Question: Load Kirin USA Inc. case Answer the questions provided below: Question 1: Conduct a needs-based segmentation analysis to determine if the import bear market could
Load Kirin USA Inc. case
Answer the questions provided below:
Question 1: Conduct a needs-based segmentation analysis to determine if the import bear market could be segmented in a useful way. Use Segmentation Data for your analysis. Determine if there are any targetable segments that emerge from this analysis.
(1) What is the number of segments?
(2) Describe each segment by its needs and name each segment.
(3) Build a profile of each segment with using the output of the discriminant analysis.

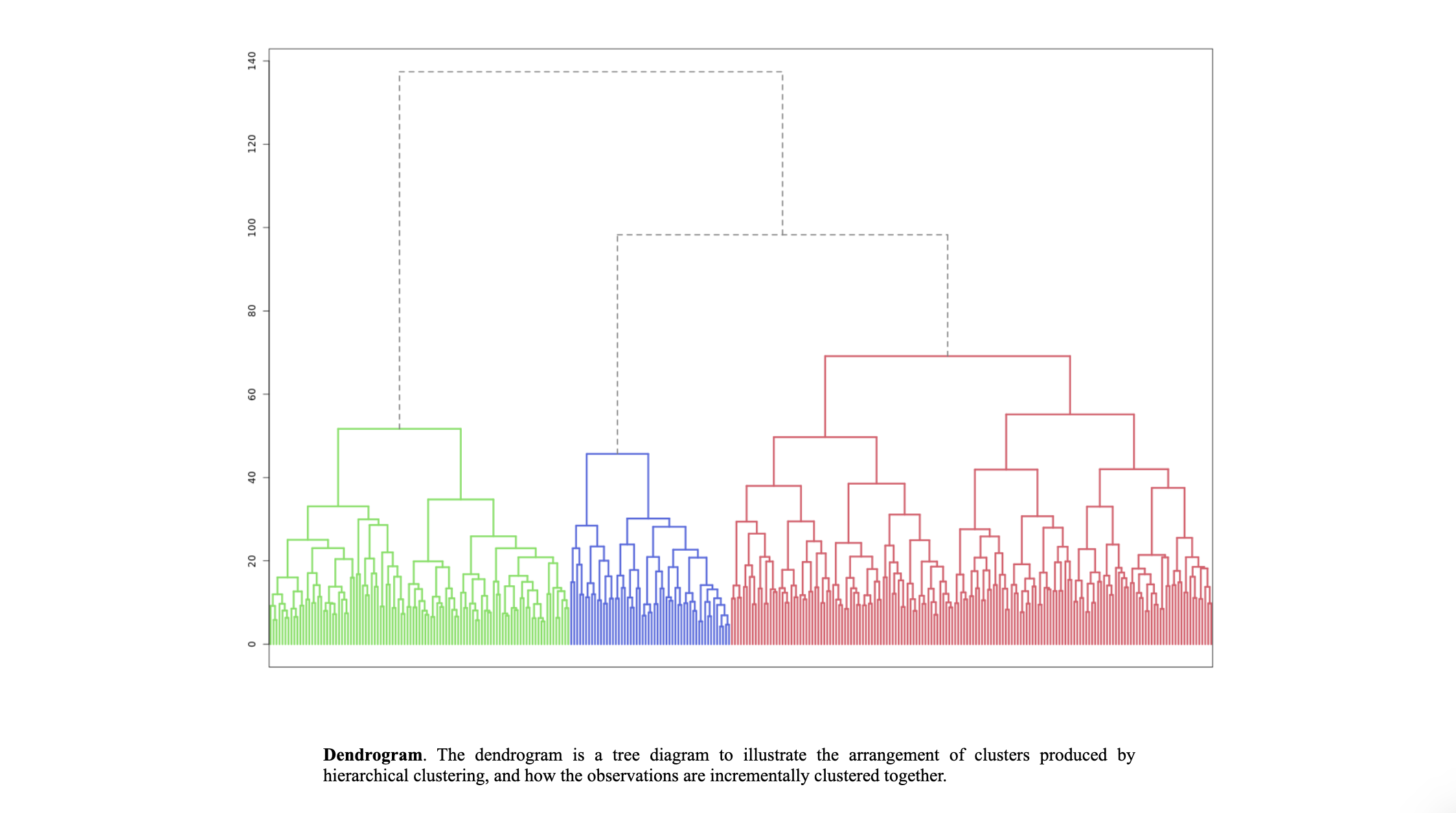 \
\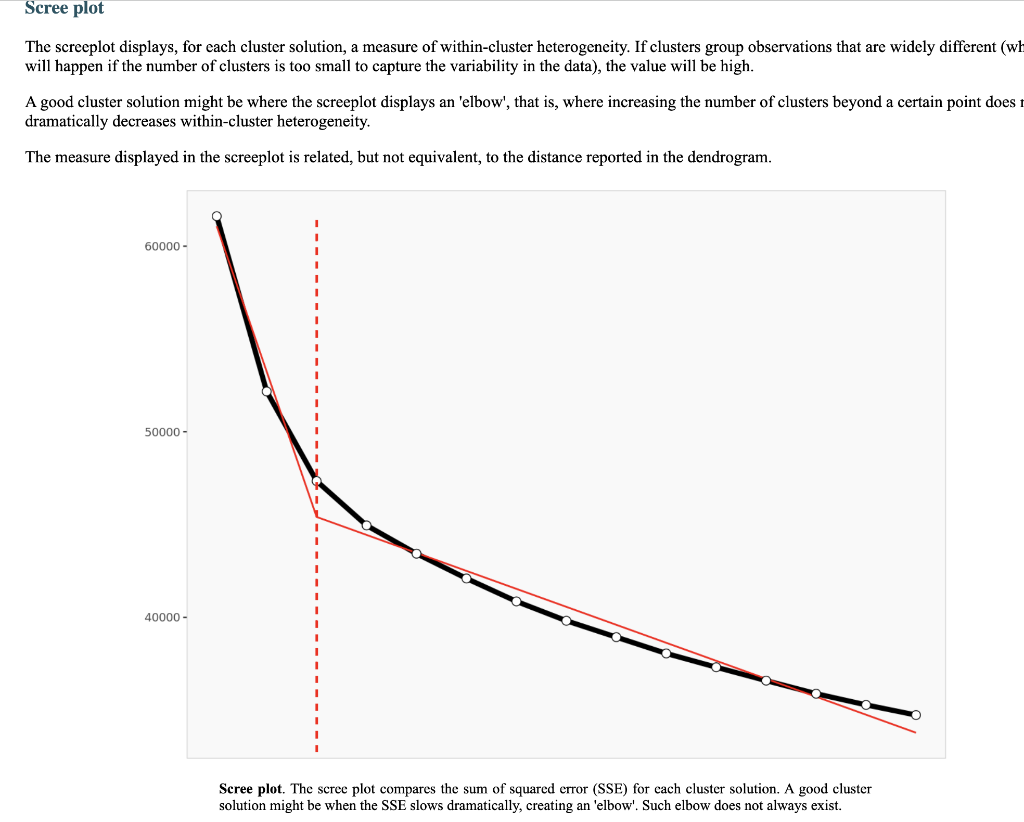
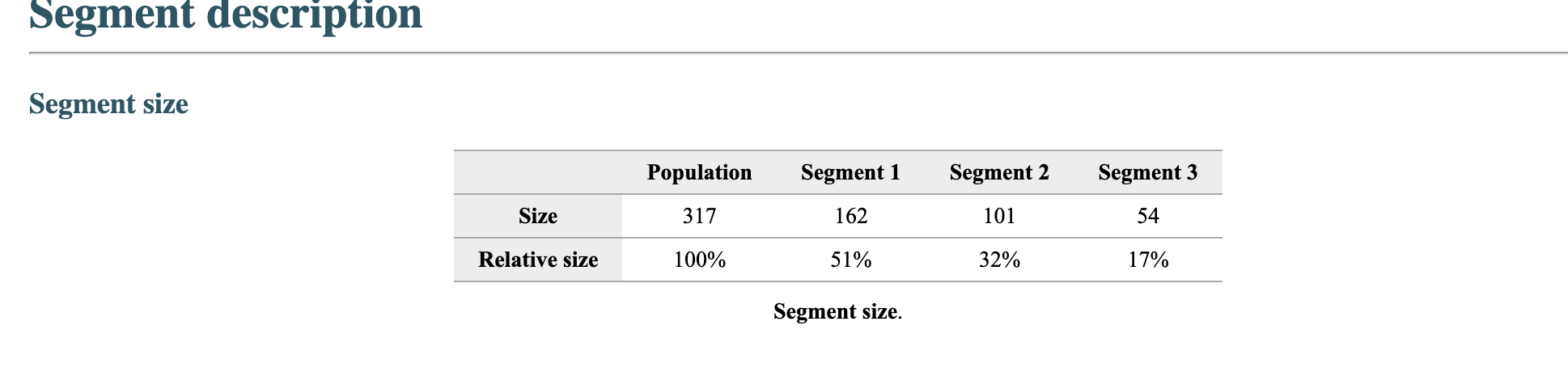
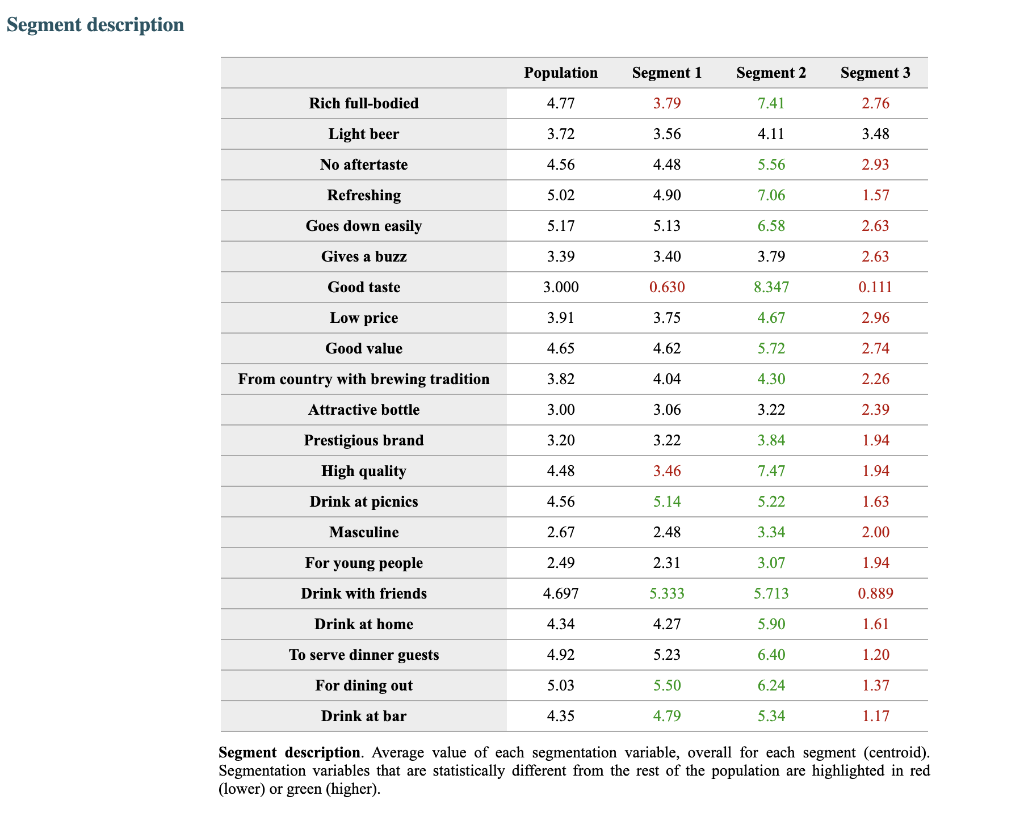
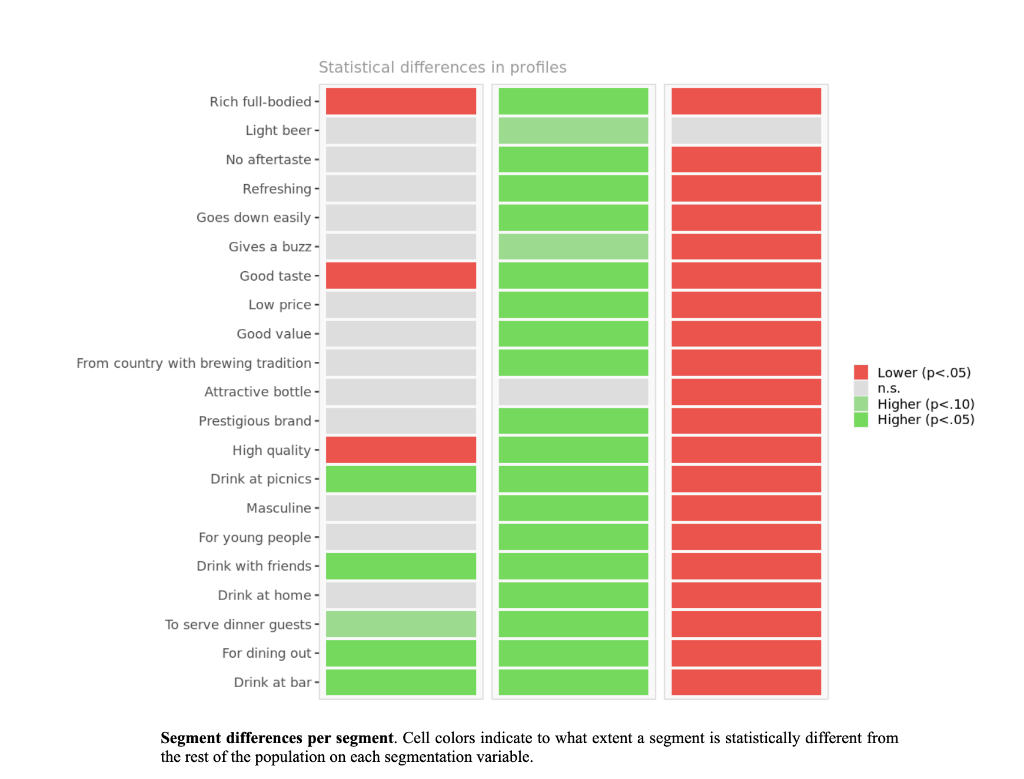
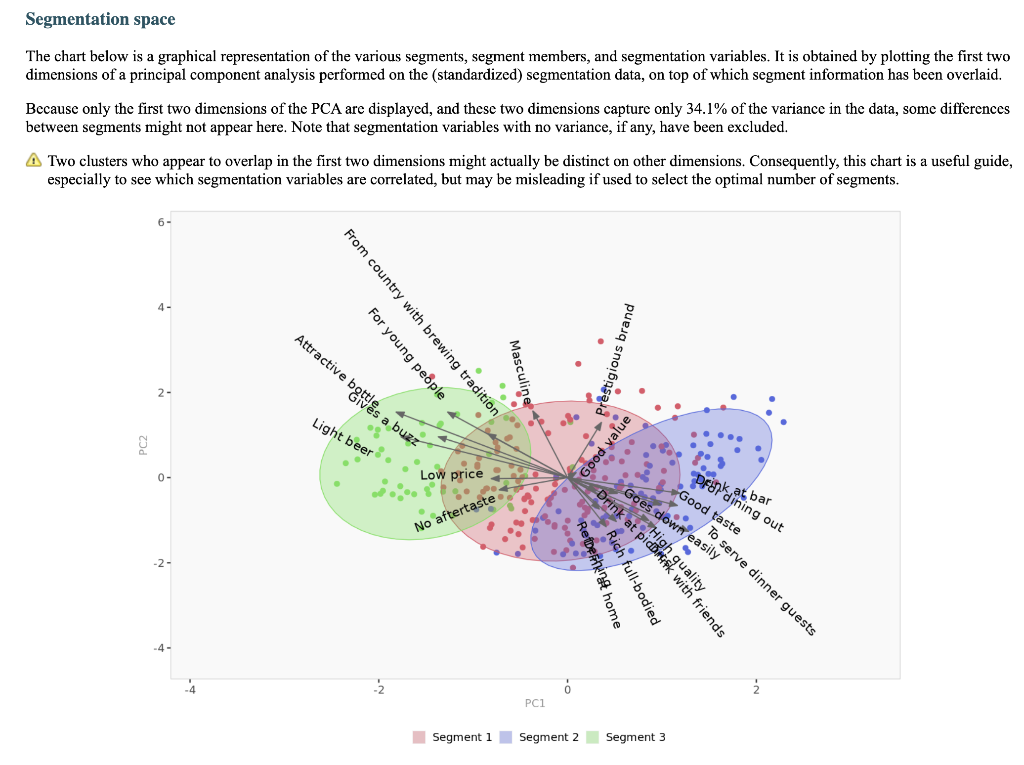
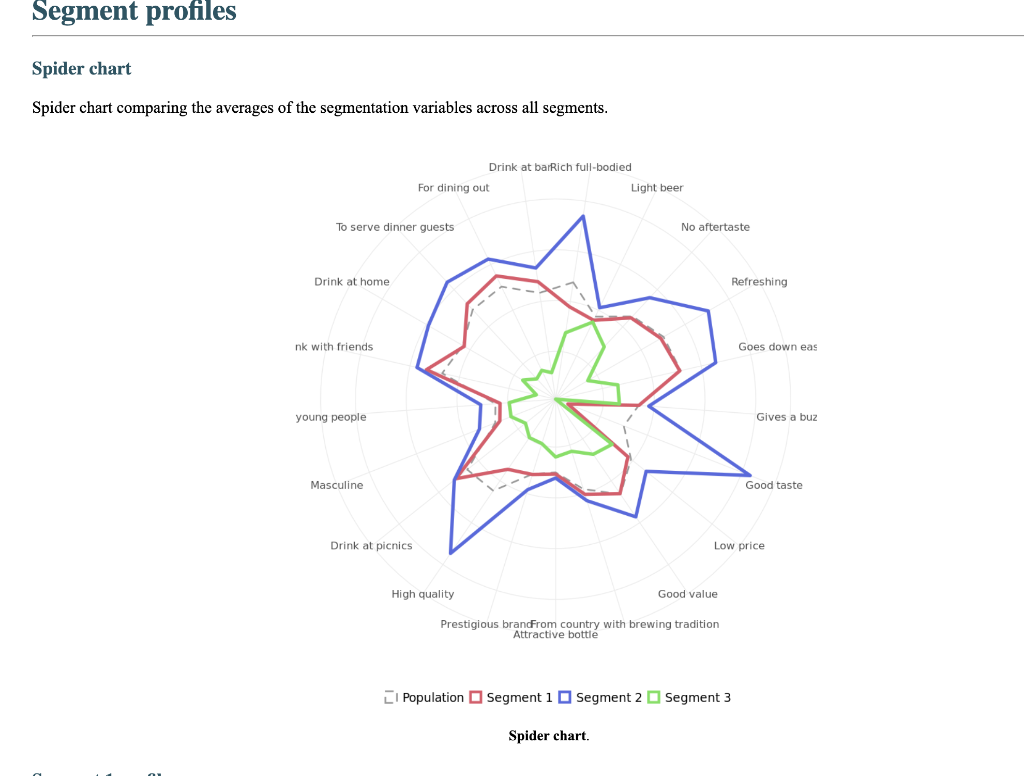
