Question: Let w e R is an n-dimensional column vector, and f(w) ER is a function of w. In Lecture 2, we have defined the
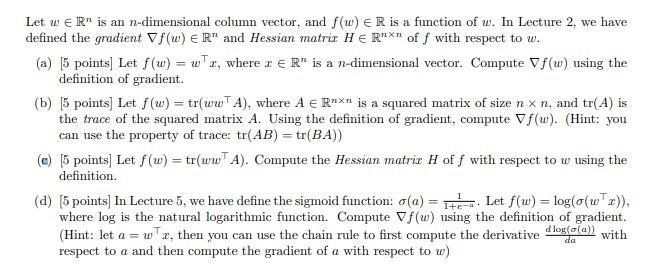
Let w e R" is an n-dimensional column vector, and f(w) ER is a function of w. In Lecture 2, we have defined the gradient Vf(w) E R" and Hessian matrir HE R"xn of f with respect to w. (a) 5 points] Let f(u) = wTr, where r R" is a n-dimensional vector. Compute Vf(w) using the definition of gradient. (b) 5 points] Let f(w) = tr(wwTA), where A Rxn is a squared matrix of size n x n, and tr(A) is the trace of the squared matrix A. Using the definition of gradient, compute Vf(u). (Hint: you can use the property of trace: tr(AB) = tr(BA)) (e) 5 points] Let f (w) = tr(uw" A). Compute the Hessian matriz H of f with respect to w using the definition. HE. Let f(w) = log(o(wTr)), (d) [5 points] In Lecture 5, we have define the sigmoid function: o(a) %3D where log is the natural logarithmic function. Compute Vf(w) using the definition of gradient. d log(a(a) with wx, then you can use the chain rule to first compute the derivative (Hint: let a = respect to a and then compute the gradient of a with respect to w) da
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets solve each part step by step Part a Given fw wT x where w in mathbbRn and x in mathbbRn G... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


