height difference (mmHg) 8 Vapor pressure of water (see chart) 9 Pressure of hydrogen (mmHg) (Show calculation) 10 # mole of H2 gas collected (Show calculation) 11 Total mass of H2 gas collected (Show calculation) 12 Experimental Value for Equivalent weight of Magnesium (show calculation) 13 Theoretical value for the Equivalent Weight of Magnesium. (Show calculation) 14 Percent error (Show calculation)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