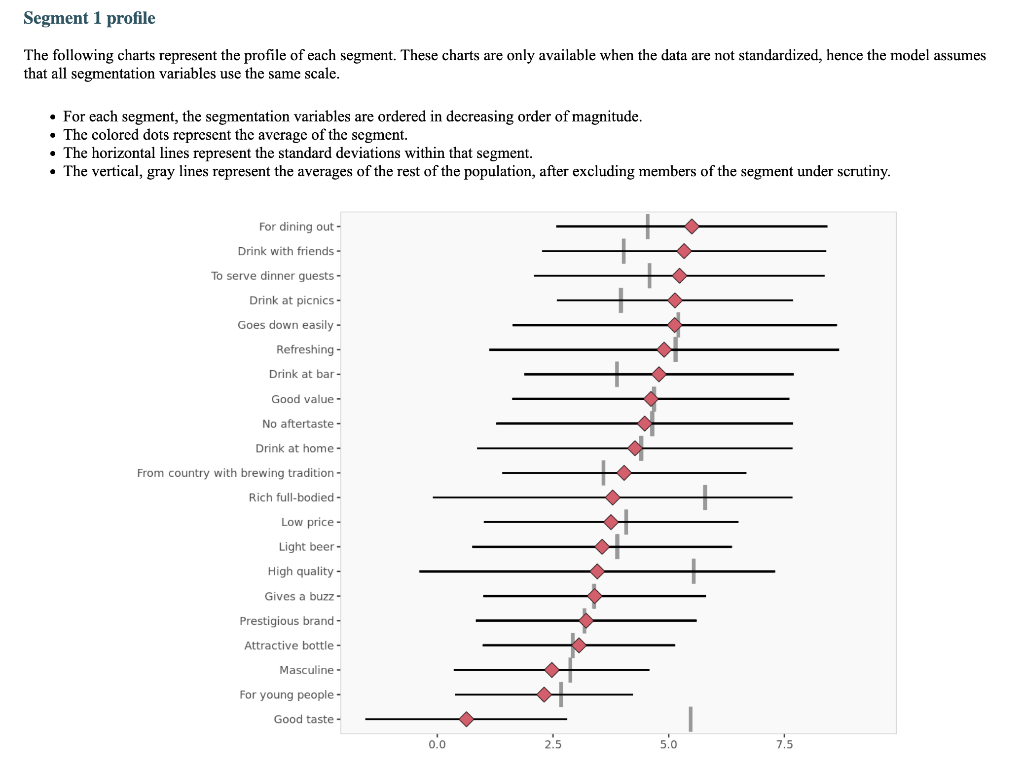
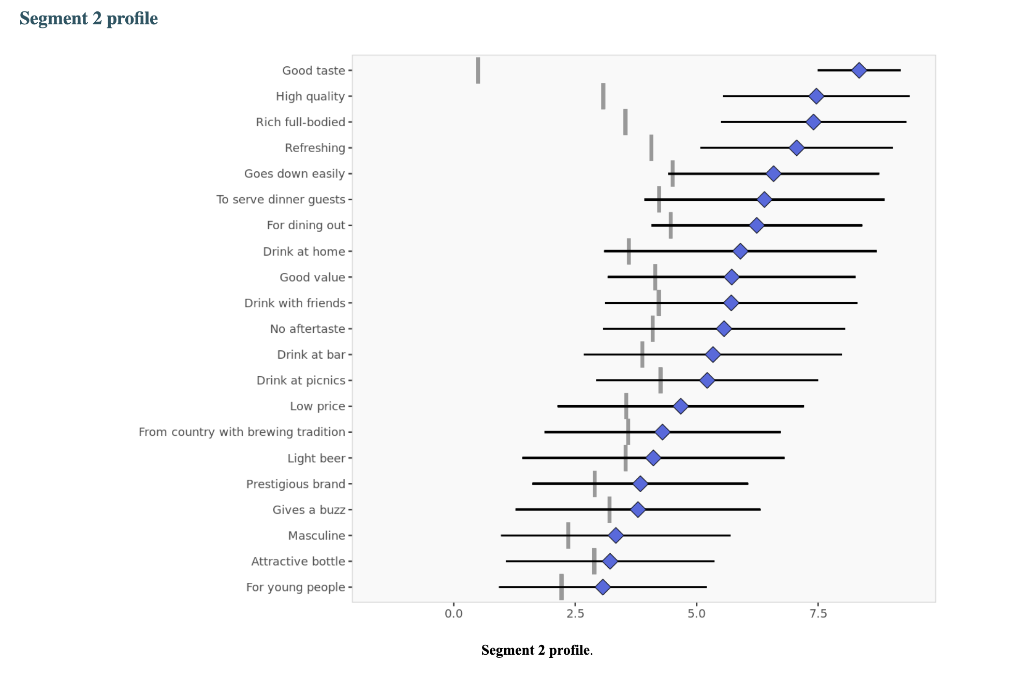
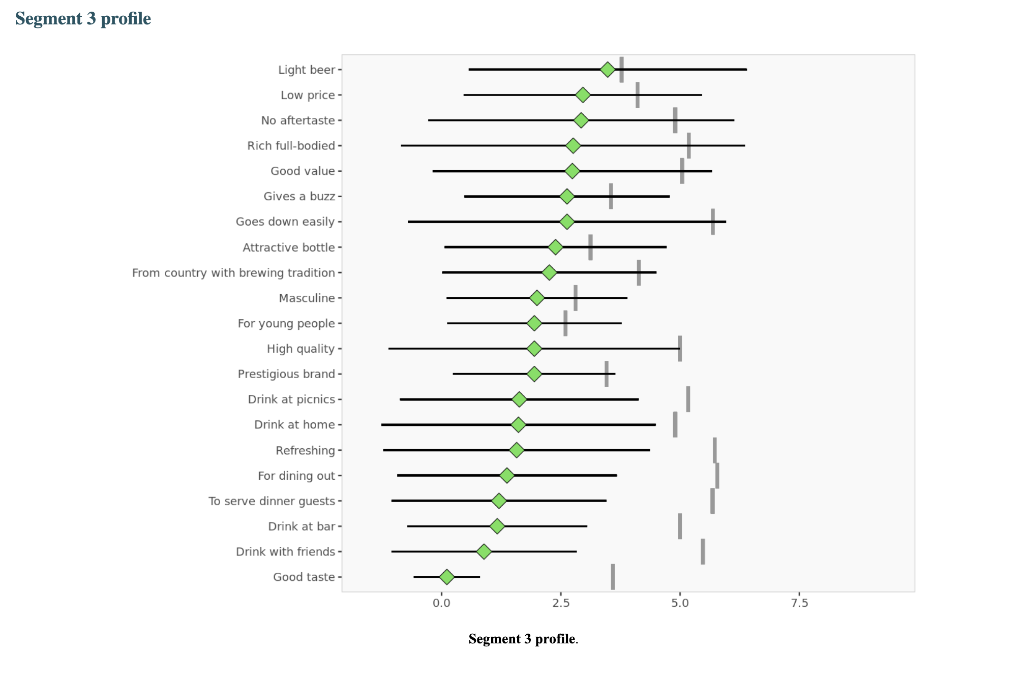
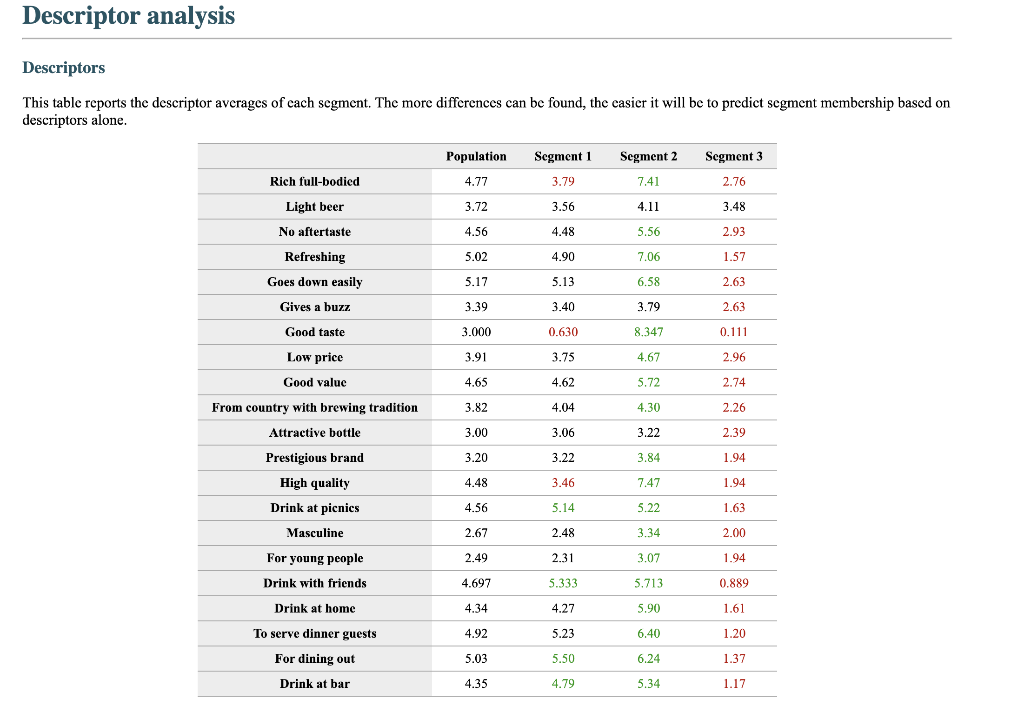
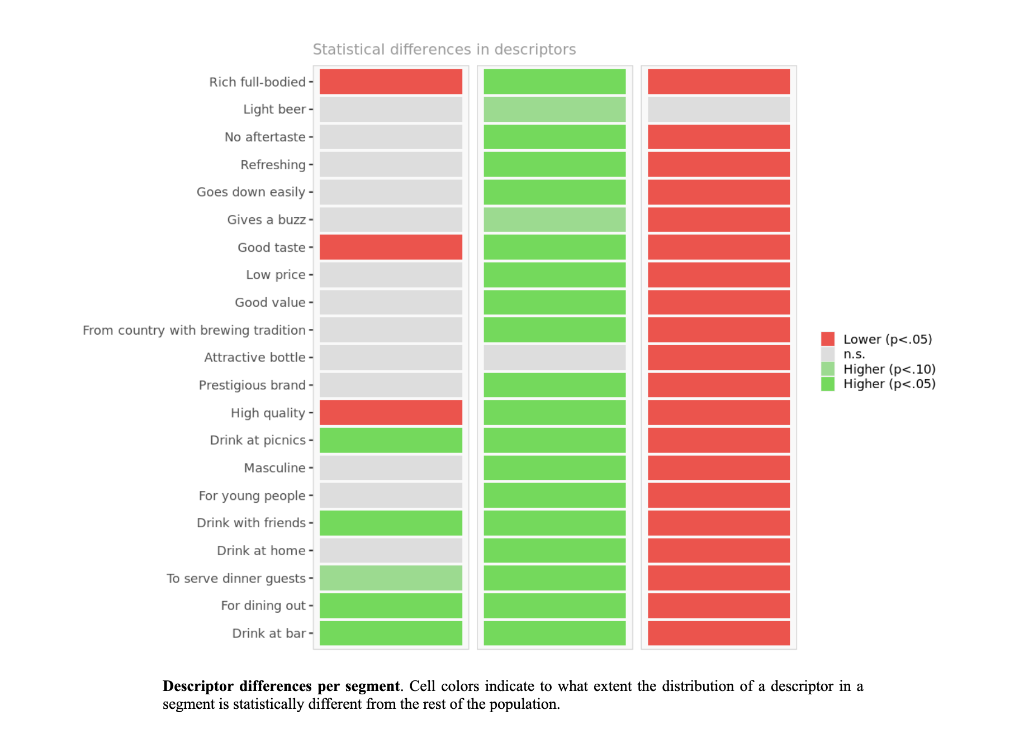
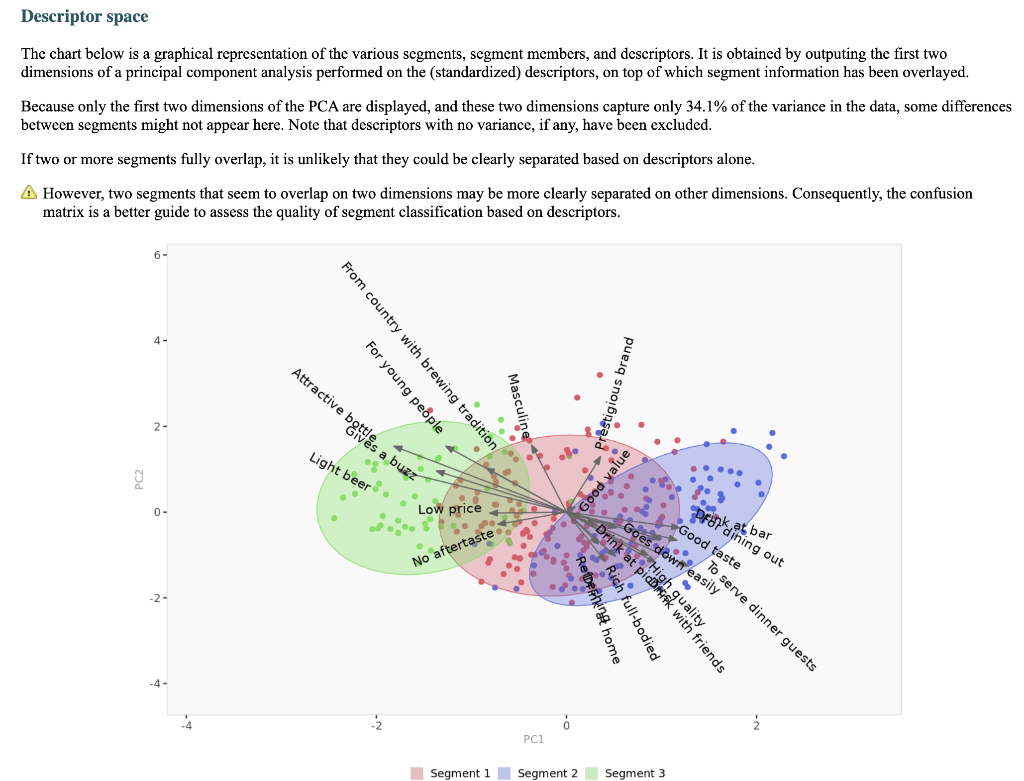

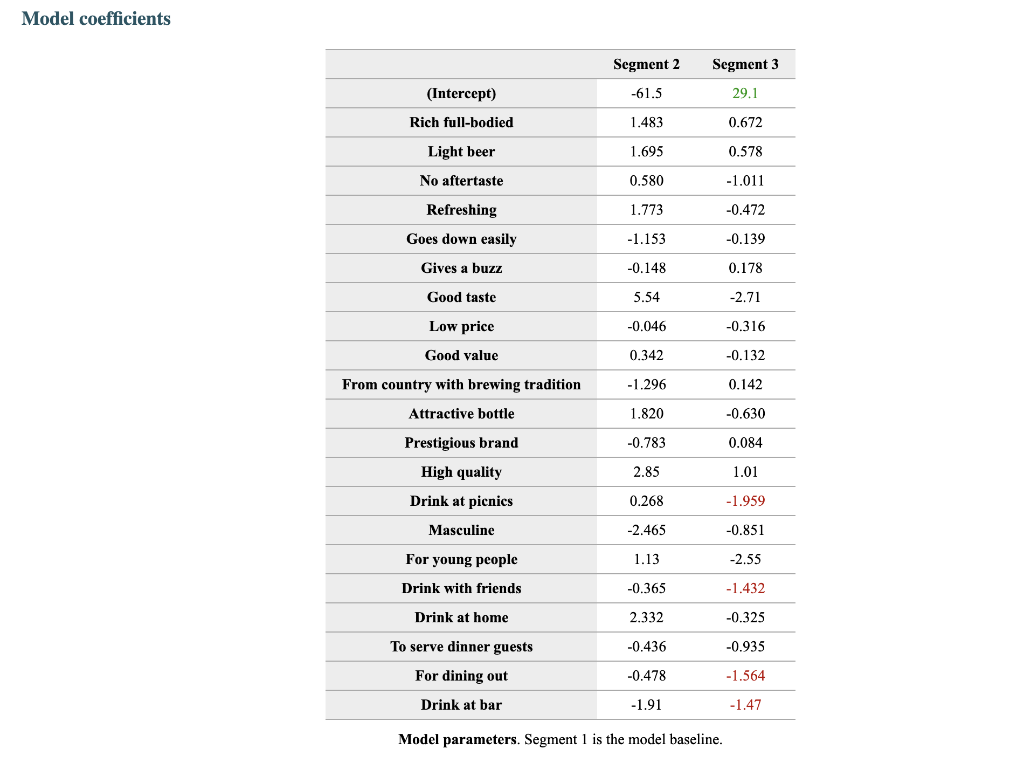
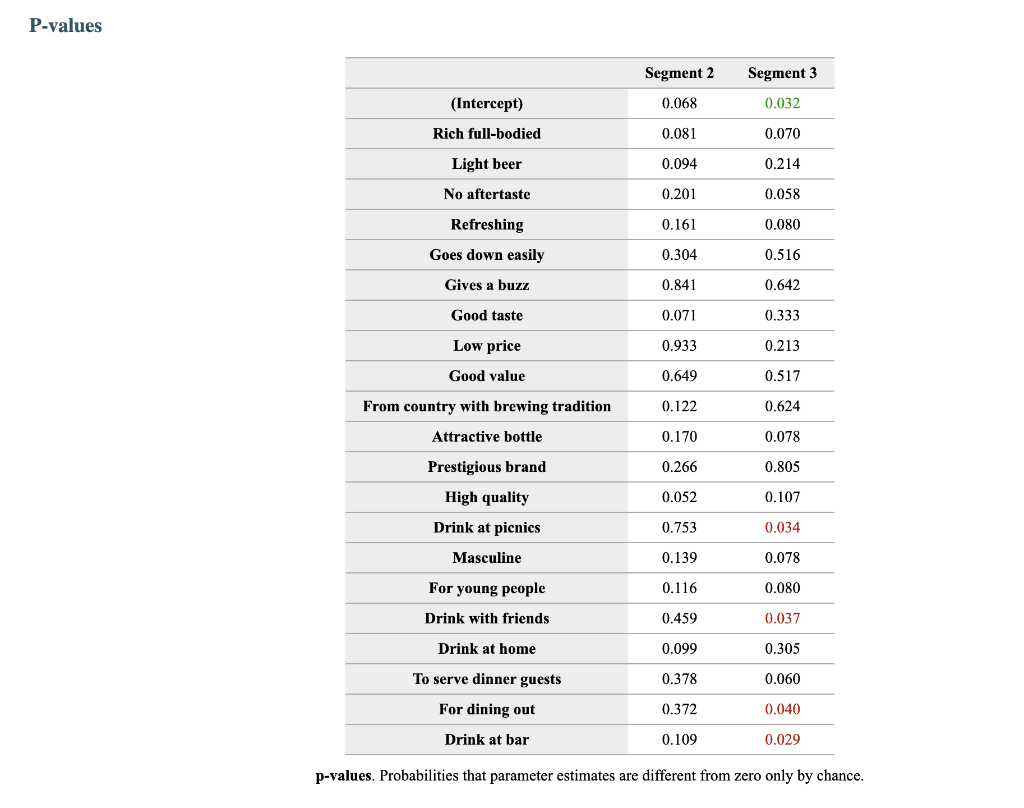
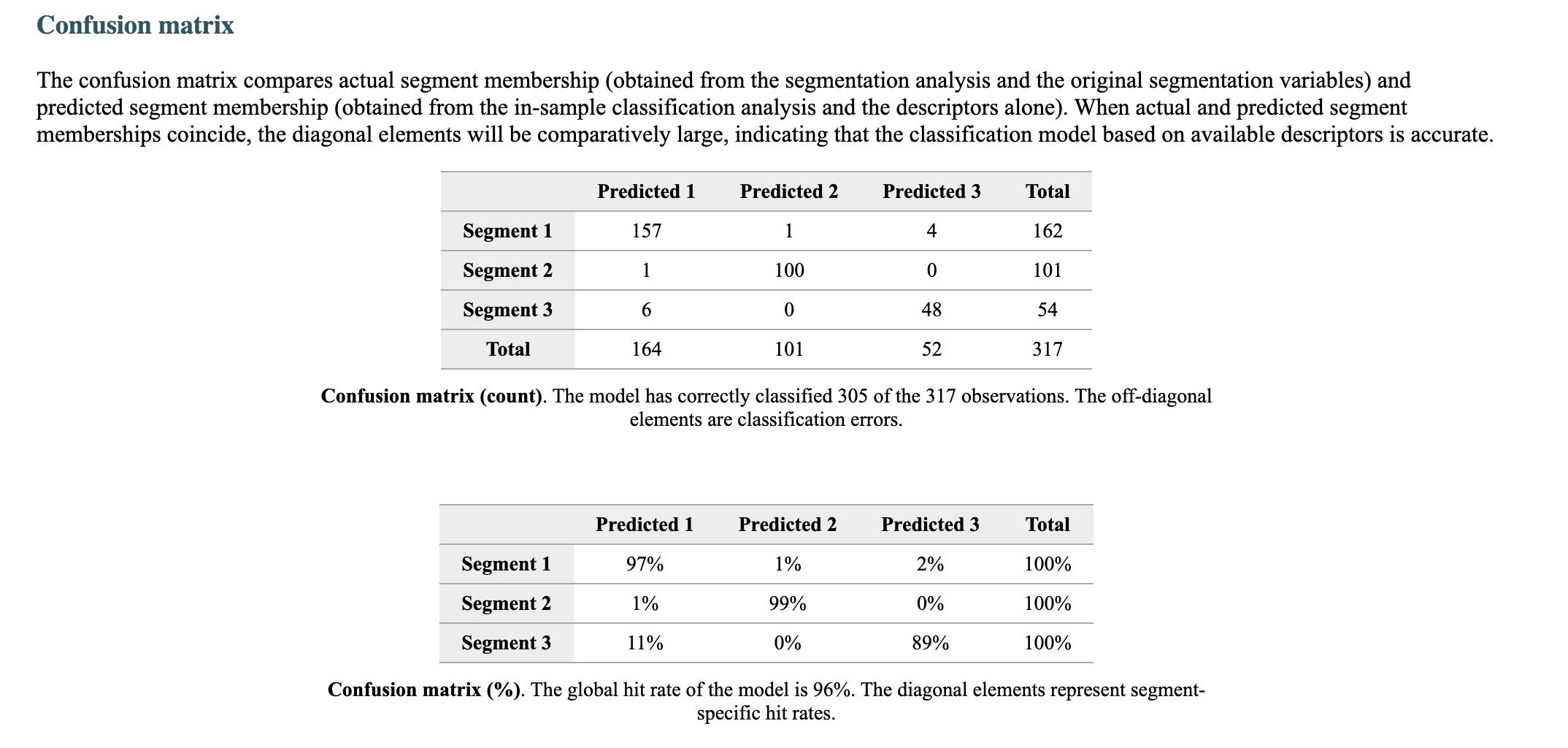
Segment solution 3-segment solution The ideal number of segments is a function of statistical fit (what the data say), managerial relevance (what makes the most sense from a managerial point of view), and targetability (can the segments be easily targeted). When the three criteria do not perfectly converge, selecting the right number of segments becomes a judgment call. Using a statistical criteria exclusively (see scree plot analysis below), we have retained 3 segments. The segmentation method relies on the hierarchical clustering approach. This approach generates a dendrogram that we display next. Dendrogram The dendrogram