Question: Mastery Problem: Job Order Costing (Basic) A job order costing system is used when a company produces a product or provides a service that is
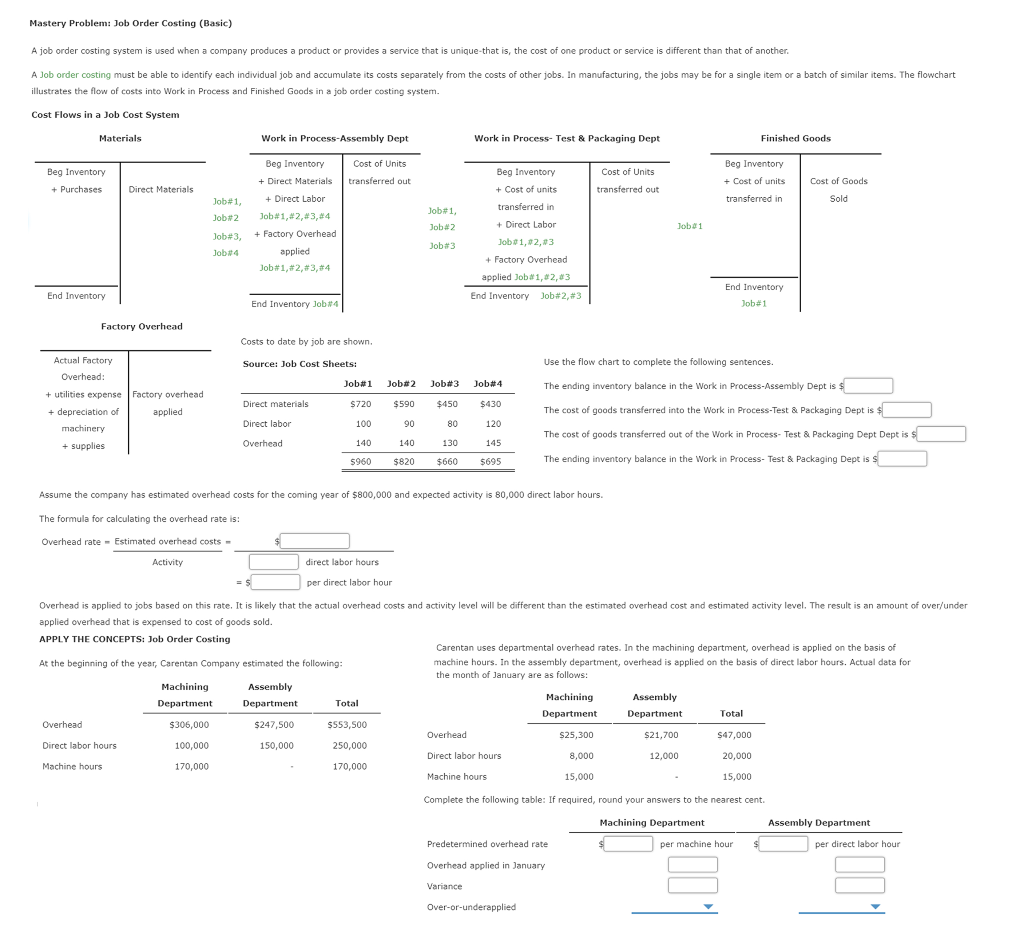
Mastery Problem: Job Order Costing (Basic) A job order costing system is used when a company produces a product or provides a service that is unique that is, the cost of one product or service is different than that of another A Job order costing must be able to identify each individual job and accumulate its costs separately from the costs of other jobs. In manufacturing, the jobs may be for a single item or a batch of similar items. The flowchart illustrates the flow of costs into Work in Process and Finished Goods in a job order costing system. Cost Flows in a Job Cost System Materials Work in Process Assembly Dept Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept Finished Goods Beg Inventory + Purchases Cost of Units transferred out Beg Inventory + Cost of units transferred in Cost of Units transferred out Beg Inventory + Cost of units transferred in Direct Materials Cost of Goods Sold Job#1, Job#2 Job#3, Job4 Beg Inventory + Direct Materials + Direct Labor Job#1, #2,#3,#4 + Factory Overhead applied Job#1, #2, #3,#4 + Direct Labor Job#1, Job#2 Job#3 Job 1 Job 1,2,3 + Factory Overhead applied Job#1,2,3 End Inventory Job#2, #3 End Inventory End Inventory Job#1 End Inventory Job 14 Factory Overhead Costs to date by job are shown. Actual Factory Overhead: Source: Job Cost Sheets: Use the flow chart to complete the following sentences. Job#1 Job#2 Job#3 Job#4 The ending inventory balance in the Work in Process-Assembly Dept is $ + utilities expense Factory overhead + depreciation of applied The cost of goods transferred into the Work in Process-Test & Packaging Dept is $ Direct materials Direct labor Overhead machinery $720 100 140 5960 $590 90 140 $820 $450 80 130 $660 $430 120 145 $695 The cost of goods transferred out of the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept Dept is s + supplies The ending inventory balance in the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept is s Assume the company has estimated overhead costs for the coming year of $800,000 and expected activity is 80,000 direct labor hours. The formula for calculating the overhead rate is: Overhead rate - Estimated overhead costs - Activity direct labor hours per direct labor hour Overhead is applied to jobs based on this rate. It is likely that the actual overhead costs and activity level will be different than the estimated overhead cost and estimated activity level. The result is an amount of over/under applied overhead that is expensed to cost of goods sold. APPLY THE CONCEPTS: Job Order Costing Carentan uses departmental overhead rates. In the machining department, overhead is applied on the basis of At the beginning of the year, Carentan Company estimated the following: machine hours. In the assembly department, overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. Actual data for the month of January are as follows: Machining Assembly Machining Assembly Department Department Total Department Department Total Overhead $306,000 $247,500 $553,500 Overhead S25,300 $21,700 S47,000 Direct labor hours 100,000 150,000 250,000 Direct labor hours 8,000 12,000 20,000 Machine hours 170,000 170,000 Machine hours 15,000 15,000 Complete the following table: If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. Machining Department Assembly Department Predetermined overhead rate $ per machine hour $ per direct