Question: Material cost is 78 Please do the Mixed plan only Background: Your company has just acquired a new subsidiary that manufactures two products-Clodhopper and Clodbuster.

Material cost is 78
Please do the Mixed plan only
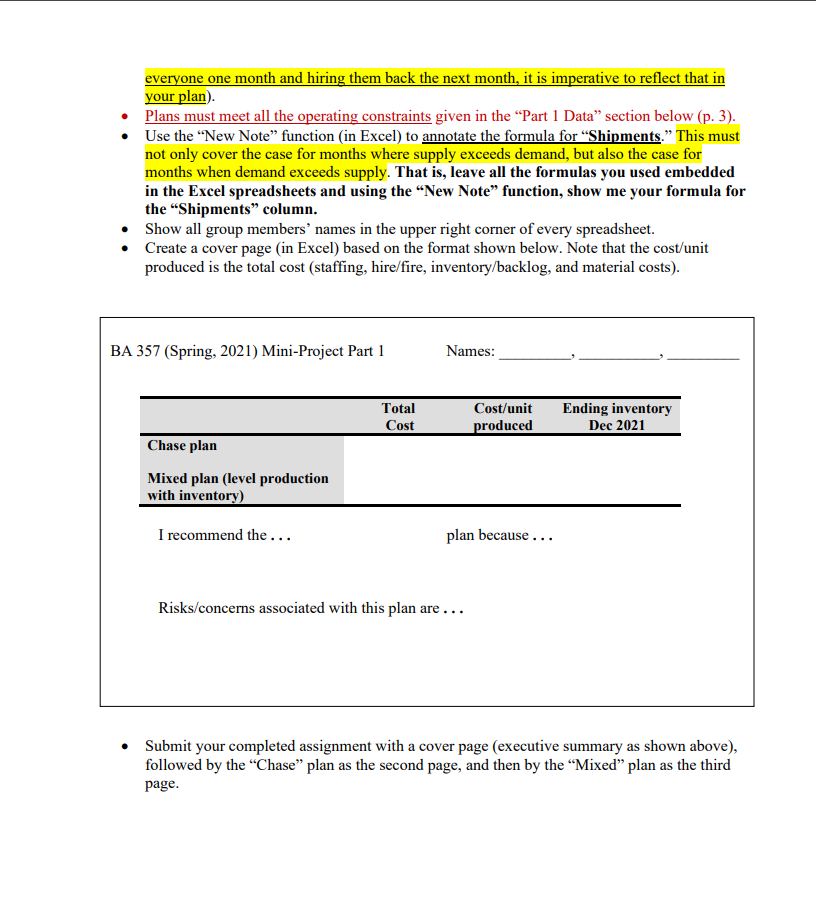
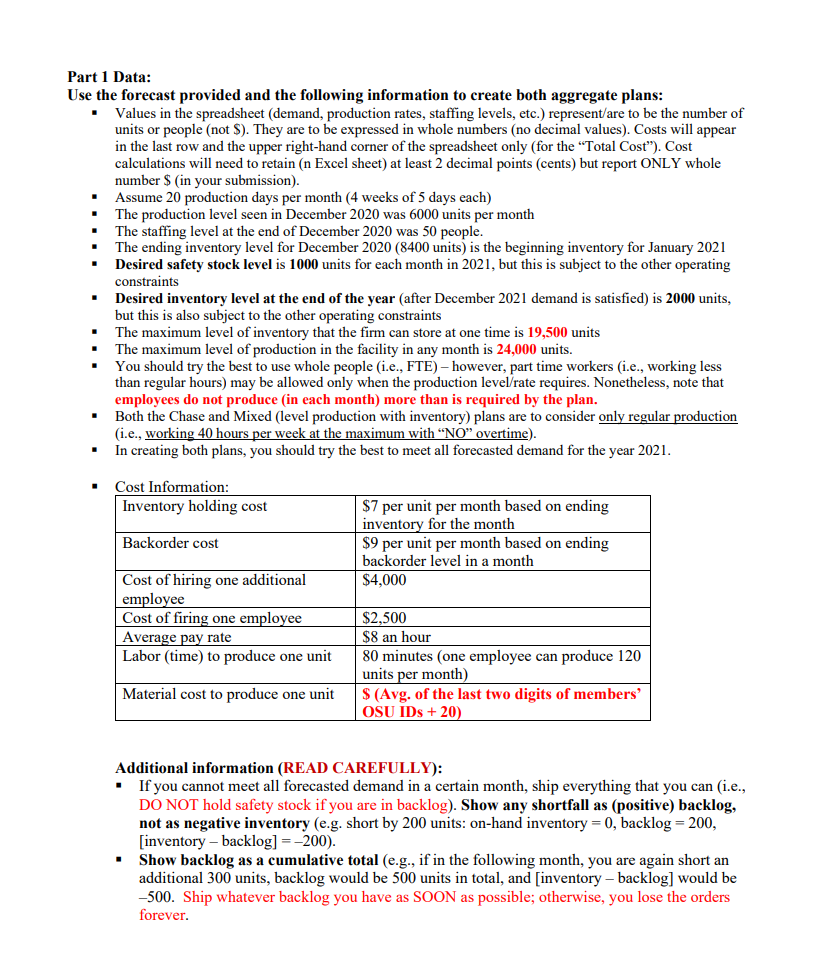
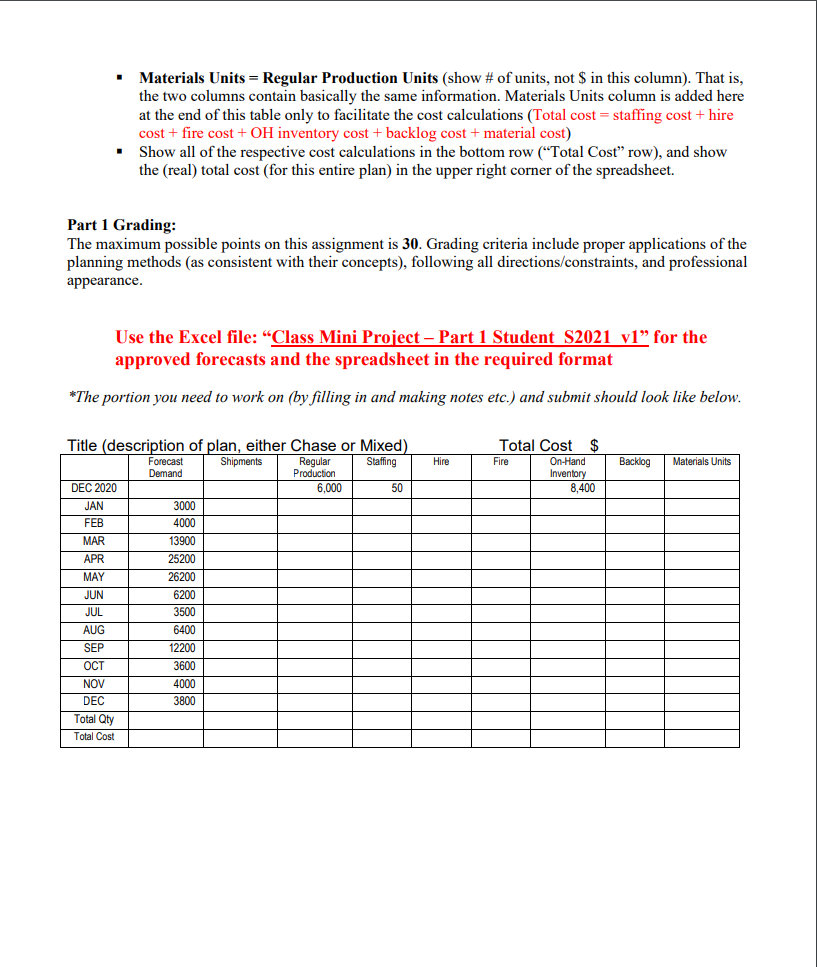
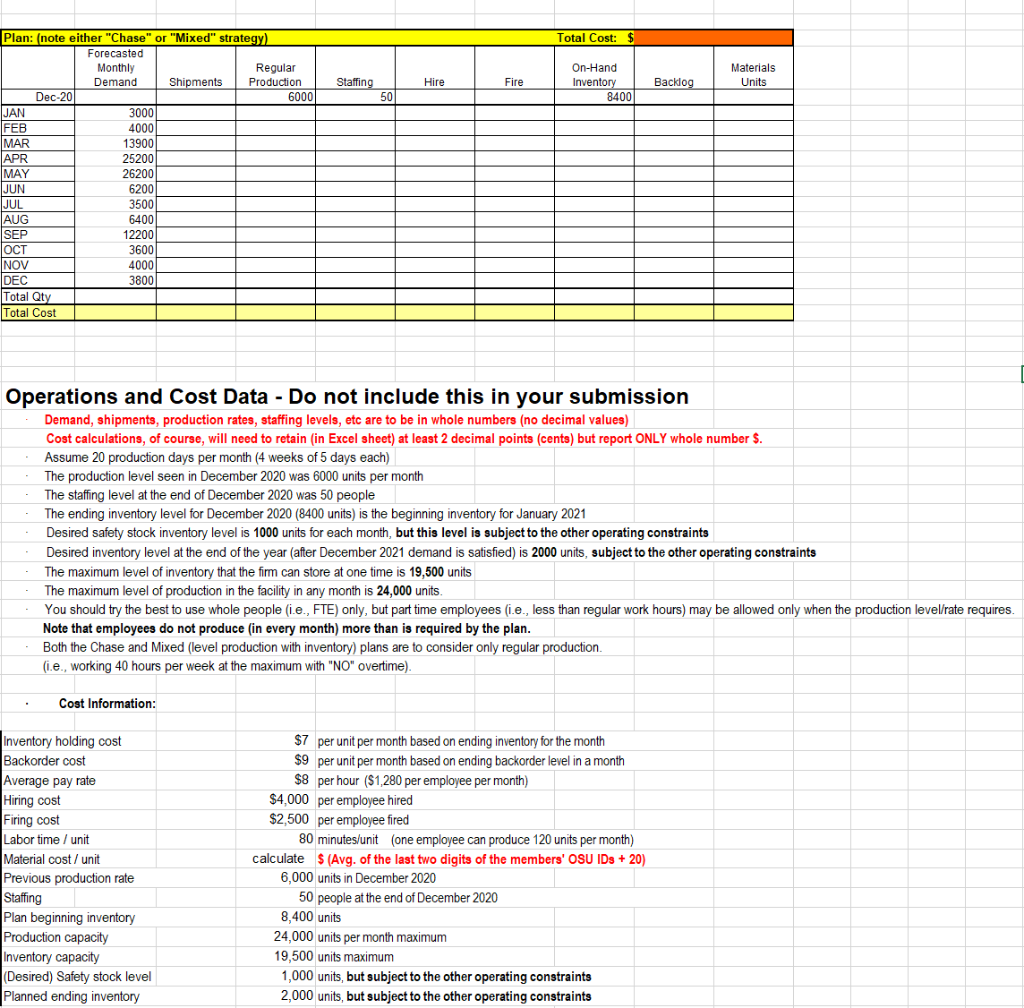
Background: Your company has just acquired a new subsidiary that manufactures two products-Clodhopper and Clodbuster. The Clodhopper is intended for the general consumer market and its demand is higher and more seasonal than the Clodbuster, which is intended for the commercial user market. Both products share a number of component parts and subassemblies, primarily differing in their engines and tiller subassemblies. All of the managers at the acquired company quit the day your company took possession. You are the person who has been assigned to run this acquisition. Since all of the managers quit, the only information you have available for planning is historical data. Assignment: Your task is to create two aggregate plans for 2021: one based on the Chase strategy, and another on the Mixed strategy (i.e., level production with inventory). Use the aggregate planning form supplied (in Excel format) to develop an aggregate plan for each strategy and create the results in Excel spreadsheets (in landscape). In doing so, report the planning analysis results of the two strategies in separate spreadsheets (i.e., a