Question: L' regularization on the model parameter w is defined as Ilwlh = Elwil In this question, you are asked to apply L' regularization to a
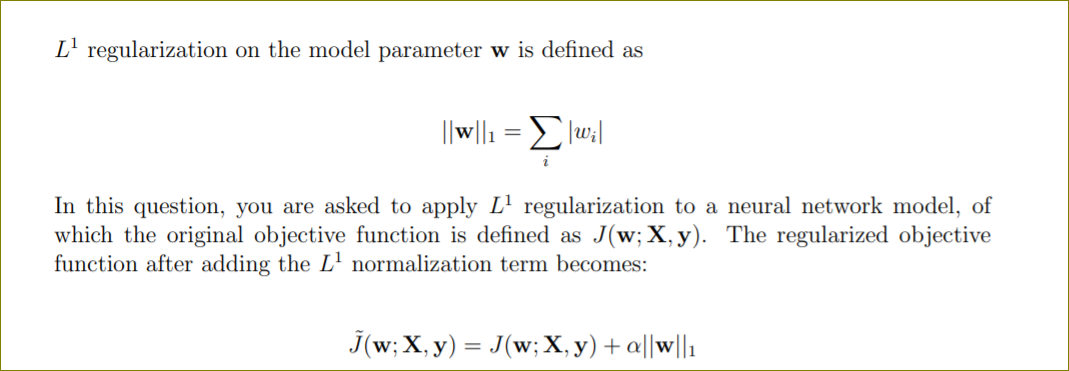


L' regularization on the model parameter w is defined as Ilwlh = Elwil In this question, you are asked to apply L' regularization to a neural network model, of which the original objective function is defined as J(w; X, y). The regularized objective function after adding the L' normalization term becomes: j ( w; X, y) = J(w; X,y) + allwll. We apply Taylor expansion to J(w; X, y) and discard high-order terms. Specific cally, we approximate the original objective function J with J ( w; X,y) = J(w*) + ( w - w*)"H(w -w*) , where w* is the optimal parameter for the objective function without the regu- larization term and H is the Hessian matrix. . We assume the Hessian is diagonal, H = diag([H1,1, ..., Hn,n]), where each Hii > 0. This assumes that there is no correlation between the input features.Now, write down an analytical solution for each element 10,- of w when the gradient equals to zero. Your answer should be expressed with weights to: (w* is the the optimal weights for an unregularized object function), Hesian matrix elements Hg,\" and coefcient a. Hint: the gradient of |;r| at a: = 0 can take any value between [1,1]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


