Question: Let's solve the above problem with different parameters as given below: Problem Cases Original Total Strain (in/in) length (in) deformation (in) Guided Practice 11 0.02
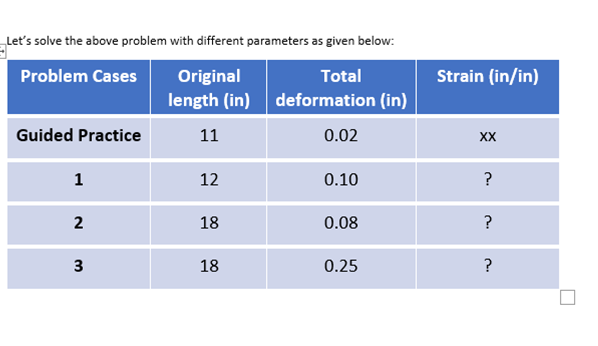
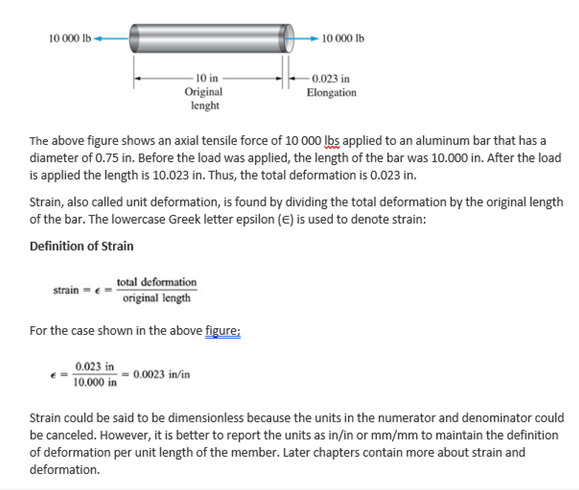
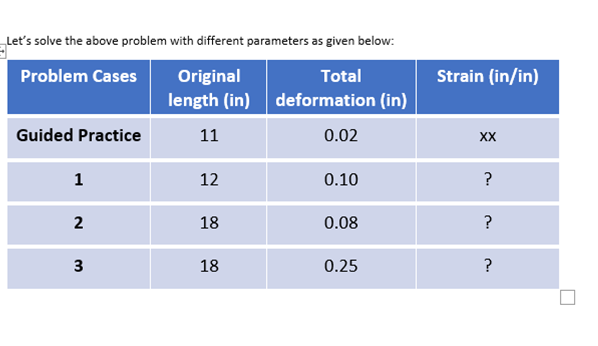
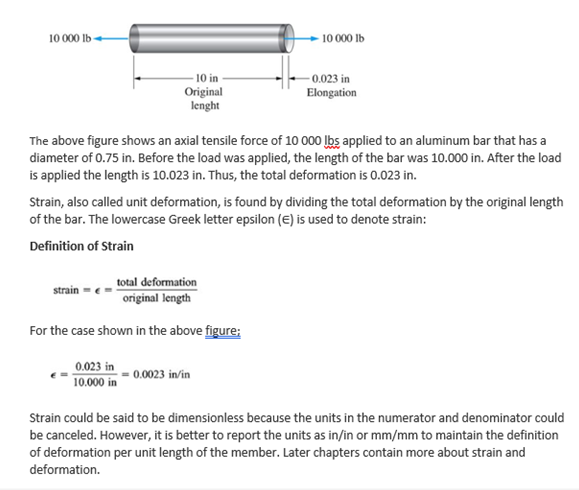
Let's solve the above problem with different parameters as given below: Problem Cases Original Total Strain (in/in) length (in) deformation (in) Guided Practice 11 0.02 XX H 12 0.10 N 18 0.08 3 18 0.2510 000 lb - -10 000 1b - 10 in - 0.023 in Original Elongation lenght The above figure shows an axial tensile force of 10 000 lbs applied to an aluminum bar that has a diameter of 0.75 in. Before the load was applied, the length of the bar was 10.000 in. After the load is applied the length is 10.023 in. Thus, the total deformation is 0.023 in. Strain, also called unit deformation, is found by dividing the total deformation by the original length of the bar. The lowercase Greek letter epsilon (E) is used to denote strain: Definition of Strain strain = = total deformation original length For the case shown in the above figure; 0.023 in = 0.0023 in/in 10.000 in Strain could be said to be dimensionless because the units in the numerator and denominator could be canceled. However, it is better to report the units as in/in or mm/mm to maintain the definition of deformation per unit length of the member. Later chapters contain more about strain and deformation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


