Question: Markov chains. fConsider a Markov chain {X, : n = 0, 1,2, ...} with state space {1, 2,3} and one-step transition probability matrix P =
Markov chains.
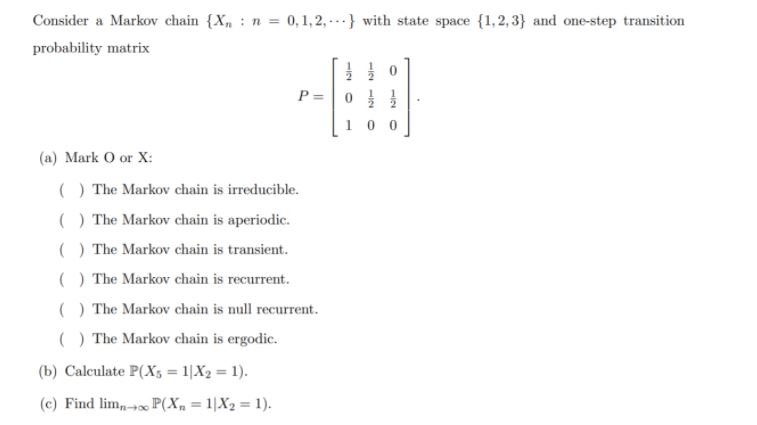
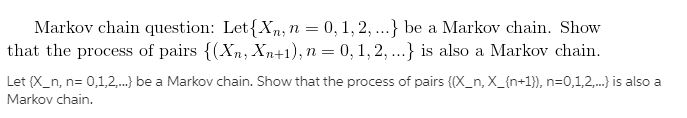
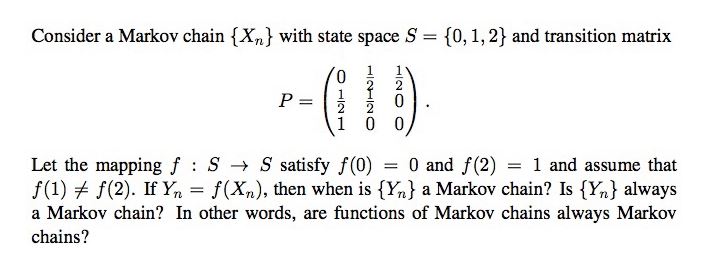
\fConsider a Markov chain {X, : n = 0, 1,2, ...} with state space {1, 2,3} and one-step transition probability matrix P = 0 0 (a) Mark O or X: ( ) The Markov chain is irreducible. ( ) The Markov chain is aperiodic. ( ) The Markov chain is transient. ( ) The Markov chain is recurrent. ( ) The Markov chain is null recurrent. ( ) The Markov chain is ergodic. (b) Calculate P(Xs = 1[X2 = 1). (c) Find limn +2 P(X, = 1/X2 = 1).Markov chain question: Let {X,, n = 0, 1, 2, ...} be a Markov chain. Show that the process of pairs {(Xn, Xn+1), n = 0, 1, 2, ...} is also a Markov chain. Let (X_n, n= 0,1,2,.} be a Markov chain. Show that the process of pairs ((X_n, X_(n+1)), n=0,1,2,.} is also a Markov chain.Consider a Markov chain { Xn } with state space S = {0, 1, 2} and transition matrix P = Let the mapping f : S -> S satisfy f(0) = 0 and f(2) = 1 and assume that f(1) + f(2). If Yn = f(Xn), then when is {Y} a Markov chain? Is {Yn } always a Markov chain? In other words, are functions of Markov chains always Markov chains
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


