Question: Margin Analysis Margin Analysis Being able to calculate a healthy Margin Analysis will help the Research & Development Department understand how to change the cost
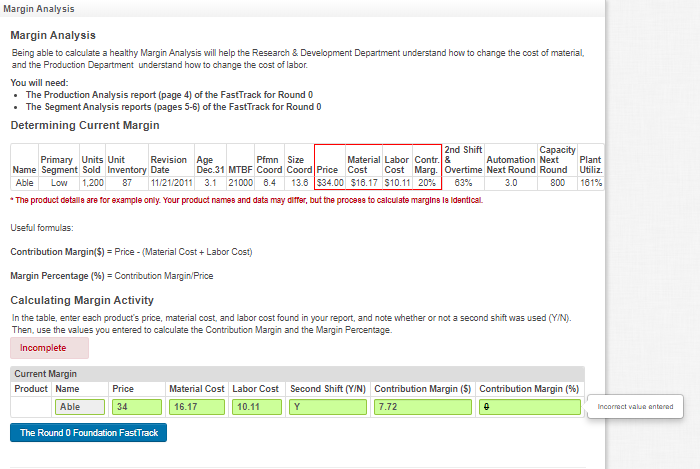
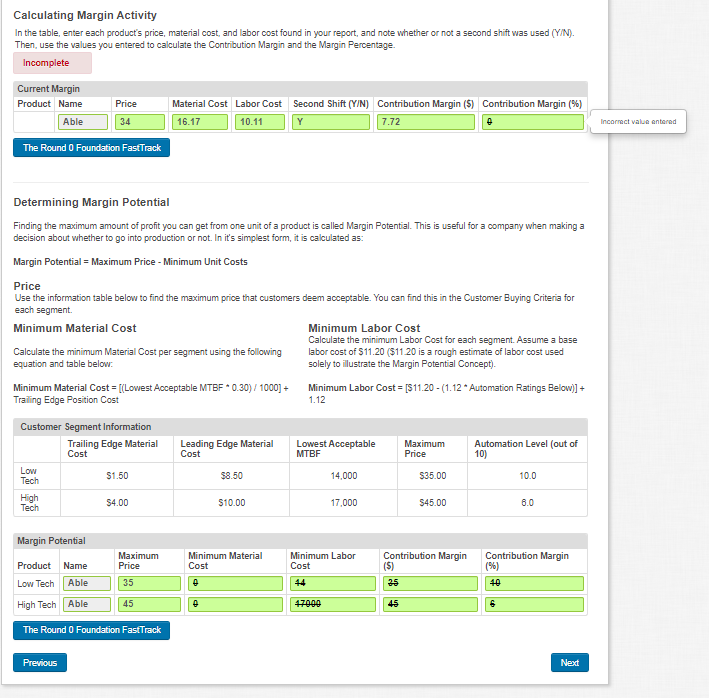
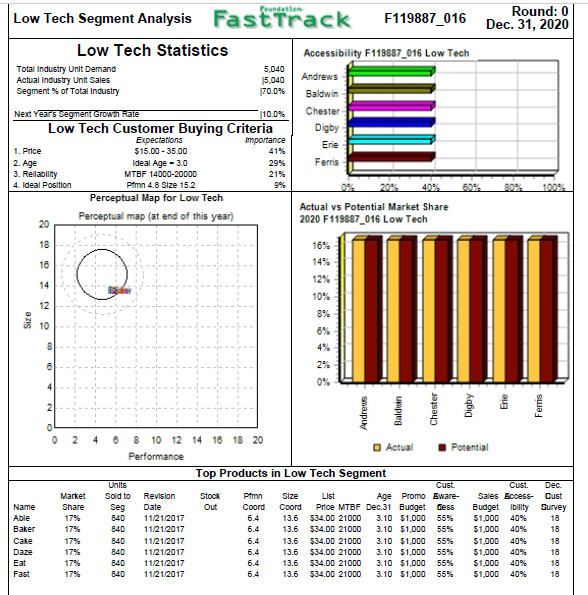
Margin Analysis Margin Analysis Being able to calculate a healthy Margin Analysis will help the Research & Development Department understand how to change the cost of material, and the Production Department understand how to change the cost of labor. You will need: The Production Analysis report (page 4) of the FastTrack for Round 0 The Segment Analysis reports (pages 5-6) of the FastTrack for Round 0 Determining Current Margin 2nd Shift Capacity Primary Units Unit Revision Age Pfmn Size Material Labor Contr. & Automation Next Plant Name Segment Sold Inventory Date Dec.31 MTBF Coord Coord Price Cost Cost Marg. Overtime Next Round Round Utiliz. Able Low 1,200 87 11/21/2011 3.1 21000 6.4 13.8 $34.00 $16.17 $10.11 20% 63% 3.0 800 181% * The product details are for example only. Your product names and data may difer, but the process to calculate margine la identical. Useful formulas: Contribution Margin($) = Price - (Material Cost +Labor Cost) Margin Percentage (%) = Contribution Margin/Price Calculating Margin Activity In the table, enter each product's price, material cost and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Able Price Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin ($) Contribution Margin (%) 16.17 10.11 Y 7.72 34 Incorrect value entered The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Calculating Margin Activity In the table, enter each product's price, material cost and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Able Price 34 Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin (5) Contribution Margin (%) 16.17 10.11 Y 7.72 Incorrect value entered The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Determining Margin Potential Finding the maximum amount of profit you can get from one unit of a product is called Margin Potential. This is useful for a company when making a decision about whether to go into production or not. In it's simplest form, it is calculated as: Margin Potential = Maximum Price - Minimum Unit Costs Price Use the information table below to find the maximum price that customers deem acceptable. You can find this in the Customer Buying Criteria for each segment Minimum Material Cost Minimum Labor Cost Calculate the minimum Labor Cost for each segment. Assume a base Calculate the minimum Material Cost per segment using the following labor cost of $11.20 ($1120 is a rough estimate of labor cost used equation and table below: solely to illustrate the Margin Potential Concept). Minimum Material Cost = [(Lowest Acceptable MTBF*0.30) / 1000] = Minimum Labor Cost = [$11.20 - (1.12 * Automation Ratings Below)] + Trailing Edge Position Cost 1.12 Customer Segment