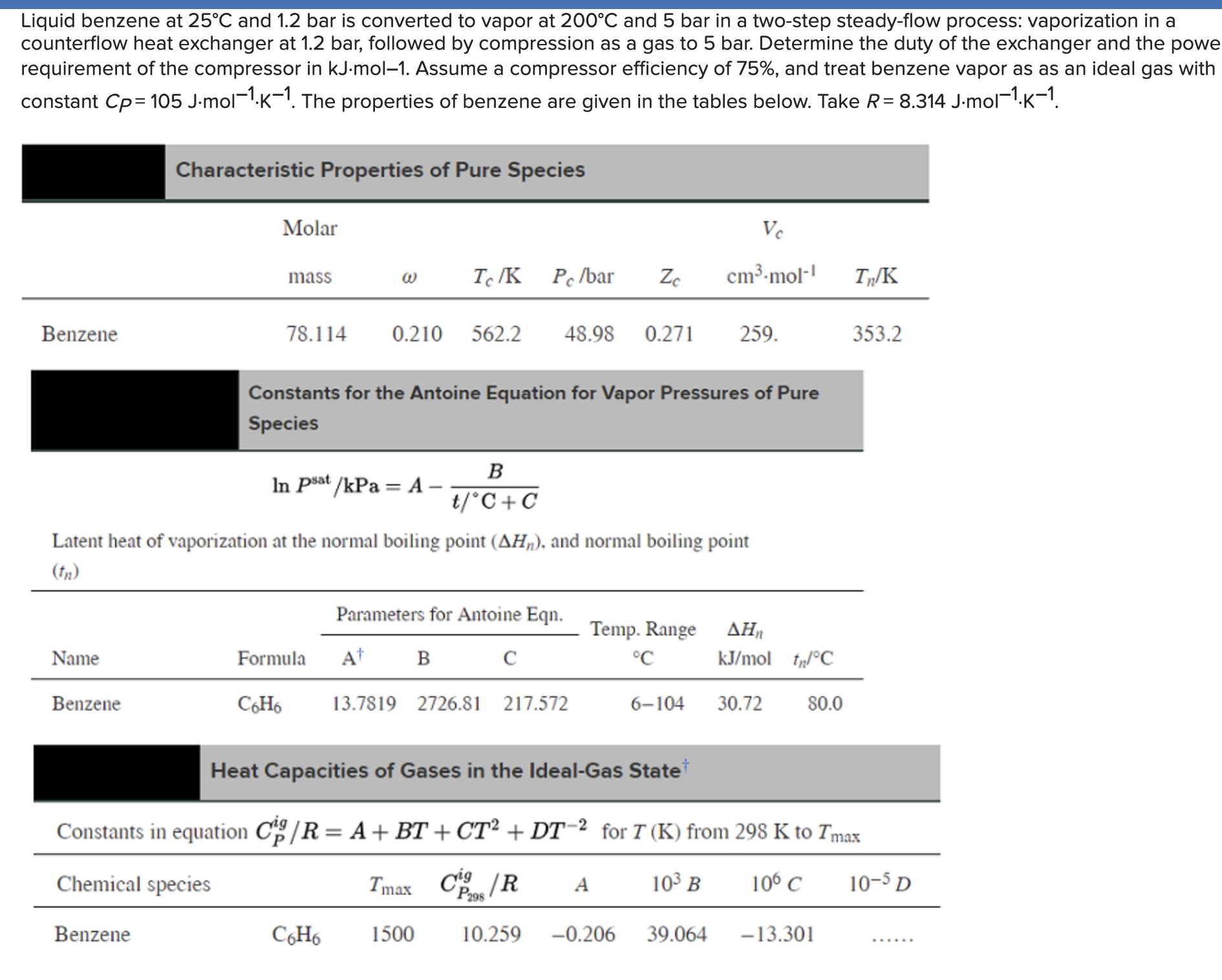
Question: Liquid benzene at 2 5 C and 1 . 2 bar is converted to vapor at 2 0 0 C and 5 bar in a
Liquid benzene at and bar is converted to vapor at and bar in a twostep steadyflow process: vaporization in a
counterflow heat exchanger at bar, followed by compression as a gas to bar. Determine the duty of the exchanger and the powe
requirement of the compressor in Assume a compressor efficiency of and treat benzene vapor as as an ideal gas with
constant The properties of benzene are given in the tables below. Take
Characteristic Properties of Pure Species
Constants for the Antoine Equation for Vapor Pressures of Pure
Species
Latent heat of vaporization at the normal boiling point and normal boiling point
Heat Capacities of Gases in the IdealGas State
Constants in equation for from to
The duty of the exchanger is kJmol
The power requirement of the compressor is kJmol
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


