Question: kinetics The process below describes the mechanism in which mercaptan/thiol (RSH) and oxygen molecules interact with cobalt(II) pthalocyanine catalysts to produce thiol radicals (). The
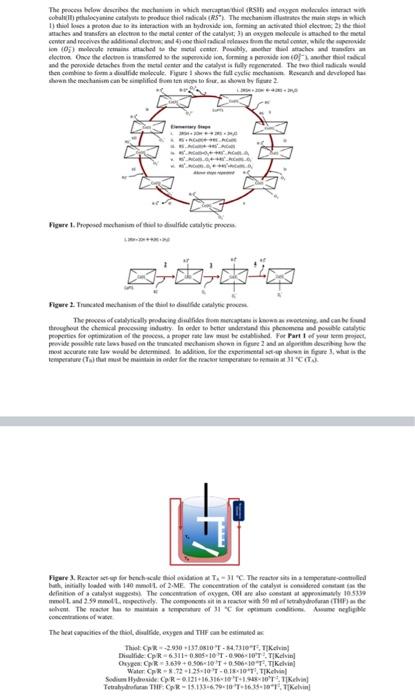

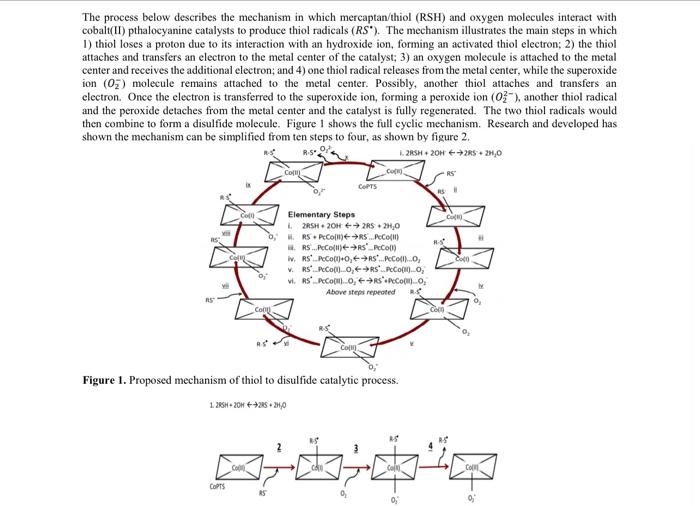

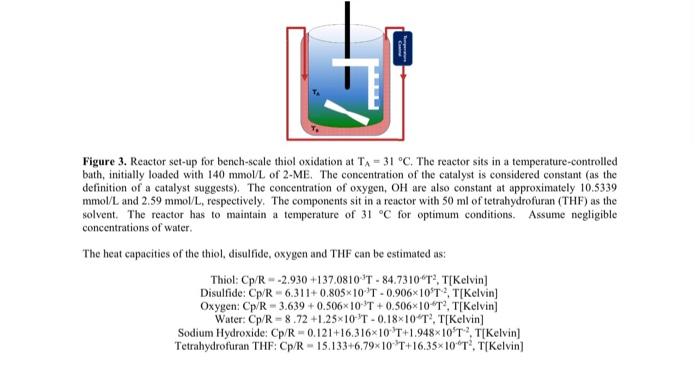
The clowns the mechanin which marca RSI and my mind cobalipthalecyanine cataly to produce the RS The mechanism illustrates the main steps in which taches of catalyst die beste due to its interaction with a hydroxide, forming an activated them and receive the imala 14 in (03) malcole remains attached to the them the metal whe dectroOne des remed to the preside informing provide Publy, mother the attaches and we her and the preside detaches from the metal center and the catalyst a fully regated. The two chill radical wald then come se forma delide melcule. Figure we full eye mechi can and developed as down the mechanism can be simplified from ten wir, wie da un any dete s nached to the ele SA Fire I. Proposed memofthe catalytics Figure 2. The main of the distadele The process of catalytical producing die idee om pasi kwa watening and casin thout the chemin duty in order to better understand this place pouble clic peperties for a propera te till. Fer Part 1 of project wewe peke uteles de literated his shown in figure and in den beide most recente mate world be determined to add for the experimentale per le figure what is the temperature that must be maintain in order for the rest operatorem C Figure 3. Reactor bechscales TICThe rest in a temperature initially loaded with 140 mmollo 2.ME The concentration of the city is in the definition of a catalysts The concentration of types of are also constant at approximately 105330 me Land 259 moltmopetely. The compositin artera 50 ml fitrahydrofuran (Tilhas the it. The actor home of " for optimum condimente concert of wat The best capacities of the thiet, dilfide, nypes and The can he estimated Thiel Op 29301370510T -4,73101 TK Diside CpR6311-08-10 1.09060TTIK Cheyen C3.630 +0.5060T+0.5060 TTiKch in Water Cpx - 72125-10-08-10T, TIXcial Sedium Hydroxide CR-0121163160 TOT TIKelvin Tetrahydfra TIF CAR-15.1330670-10 T6.16.10.11 Kevin Additional Information: K K(L/ mol) K (L/mmol) k, (hr) Cat) (mmol/L) UA (cal(min-K-L)) Heat of formation (kJ/mol 1.14x10 3.46x10 0.19 1730 0.01 -389.61 Due to the high degree of dilution, the physical properties of the THF can be used for the batch. Part 2 57.15 In addition, you are required to provide a written report about the sweetening process. The written report should give a background on the industry, applications and description of the sweetening process (different companies have different processes - for the purpose of this class, one process will suffice). What safety precautions are taken by facilities that handle sulfur processing? What type of ethical decisions may engineers face while working in such facilities? What environmental constraints and standards must be met in order for these type of facilities to operate globally, while considering both company bottom-linc (economics) and the society in which it exists? The process below describes the mechanism in which mercaptan/thiol (RSH) and oxygen molecules interact with cobalt(II) pthalocyanine catalysts to produce thiol radicals (RS'). The mechanism illustrates the main steps in which 1) thiol loses a proton due to its interaction with an hydroxide ion, forming an activated thiol electron; 2) the thiol attaches and transfers an electron to the metal center of the catalyst; 3) an oxygen molecule is attached to the metal center and receives the additional electron; and 4) one thiol radical releases from the metal center, while the superoxide ion (02) molecule remains attached to the metal center. Possibly, another thiol attaches and transfers an electron. Once the electron is transferred to the superoxide ion, forming a peroxide ion (03-), another thiol radical and the peroxide detaches from the metal center and the catalyst is fully regenerated. The two thiol radicals would then combine to form a disulfide molecule. Figure I shows the full cyclic mechanism. Research and developed has shown the mechanism can be simplified from ten steps to four, as shown by figure 2. L2RSH+20H2RS 2.0 02 Com CO 0, COPTS Coro CO Cat Elementary Steps L2RSH2OH2RSO H. RS. PeCoR...) RS...PeCoR.PcColl) iv. RSPC001+0, RS...PeColl. V.RS...Peo00.0, PCO, RSPeComo, 'Peo)..0, Above steps repeated R. Con co Com Figure 1. Proposed mechanism of thiol to disulfide catalytic process. 