Information Trailing Edge Material Cost Leading Edge Material Cost Lowest Acceptable MTBF Maximum Price Automation Level (out of 10) Low Tech $1.50 $8.50 14,000 $35.00 10.0 High $4.00 $10.00 Tech 17,000 $45.00 8.0 Margin Potential Minimum Material Cost Maximum Price 35 Minimum Labor Cost Contribution Margin (S) Contribution Margin (%) Product Low Tech Name Able 44 40 High Tech Able 45 47000 45 6 The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Previous Next Round: 0 Dec 31, 2020 5.040 Foundation Low Tech Segment Analysis Fast Track F119887_016 Low Tech Statistics Accessibility F119887_016 Low Tech Total Industry Unit Demand Actual Industry Unit Sales 15.040 Andrews Segment % of Total Industry 170.0% Baldwin Next Year's Segment Growth Rate 10.0% Chester Low Tech Customer Buying Criteria Digby Expectations Importance Erie 1. Price $15.00 - 35.00 2. Age Ideal Age - 3.0 29% Ferris 3. Reliability MTBF 14000-20000 21% 4. Ideal Position Pflmn 4.8 Size 15.2 20% 40% 60% Perceptual Map for Low Tech Actual vs Potential Market Share Perceptual map (at end of this year) 20 2020 F119887_016 Low Tech 90% 100% 18 16 Q 16% 14% 12% 10% 14 12 Size 10 8 0% 2 0 2 4 Name Able Baker Cake Daze Eat Fast Market Share 17% 17% 17% 17% 17% 17% 8 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 O Actual Potential Performance Top Products in Low Tech Segment Units Cust. Cust. Sold to Revision Stock Pimn Size List Age Promo Eware Sales Bccess- Seg Date Out Coord Coord Price MTBF Dec.31 Budget Dess Budget Ibility 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% Dec Cust Survey 18 18 18 18 18 18 Margin Analysis Margin Analysis Being able to calculate a healthy Margin Analysis will help the Research & Development Department understand how to change the cost of material, and the Production Department understand how to change the cost of labor. You will need: The Production Analysis report (page 4) of the FastTrack for Round 0 The Segment Analysis reports (pages 5-6) of the FastTrack for Round 0 Determining Current Margin 2nd Shift Capacity Primary Units Unit Revision Age Pfmn Size Material Labor Contr. & Automation Next Plant Name Segment Sold Inventory Date Dec.31 MTBF Coord Coord Price Cost Cost Marg. Overtime Next Round Round Utiliz. Able Low 1,200 87 11/21/2011 3.1 21000 6.4 13.8 $34.00 $16.17 $10.11 20% 63% 3.0 800 181% * The product details are for example only. Your product names and data may difer, but the process to calculate margine la identical. Useful formulas: Contribution Margin($) = Price - (Material Cost +Labor Cost) Margin Percentage (%) = Contribution Margin/Price Calculating Margin Activity In the table, enter each product's price, material cost and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Able Price Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin ($) Contribution Margin (%) 16.17 10.11 Y 7.72 34 Incorrect value entered The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Calculating Margin