represents the grouping process of observations into clusters. The chart reads from bottom (all initial observations are separated) to top (all observations are clustered into one unique segment). The height represents the distance between the two groups of observations being merged at each step. If two very distant groups are being merged, this will create a 'jump' in the dendrogram, indicating that it might be wise to stop the clustering process before. 140 120 100 08 09 40 20 Whabar Dendrogram. The dendrogram is a tree diagram to illustrate the arrangement of clusters produced by hierarchical clustering, and how the observations are incrementally clustered together. Scree plot The screeplot displays, for each cluster solution, a measure of within-cluster heterogeneity. If clusters group observations that are widely different (wh will happen if the number of clusters is too small to capture the variability in the data), the value will be high. A good cluster solution might be where the screeplot displays an 'elbow', that is, where increasing the number of clusters beyond a certain point does n dramatically decreases within-cluster heterogeneity. The measure displayed in the screeplot is related, but not equivalent, to the distance reported in the dendrogram. 60000- 50000- 40000- Scree plot. The scree plot compares the sum of squared error (SSE) for each cluster solution. A good cluster solution might be when the SSE slows dramatically, creating an 'elbow'. Such elbow does not always exist. Segment description Segment size Size Relative size Population 317 100% Segment 1 Segment 2 162 101 51% 32% Segment size. Segment 3 54 17% Segment description Population Segment 1 Segment 2 Rich full-bodied 4.77 3.79 7.41 Light beer 3.72 3.56 4.11 No aftertaste 4.56 4.48 5.56 Refreshing 5.02 4.90 7.06 Goes down easily 5.17 5.13 6.58 2.63 Gives a buzz 3.39 3.40 3.79 2.63 Good taste 3.000 0.630 8.347 0.111 Low price 3.91 3.75 4.67 2.96 Good value 