Question: less than 150wrds more than 100!! try using key terms if applicable please and thank you. 8. What is a big limitation of the audit
less than 150wrds more than 100!! try using key terms if applicable please and thank you.
8. What is a big limitation of the audit risk model, given what the book says on p. 280? You gave two sets of risk assessments to two audit assistants and asked them to calculate PDR using the audit risk model. One reports back to you that the PDR is zero. The other reports back to you that the PDR is minus 1. You told them that these two numbers do not make sense. Why? What could be wrong?
pg. 280

key terms:
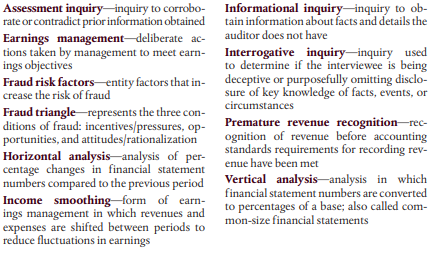
Measurement Limitations One major limitation in the application of the audit risk model is the difficulty of measuring the components of the model. Despite the auditor's best efforts in plan- ning, the assessments of acceptable audit risk, inherent risk, and control risk, and therefore planned detection risk, are highly subjective and are only approximations of reality. Imagine, for example, attempting to precisely assess inherent risk by determin- ing the impact of factors such as the misstatements discovered in prior years' audits and technology changes in the client's industry. To offset this measurement problem, many auditors use broad and subjective measurement terms, such as low, medium, and high. As Table 9-3 shows, auditors can use this information to decide on the appropriate amount and types of evidence to accumulate. For example, in situation 1, the auditor has decided on a high acceptable audit risk for an account or objective. The auditor has concluded a low risk of mis- statement in the financial statements exists and that internal controls are effective. Therefore, a high planned detection risk is appropriate. As a result, a low level of evi- dence is needed. Situation 3 is at the opposite extreme. If both inherent and control risks are high and the auditor wants a low acceptable audit risk, considerable evidence is required. The other three situations fall between these two extremes. It is equally difficult to measure the amount of evidence implied by a given planned detection risk. A typical audit program intended to reduce detection risk to the planned level is a combination of several audit procedures, each using a different type of evidence that is applied to different audit objectives. Auditors' measurement methods are too imprecise to permit an accurate quantitative measure of the com- bined evidence. Instead, auditors subjectively evaluate whether sufficient appropriate evidence has been planned to satisfy a planned detection risk of low, medium, or high. Presumably, measurement methods are sufficient to permit an auditor to determine whether more or different types of evidence are needed to satisfy a low planned detec- tion risk than for medium or high. Considerable professional judgment is needed to decide how much more. Assessment inquiry-inquiry to corrobo- Informational inquiryinquiry to ob- rate or contradict prior information obtained tain information about facts and details the Earnings management-deliberate ac- auditor does not have tions taken by management to meet earn- Interrogative inquiry-inquiry used ings objectives to determine if the interviewee is being Fraud risk factors-entity factors that in- deceptive or purposefully omitting disclo- crease the risk of fraud sure of key knowledge of facts, events, or Fraud triangle represents the three con- circumstances ditions of fraud: incentives/pressures, op- Premature revenue recognition-rec- portunities, and attitudes/rationalization ognition of revenue before accounting Horizontal analysis analysis of per- standards requirements for recording rev- enue have been met centage changes in financial statement numbers compared to the previous period Vertical analysis-analysis in which Income smoothing form of earn- financial statement numbers are converted ings management in which revenues and to percentages of a base; also called com- mon-size financial statements expenses are shifted between periods to reduce fluctuations in earnings
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