labor hour Overhead applied in January Variance Over-or-underapplied Mastery Problem: Job Order Costing (Basic) A job order costing system is used when a company produces a product or provides a service that is unique that is, the cost of one product or service is different than that of another A Job order costing must be able to identify each individual job and accumulate its costs separately from the costs of other jobs. In manufacturing, the jobs may be for a single item or a batch of similar items. The flowchart illustrates the flow of costs into Work in Process and Finished Goods in a job order costing system. Cost Flows in a Job Cost System Materials Work in Process Assembly Dept Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept Finished Goods Beg Inventory + Purchases Cost of Units transferred out Beg Inventory + Cost of units transferred in Cost of Units transferred out Beg Inventory + Cost of units transferred in Direct Materials Cost of Goods Sold Job#1, Job#2 Job#3, Job4 Beg Inventory + Direct Materials + Direct Labor Job#1, #2,#3,#4 + Factory Overhead applied Job#1, #2, #3,#4 + Direct Labor Job#1, Job#2 Job#3 Job 1 Job 1,2,3 + Factory Overhead applied Job#1,2,3 End Inventory Job#2, #3 End Inventory End Inventory Job#1 End Inventory Job 14 Factory Overhead Costs to date by job are shown. Actual Factory Overhead: Source: Job Cost Sheets: Use the flow chart to complete the following sentences. Job#1 Job#2 Job#3 Job#4 The ending inventory balance in the Work in Process-Assembly Dept is $ + utilities expense Factory overhead + depreciation of applied The cost of goods transferred into the Work in Process-Test & Packaging Dept is $ Direct materials Direct labor Overhead machinery $720 100 140 5960 $590 90 140 $820 $450 80 130 $660 $430 120 145 $695 The cost of goods transferred out of the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept Dept is s + supplies The ending inventory balance in the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept is s Assume the company has estimated overhead costs for the coming year of $800,000 and expected activity is 80,000 direct labor hours. The formula for calculating the overhead rate is: Overhead rate - Estimated overhead costs - Activity direct labor hours per direct labor hour Overhead is applied to jobs based on this rate. It is likely that the actual overhead costs and activity level will be different than the estimated overhead cost and estimated activity level. The result is an amount of over/under applied overhead that is expensed to cost of goods sold. APPLY THE CONCEPTS: Job Order Costing Carentan uses departmental overhead rates. In the machining department, overhead is applied on the basis of At the beginning of the year, Carentan Company estimated the following: machine hours. In the assembly department, overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. Actual data for the month of January are as follows: Machining Assembly Machining Assembly Department Department Total Department Department Total Overhead $306,000 $247,500 $553,500 Overhead S25,300 $21,700 S47,000 Direct labor hours 100,000 150,000 250,000 Direct labor hours 8,000 12,000 20,000 Machine hours 170,000 170,000 Machine hours 15,000 15,000 Complete the following table: If required, round your answers to the nearest cent. Machining Department Assembly Department Predetermined overhead rate $ per machine hour $ per direct labor hour Overhead applied in January Variance Over-or-underapplied
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