4.65 4.62 5.72 2.74 From country with brewing tradition 3.82 4.04 4.30 2.26 Attractive bottle 3.00 3.06 3.22 2.39 Prestigious brand 3.20 3.22 3.84 1.94 High quality 4.48 3.46 7.47 1.94 Drink at picnics 4.56 5.14 5.22 1.63 Masculine 2.67 2.48 3.34 2.00 For young people 2.49 2.31 3.07 1.94 Drink with friends 4.697 5.333 5.713 0.889 Drink at home 4.34 4.27 5.90 1.61 To serve dinner guests 4.92 5.23 6.40 1.20 For dining out 5.03 5.50 6.24 1.37 Drink at bar 4.35 4.79 5.34 1.17 Segment description. Average value of each segmentation variable, overall for each segment (centroid). Segmentation variables that are statistically different from the rest of the population are highlighted in red (lower) or green (higher). Segment 3 2.76 3.48 2.93 1.57 Statistical differences in profiles Rich full-bodied- Light beer- No aftertaste- Refreshing - Goes down easily - Gives a buzz- Good taste- Low price - Good value- From country with brewing tradition - Attractive bottle - Prestigious brand- High quality - Drink at picnics- Masculine - For young people- Drink with friends- Drink at home - To serve dinner guests - For dining out- Drink at bar- Segment differences per segment. Cell colors indicate to what extent a segment is statistically different from the rest of the population on each segmentation variable. Lower (p<.05 n.s. higher segmentation space the chart below is a graphical representation of various segments segment members and variables. it obtained by plotting first two dimensions principal component analysis performed on data top which information has been overlaid. because only pca are displayed these capture variance in some differences between might not appear here. note that variables with no if any have excluded. clusters who to overlap actually be distinct other dimensions. consequently this useful guide especially see correlated but may misleading used select optimal number segments. for young people from country brewing tradition