Question: llings Review View Help Problem 3 Consider NFA M in the figure: Figure 1: NFA M of Problem 3 qd 90 qc I Figure 2:
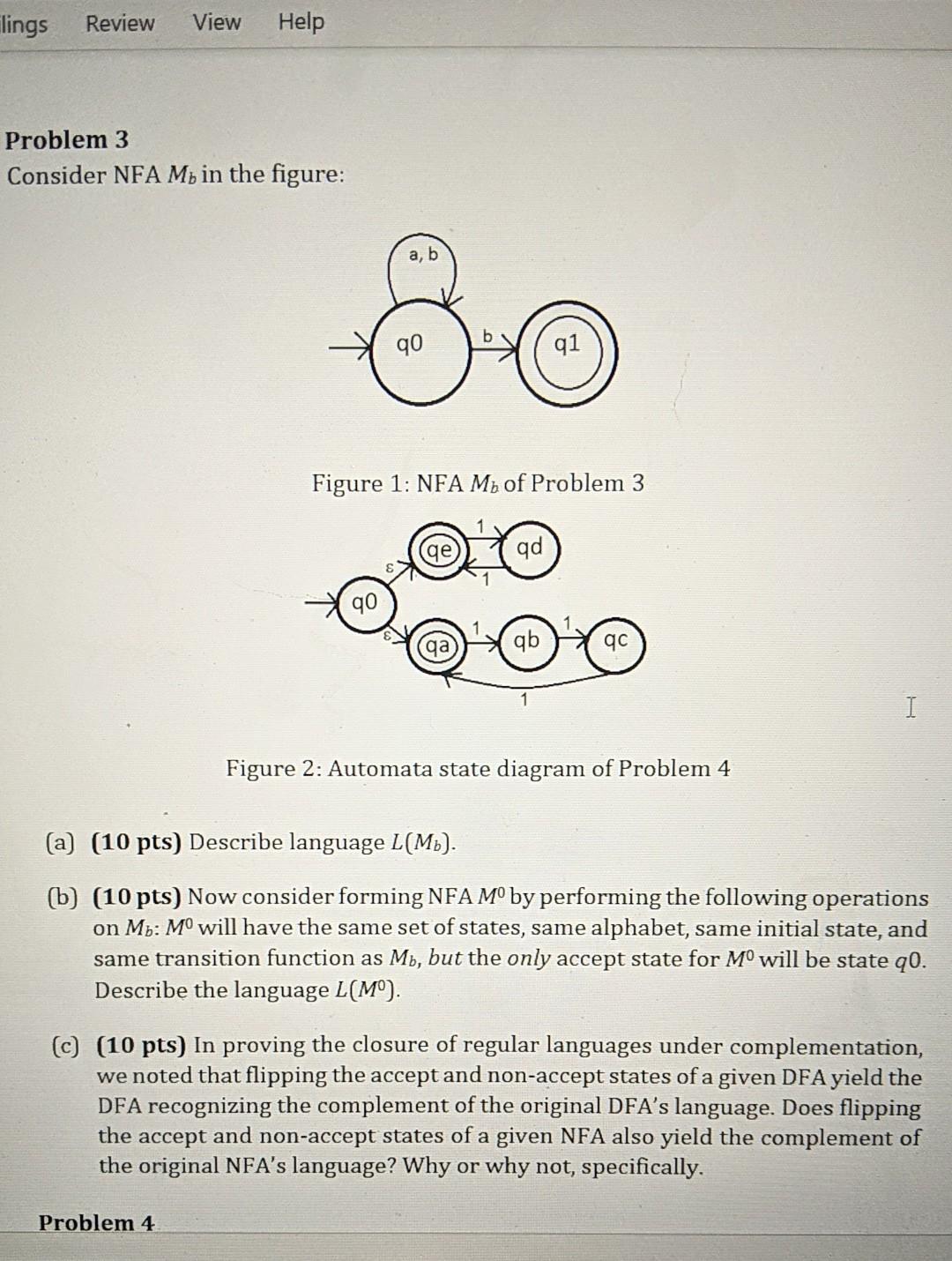
llings Review View Help Problem 3 Consider NFA M in the figure: Figure 1: NFA M of Problem 3 qd 90 qc I Figure 2: Automata state diagram of Problem 4 (a) (10 pts) Describe language L(Mb). (b) (10 pts) Now consider forming NFA Mby performing the following operations on Mo: M will have the same set of states, same alphabet, same initial state, and same transition function as Mb, but the only accept state for M will be state 20. Describe the language L(M). C) (10 pts) In proving the closure of regular languages under complementation, we noted that flipping the accept and non-accept states of a given DFA yield the DFA recognizing the complement of the original DFA's language. Does flipping the accept non-accept states of a given NFA also yield the complement of the original NFA's language? Why or why not, specifically. Problem 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


