Question: Last 4 pages are the starter code for the program and tests. Mod 4 Homework - Enhanced DoublyLinkedList Doubly Linked Lists (DLLs) support O(1) addition



 Last 4 pages are the starter code for the program and tests.
Last 4 pages are the starter code for the program and tests.
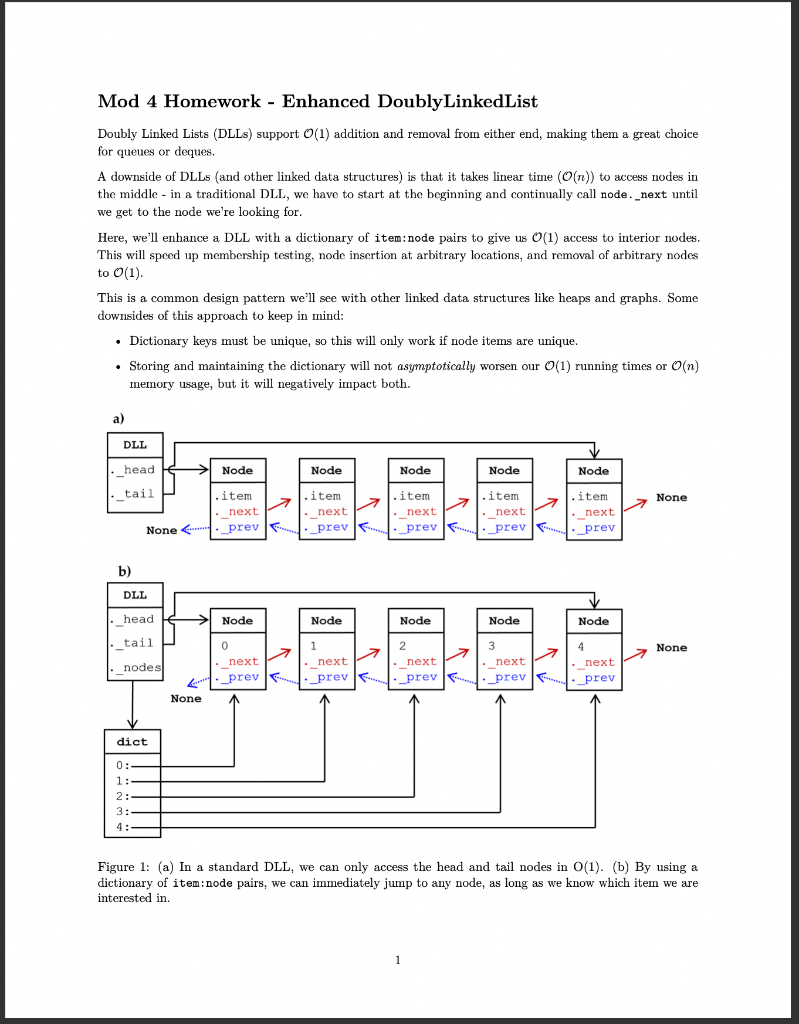
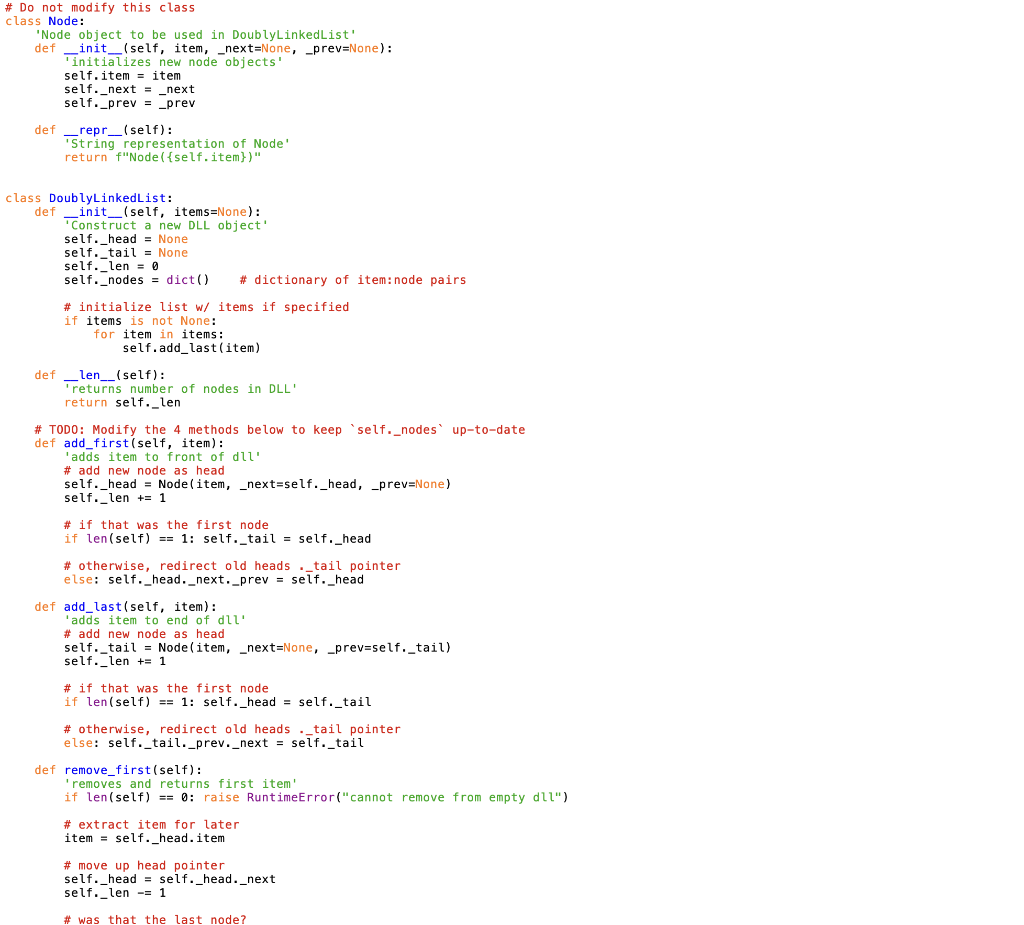
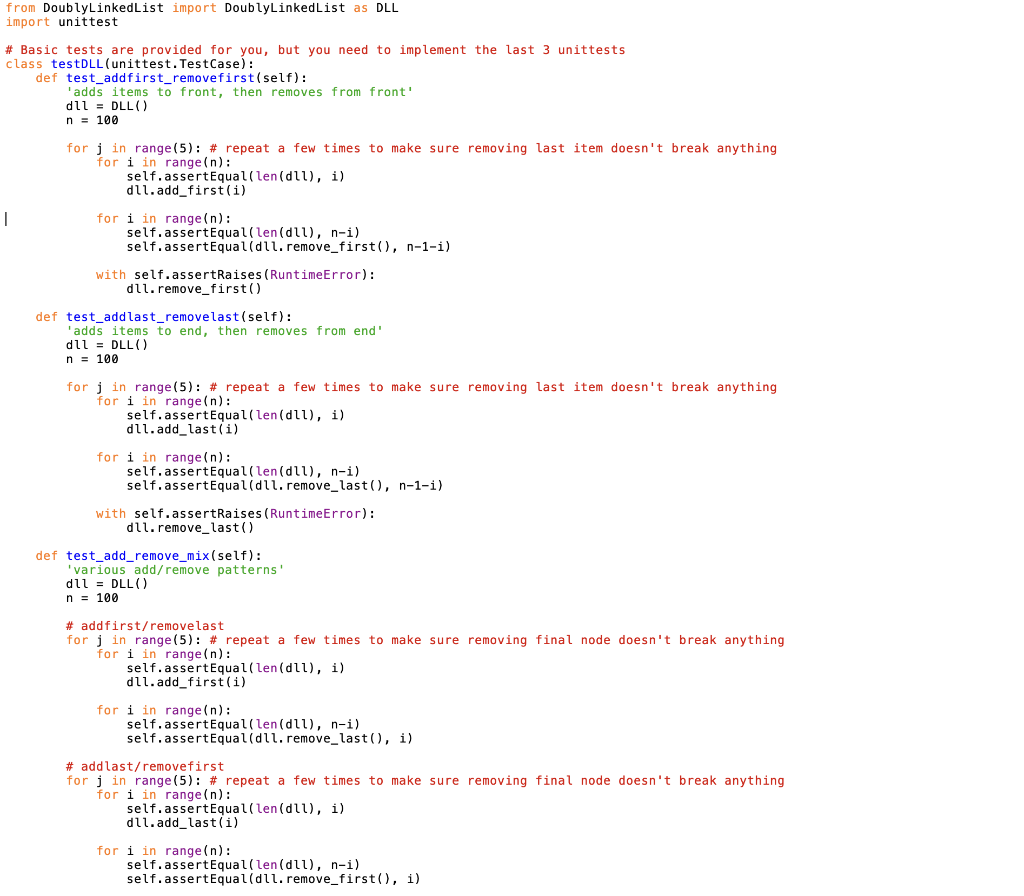
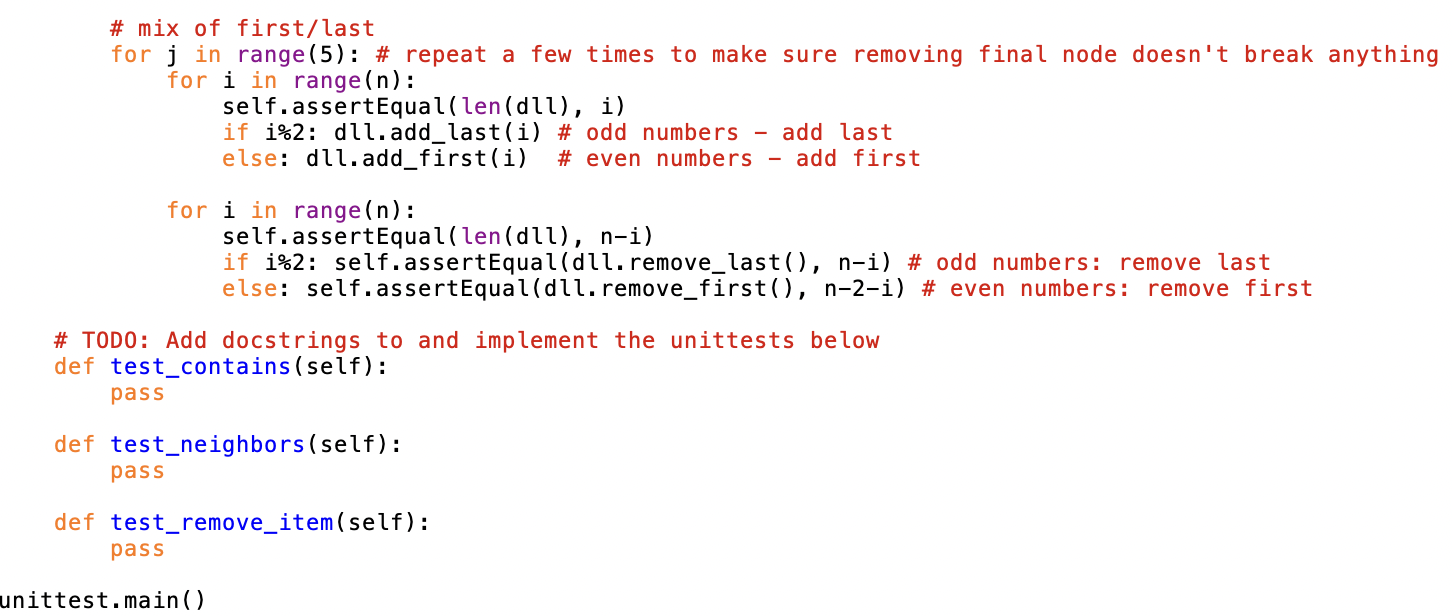
Mod 4 Homework - Enhanced DoublyLinkedList Doubly Linked Lists (DLLs) support O(1) addition and removal from either end, making them a great choice for queues or deques. A downside of DLLs (and other linked data structures) is that it takes linear time (O(n)) to access nodes in the middle - in a traditional DLL, we have to start at the beginning and continually call node. next until we get to the node we're looking for. Here, we'll enhance a DLL with a dictionary of item: node pairs to give us O(1) access to interior nodes. This will speed up membership testing, node insertion at arbitrary locations, and removal of arbitrary nodes to O(1). This is a common design pattern we'll see with other linked data structures like heaps and graphs. Some downsides of this approach to keep in mind: - Dictionary keys must be unique, so this will only work if node items are unique. - Storing and maintaining the dictionary will not asymptotically worsen our O(1) running times