attractive bottes buzz light beer low price s aftertaste pc1 repering home rich full-bodied good value drink at bar dining out taste serve dinner guests. goes d down easily qua rink piddfk friends membership each member population belongs to. complete list available excel formatted output. profiles spider comparing averages across all barrich guests nk masculine picnics high quality prestigious brandfrom bottle chart. refreshing eas gives buz profile following charts represent segment. when standardized hence model assumes use same scale. ordered decreasing order magnitude. colored dots average horizontal lines standard deviations within vertical gray rest after excluding under scrutiny. out- friends- picnics- refreshing- bar- value- home- tradition- full-bodied- price- beer- buzz- brand- bottle- people- taste- easily- guests- aftertaste- profile. descriptor descriptors table reports more can found easier will predict based alone. brand statistical per cell colors indicate what extent distribution statistically different population. lower descriptors. outputing overlayed. or fully unlikely they could clearly separated however seem confusion matrix better assess classification refering alue drinkining pidi guality introduction often customer managers customers available. section we explore whether alone sufficient accuracy. hit rates accurate enough. enginius uses multinomial logit one multiple alternatives predictive modeling module. largest selected as default option identifies most significant predicting cluster memberships. highly its p-values close zero cells green red coefficients parameters. baseline. p-values. probabilities parameter estimates chance. compares actual original predicted in-sample memberships coincide diagonal elements comparatively large indicating accurate. total col correctly classified observations. off-diagonal errors. global rate segment- specific>
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


