Question: K&N Management, Inc.57 is the developer and licensing agent for Rudy's Country Store and Bar-B-Q, as well as Mighty Fine Burgers, Fries, and Shakes outlets
K&N Management, Inc.57 is the developer and licensing agent for Rudy's Country Store and Bar-B-Q, as well as Mighty Fine Burgers, Fries, and Shakes outlets in the Austin, Texas market. K&N started with a limited menu driven by high quality food, speed of service, and a focus on doing a few things excellently instead of many things just average. By 2005, the company had expanded from one to four Rudy's locations. In 2009, after only two years of operation, Mighty Fine Burgers, Fries and Shakes, boasting an innovative concept in fast-casual food, demonstrated that it was one of the best start-up fast-casual concepts in the nation. That year, they added two additional stores to their rapidly growing chain.
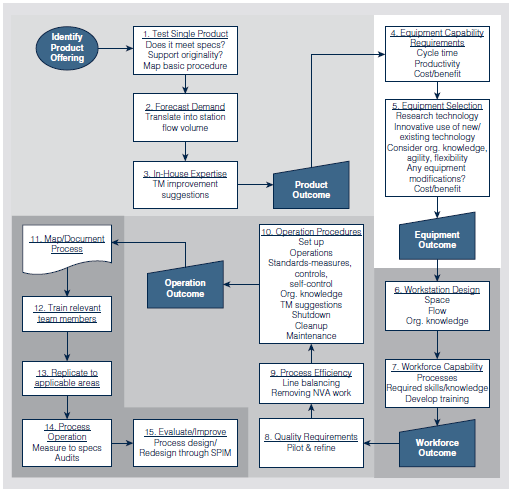
Customers require high-quality food served quickly and accurately by friendly team members (K&N's terminology for their employees) in a clean environment. This requires well-defined processes with clearly defined requirements and measurements. K&N uses a comprehensive system for process management that incorporates design, control, and improvement (Figure 5.7). Design of work processes is linked to product offerings; as new or improved products are designed (boxes 1-3 in Figure 5.7), redesign of work processes may be necessary. First, equipment needs are analyzed, based on the equipment capability requirements and selection characteristics (boxes 4 and 5). Next, workforce needs are determined, including the design of workstations and the capabilities needed in the workforce (boxes 6 and 7). Design of the operations addresses quality requirements, process efficiency, and operating procedures (boxes 8, 9, and 10). Because the restaurant industry experiences seasonal fluctuations, K&N designs work processes to meet varying levels of demand. Cycle time (boxes 4, 5, 6, and 10), productivity (box 9), and cost control factors (boxes 5, 10, and 13) are considered during the design/redesign process.
Process control and improvement are addressed in the remaining steps of the process (boxes 11-15). This includes mapping and documenting the process, training team members, replicating (i.e., implementing) the process to all applicable areas, measuring and auditing to specifications, and evaluation and improvement. K&N applies lean principles and removes non-value-added steps from the process in order to improve quality and productivity. Employee training in self-management includes basic knowledge of how to identify and correct problems, and the critical importance of not passing on product that does not fully meet the standard.
Each process is designed so the process requirements are translated to operational steps, which are a set of behaviors and methods that if they are performed to standard will result in the product meeting standards. K&N uses measures to control process output using visual standards that allow team members to see if standards are being met. Following the process steps and the associated behaviors and methods, along with visual standards, provides inprocess controls. In most work processes there are in-process indicators which show if the process is performing to standard. For example, prep team members check portion weights and visually compare the product to standards. If the fries do not look like the right color coming out of the fryer, team members correct or throw out the product. Various checks are used as mistake-proofing devices. For example, every burger is checked with the guest's order before wrapping; the cashier reads back the order to the guest to verify it is complete; team members use a triple-check system to verify accuracy on Group Meal orders; and the cashier checks items off of a to-go pad before placing them in the to-go bag.
Each operation is designed so the team member is in a state of self-control, meaning that they know the standards, have the skills to check to see if the process output meets the standards, and are empowered to correct it or stop the product unless it meets 100 percent of the standards. Team members are given the necessary coaching, materials, and knowledge of, and access to, equipment. They are provided with an understanding of the process, standards, and expectations for results. They are empowered with the ability to not only carry out the process, but to stop the process if anything is found to be less than 100 percent compliant with the standards.
FIGURE 5.7 Process Management Framework at K & N Management
Data that indicate the need for work process improvements come from operations inspections, process audits, team members, and guest feedback. Even senior leaders use a systematic approach for evaluating and improving their own work processes. Work process improvements and lessons learned are deployed to other locations in order to integrate organizational learning and innovation. If a new process or a process change is approved, the standard is changed, and it is rolled out to all applicable locations. After the change is implemented, an audit is performed using the new standard and discrepancies are corrected. When the cause of a problem is not known, a special problem-solving process is used. This includes finding the root cause of the problem, determining the best solution, designing an improvement and implementing it, determining if the results are positive, and if so, standardizing the solution. The problem-solving process has assisted K&N in reducing variability in processes across the organization, improving production and service processes, and achieving better performance.
QUESTIONS:
1- IS THERE A PROBLEM/SYMPTOMS IN K&N PROCESS MANAGEMENT?
2- SUGGEST AN APPROACH/METHOD TO IMPROVE THEIR PROCESS MANAGEMENT?
3- IS THERE AN EXISTING AREA IN THEIR PROCESS MANAGEMENT THAT NEEDS MORE FOCUS AND IMPROVEMENT? AND HOW?
Identify 1. Test Single Product 4. Equipment Capability Product Does it meet specs? Requirements Offering Support originality? Cycle time Map basic procedure Productivity Cost/benefit 2. Forecast Demand 5. Equipment Selection Translate into station Research technology flow volume Innovative use of new existing technology Consider org. knowledge, agility, flexibility 3. In-House Expertise Any equipment TM improvement Product modifications? Outcome Cost/benefit suggestions 10. Operation Procedures 11. Map Document Set up Equipment Outcome Process Operations Standards-measures, controls, Operation self-control Outcome Org. knowledge 6. Workstation Design SPACE 12. Train relevant TM suggestions Shutdown Flow Cleanup Org. knowledge Maintenance 13. Replicate to 9. Process Efficiency 7. Workforce Capabilit Line balancing Processes applicable areas Removing INVA work Required skills/knowledge Develop training 14. Process Operation 15. Evaluate/Improve Process design 8. Quality Requirements Measure to specs Redesign through SPIM Pilot & refine Workforce Audits Outcome
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


