Question: Let s consider the limiting values that result from the Basic PageRank Update Rule ( i . e . the version where we don t
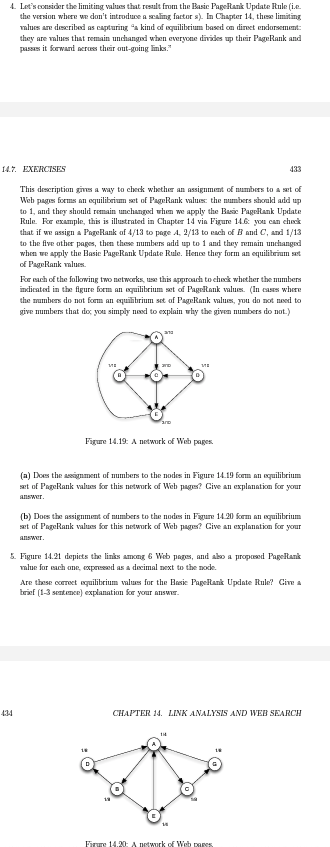
Lets consider the limiting values that result from the Basic PageRank Update Rule ie the version where we dont introduce a scaling factor s In Chapter these limiting values are described as capturing a kind of equilibrium based on direct endorsement: they are values that remain unchanged when everyone divides up their PageRank and passes it forward across their outgoing links. EXERCISES This description gives a way to check whether an assignment of numbers to a set of Web pages forms an equilibrium set of PageRank values: the numbers should add up to and they should remain unchanged when we apply the Basic PageRank Update Rule. For example, this is illustrated in Chapter via Figure : you can check that if we assign a PageRank of to page A to each of B and C and to the five other pages, then these numbers add up to and they remain unchanged when we apply the Basic PageRank Update Rule. Hence they form an equilibrium set of PageRank values. For each of the following two networks, use this approach to check whether the numbers indicated in the figure form an equilibrium set of PageRank values. In cases where the numbers do not form an equilibrium set of PageRank values, you do not need to give numbers that do; you simply need to explain why the given numbers do not. A B C E D Figure : A network of Web pages. a Does the assignment of numbers to the nodes in Figure form an equilibrium set of PageRank values for this network of Web pages? Give an explanation for your answer. b Does the assignment of numbers to the nodes in Figure form an equilibrium set of PageRank values for this network of Web pages? Give an explanation for your answer.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