Activity In the table, enter each product's price, material cost and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Able Price 34 Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin (5) Contribution Margin (%) 16.17 10.11 Y 7.72 Incorrect value entered The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Determining Margin Potential Finding the maximum amount of profit you can get from one unit of a product is called Margin Potential. This is useful for a company when making a decision about whether to go into production or not. In it's simplest form, it is calculated as: Margin Potential = Maximum Price - Minimum Unit Costs Price Use the information table below to find the maximum price that customers deem acceptable. You can find this in the Customer Buying Criteria for each segment Minimum Material Cost Minimum Labor Cost Calculate the minimum Labor Cost for each segment. Assume a base Calculate the minimum Material Cost per segment using the following labor cost of $11.20 ($1120 is a rough estimate of labor cost used equation and table below: solely to illustrate the Margin Potential Concept). Minimum Material Cost = [(Lowest Acceptable MTBF*0.30) / 1000] = Minimum Labor Cost = [$11.20 - (1.12 * Automation Ratings Below)] + Trailing Edge Position Cost 1.12 Customer Segment Information Trailing Edge Material Cost Leading Edge Material Cost Lowest Acceptable MTBF Maximum Price Automation Level (out of 10) Low Tech $1.50 $8.50 14,000 $35.00 10.0 High $4.00 $10.00 Tech 17,000 $45.00 8.0 Margin Potential Minimum Material Cost Maximum Price 35 Minimum Labor Cost Contribution Margin (S) Contribution Margin (%) Product Low Tech Name Able 44 40 High Tech Able 45 47000 45 6 The Round 0 Foundation FastTrack Previous Next Round: 0 Dec 31, 2020 5.040 Foundation Low Tech Segment Analysis Fast Track F119887_016 Low Tech Statistics Accessibility F119887_016 Low Tech Total Industry Unit Demand Actual Industry Unit Sales 15.040 Andrews Segment % of Total Industry 170.0% Baldwin Next Year's Segment Growth Rate 10.0% Chester Low Tech Customer Buying Criteria Digby Expectations Importance Erie 1. Price $15.00 - 35.00 2. Age Ideal Age - 3.0 29% Ferris 3. Reliability MTBF 14000-20000 21% 4. Ideal Position Pflmn 4.8 Size 15.2 20% 40% 60% Perceptual Map for Low Tech Actual vs Potential Market Share Perceptual map (at end of this year) 20 2020 F119887_016 Low Tech 90% 100% 18 16 Q 16% 14% 12% 10% 14 12 Size 10 8 0% 2 0 2 4 Name Able Baker Cake Daze Eat Fast Market Share 17% 17% 17% 17% 17% 17% 8 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 O Actual Potential Performance Top Products in Low Tech Segment Units Cust. Cust. Sold to Revision Stock Pimn Size List Age Promo Eware Sales Bccess- Seg Date Out Coord Coord Price MTBF Dec.31 Budget Dess Budget Ibility 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% 840 11/21/2017 6.4 13.6 $34.00 21000 3.10 $1,000 55% $1,000 40% Dec Cust Survey 18 18 18 18 18 18