or O(n) memory usage, but it will negatively impact both. Figure 1: (a) In a standard DLL, we can only access the head and tail nodes in O (1). (b) By using a dictionary of item:node pairs, we can immediately jump to any node, as long as we know which item we are interested in. 1) Add a dictionary DoublyLinkedList.py provides basic Node and DoublyLinkedList classes that supports typical DLL operations. Modify these methods to keep the _nodes dictionary up to date with item:node pairs as you add and remove from the DLL so you can access any node in O(1). 2) Implement __contains__(item) _nodes is a private attribute, and thus should not be called explicilty in your tests. Instead, use _nodes to add a O(1) __ contains__( ) method to your DLL, and test __ contains__(): dll = DoublyLinkedList ( range (5)) 3 in dll \# O(1), even though 3 is in the middle True 5 in dll \# Note the use of 'in' to call the dunder method __ contains_() False Write a unittest that verifies contains works as expected as you add and remove nodes. 3) Implement neighbors (item) Add a method neighbors (item) to your DoublyLinkedList class that returns the items immediately before and after the node with item: dll = DoublyLinkedList (range (5)) dll.neighbors (3) (2,4) dll neighbors (0) \#Edge case - head (None, 1) dll. neighbors(4) \#Edge case - tail (3, None) - Should be O(1) - When called on the item stored in the head/tail, return None as the previousext item, as shown above - Raise a RuntimeError if someone searches for an item not in the DLL Include unittests for the above behavior (except the running time). 4) Implement remove_node (item) Add a method that removes the node containing an item from your DLL. - O(1) - Make sure to "stitch together" the adjacent nodes - Edge cases you should be able to handle: - Raise a RuntimeError if someone tries to remove an item not in the DLL - Removing the head - Removing the tail Include unittests for the above behavior (except the running time). Submitting At a minimum, submit the following files: - DoublyLinkedList.py - TestDoublyLinkedList.py Additionally, you must include any other files necessary for your code to run, such as modules containing data structures you wrote yourself. Do not import any modules you did not write yourself. The functionality added by external modules is one of the great things about python, but we restrict them for two reasons: - Some of them circumvent the purpose of these assignments, which is to develop basic algorithm design habits - Some of them are not supported by our Python install on Gradescope, making it impossible for us to run your code there (and thus slowing down our grading significantly) Students must submit individually by the due date (typically, Tuesday at 11:59 pm EST) to receive credit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