1.285H+20 +2520 COPTS Figure 2. Truncated mechanism of the thiol to disulfide catalytic process, The process of catalytically producing disulfides from mercaptans is known as sweetening, and can be found throughout the chemical processing industry. In order to better understand this phenomena and possible catalytic properties for optimization of the process, a proper rate law must be established. For Part 1 of your term project, provide possible rate laws based on the truncated mechanism shown in figure 2 and an algorithm describing how the most accurate rate law would be determined. In addition, for the experimental set-up shown in figure 3, what is the temperature (Te) that must be maintain in order for the reactor temperature to remain at 31 C (TA). Figure 3. Reactor set-up for bench-scale thiol oxidation at TA = 31 C. The reactor sits in a temperature-controlled bath, initially loaded with 140 mmol/L of 2-ME. The concentration of the catalyst is considered constant (as the definition of a catalyst suggests). The concentration of oxygen, OH are also constant at approximately 10.5339 mmol/L and 2.59 mmol/L, respectively. The components sit in a reactor with 50 ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) as the solvent. The reactor has to maintain a temperature of 31 C for optimum conditions. Assume negligible concentrations of water The heat capacities of the thiol, disulfide, oxygen and THF can be estimated as: Thiol: Cp/R - -2.930 +137.0810 T - 84.7310"T, T[Kelvin) Disulfide: Cp/R-6.311+0.805x10 T-0.906x10T2, T[Kelvin) Oxygen: Cp/R = 3.639 +0.506x10 T +0.506x10^T, T|Kelvin Water: Cp/R - 8.72 +1.25X10 T -0.18*10"T?, T[Kelvin Sodium Hydroxide: Cp/R-0.121+16,31610'T+1.948*10*T*?, T[Kelvin] Tetrahydrofuran THE Cp/R-15.133+6.79x10 'T+16,35x10T2, T[Kelvin) The clowns the mechanin which marca RSI and my mind cobalipthalecyanine cataly to produce the RS The mechanism illustrates the main steps in which taches of catalyst die beste due to its interaction with a hydroxide, forming an activated them and receive the imala 14 in (03) malcole remains attached to the them the metal whe dectroOne des remed to the preside informing provide Publy, mother the attaches and we her and the preside detaches from the metal center and the catalyst a fully regated. The two chill radical wald then come se forma delide melcule. Figure we full eye mechi can and developed as down the mechanism can be simplified from ten wir, wie da un any dete s nached to the ele SA Fire I. Proposed memofthe catalytics Figure 2. The main of the distadele The process of catalytical producing die idee om pasi kwa watening and casin thout the chemin duty in order to better understand this place pouble clic peperties for a propera te till. Fer Part 1 of project wewe peke uteles de literated his shown in figure and in den beide most recente mate world be determined to add for the experimentale per le figure what is the temperature that must be maintain in order for the rest operatorem C Figure 3. Reactor bechscales TICThe rest in a temperature initially loaded with 140 mmollo 2.ME The concentration of the city is in the definition of a catalysts The concentration of types of are also constant at approximately 105330 me Land 259 moltmopetely. The compositin artera 50 ml fitrahydrofuran (Tilhas the it. The actor home of " for optimum condimente concert of wat The best capacities of the thiet, dilfide, nypes and The can he estimated Thiel Op 29301370510T -4,73101 TK Diside CpR6311-08-10 1.09060TTIK Cheyen C3.630 +0.5060T+0.5060 TTiKch in Water Cpx - 72125-10-08-10T, TIXcial Sedium Hydroxide CR-0121163160 TOT TIKelvin Tetrahydfra TIF CAR-15.1330670-10 T6.16.10.11 Kevin Additional Information: K K(L/ mol) K (L/mmol) k, (hr) Cat) (mmol/L) UA (cal(min-K-L)) Heat of formation (kJ/mol 1.14x10 3.46x10 0.19 1730 0.01 -389.61 Due to the high degree of dilution, the physical properties of the THF can be used for the batch. Part 2 57.15 In addition, you are required to provide a written report about the sweetening process. The written report should give a background on the industry, applications and description of the sweetening process (different companies have different processes - for the purpose of this class, one process will suffice). What safety precautions are taken by facilities that handle sulfur processing? What type of ethical decisions may engineers face while working in such facilities? What environmental constraints and standards must be met in order for these type of facilities to operate globally, while considering both company bottom-linc (economics) and the society in which it exists? The process below describes the mechanism in which mercaptan/thiol (RSH) and oxygen molecules interact with cobalt(II) pthalocyanine catalysts to produce thiol radicals (RS'). The mechanism illustrates the main steps in which 1) thiol loses a proton due to its interaction with an hydroxide ion, forming an activated thiol electron; 2) the thiol attaches and transfers an electron to the metal center of the catalyst; 3) an oxygen molecule is attached to the metal center and receives the additional electron; and 4) one thiol radical releases from the metal center, while the superoxide ion (02) molecule remains attached to the metal center. Possibly, another thiol attaches and transfers an electron. Once the electron is transferred to the superoxide ion, forming a peroxide ion (03-), another thiol radical and the peroxide detaches from the metal center and the catalyst is fully regenerated. The two thiol radicals would then combine to form a disulfide molecule. Figure I shows the full cyclic mechanism. Research and developed has shown the mechanism can be simplified from ten steps to four, as shown by figure 2. L2RSH+20H2RS 2.0 02 Com CO 0, COPTS Coro CO Cat Elementary Steps L2RSH2OH2RSO H. RS. PeCoR...) RS...PeCoR.PcColl) iv. RSPC001+0, RS...PeColl. V.RS...Peo00.0, PCO, RSPeComo, 'Peo)..0, Above steps repeated R. Con co Com Figure 1. Proposed mechanism of thiol to disulfide catalytic process. 1.285H+20 +2520 COPTS Figure 2. Truncated mechanism of the thiol to disulfide catalytic process, The process of catalytically producing disulfides from mercaptans is known as sweetening, and can be found throughout the chemical processing industry. In order to better understand this phenomena and possible catalytic properties for optimization of the process, a proper rate law must be established. For Part 1 of your term project, provide possible rate laws based on the truncated mechanism shown in figure 2 and an algorithm describing how the most accurate rate law would be determined. In addition, for the experimental set-up shown in figure 3, what is the temperature (Te) that must be maintain in order for the reactor temperature to remain at 31 C (TA). Figure 3. Reactor set-up for bench-scale thiol oxidation at TA = 31 C. The reactor sits in a temperature-controlled bath, initially loaded with 140 mmol/L of 2-ME. The concentration of the catalyst is considered constant (as the definition of a catalyst suggests). The concentration of oxygen, OH are also constant at approximately 10.5339 mmol/L and 2.59 mmol/L, respectively. The components sit in a reactor with 50 ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) as the solvent. The reactor has to maintain a temperature of 31 C for optimum conditions. Assume negligible concentrations of water The heat capacities of the thiol, disulfide, oxygen and THF can be estimated as: Thiol: Cp/R - -2.930 +137.0810 T - 84.7310"T, T[Kelvin) Disulfide: Cp/R-6.311+0.805x10 T-0.906x10T2, T[Kelvin) Oxygen: Cp/R = 3.639 +0.506x10 T +0.506x10^T, T|Kelvin Water: Cp/R - 8.72 +1.25X10 T -0.18*10"T?, T[Kelvin Sodium Hydroxide: Cp/R-0.121+16,31610'T+1.948*10*T*?, T[Kelvin] Tetrahydrofuran THE Cp/R-15.133+6.79x10 'T+16,35x10T2, T[Kelvin)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