total of 3 pages/spreadsheets in the Excel file with the first being cover page, the second for Chase plan, and the third/last for Mixed plan). Fill in all appropriate data, noting a title of the plan (either "Chase or Mixed strategy). Do not make any changes to the format/layout of the provided spreadsheets. This is one place in industry where creativity in presenting data is not appreciated since many of the cells in the form are normally inter-linked, and changes can lead to significant errors in the results. In reporting the results, delete any and all extraneous items from your submission (e.g., Use this form for your aggregate plans). Both plans must follow the requirements strictly. Do not attempt to make your plans better by changing the planning strategy (for example, if the Chase plan requires firing 1 everyone one month and hiring them back the next month, it is imperative to reflect that in your plan) Plans must meet all the operating constraints given in the Part 1 Data section below (p. 3). Use the "New Note function (in Excel) to annotate the formula for Shipments. This must not only cover the case for months where supply exceeds demand, but also the case for months when demand exceeds supply. That is, leave all the formulas you used embedded in the Excel spreadsheets and using the New Note function, show me your formula for the "Shipments" column. Show all group members' names in the upper right corner of every spreadsheet. Create a cover page (in Excel) based on the format shown below. Note that the cost/unit produced is the total cost (staffing, hire/fire, inventory/backlog, and material costs). BA 357 (Spring, 2021) Mini-Project Part 1 Names: Total Cost Cost/unit produced Ending inventory Dec 2021 Chase plan Mixed plan (level production with inventory) I recommend the... plan because... Risks/concerns associated with this plan are .. Submit your completed assignment with a cover page (executive summary as shown above), followed by the Chase plan as the second page, and then by the Mixed plan as the third page. Part 1 Data: Use the forecast provided and the following information to create both aggregate plans: Values in the spreadsheet (demand, production rates, staffing levels, etc.) representare to be the number of units or people (not $). They are to be expressed in whole numbers (no decimal values). Costs will appear in the last row and the upper right-hand corner of the spreadsheet only (for the Total Cost"). Cost calculations will need to retain (n Excel sheet) at least 2 decimal points (cents) but report ONLY whole number $ (in your submission). Assume 20 production days per month (4 weeks of 5 days each) The production level seen in December 2020 was 6000 units per month The staffing level at the end of December 2020 was 50 people. The ending inventory level for December 2020 (8400 units) is the beginning inventory for January 2021 Desired safety stock level is 1000 units for each month in 2021, but this is subject to the other operating constraints Desired inventory level at the end of the year after December 2021 demand is satisfied) is 2000 units, but this is also subject to the other operating constraints The maximum level of inventory that the firm can store at one time is 19,500 units The maximum level of production in the facility in any month is 24,000 units. You should try the best to use whole people (i.e., FTE) however, part time workers (i.e., working less than regular hours) may be allowed only when the production level/rate requires. Nonetheless, note that employees do not produce in each month) more than is required by the plan. Both the Chase and Mixed (level production with inventory) plans are to consider only regular production (i.e., working 40 hours per week at the maximum with NO overtime). In creating both plans, you should try the best to meet all forecasted demand for the year 2021. Cost Information: Inventory holding cost $7 per unit per month based on ending inventory for the month $9 per unit per month based on ending backorder level in a month Backorder cost $4,000 Cost of hiring one additional employee Cost of firing one employee Average pay rate Labor (time) to produce one unit $2,500 $8 an hour 80 minutes (one employee can produce 120 units per month) $ (Avg. of the last two digits of members' OSU IDs + 20) Material cost to produce one unit Additional information (READ CAREFULLY): If you cannot meet all forecasted demand in a certain month, ship everything that you can (i.e., DO NOT hold safety stock if you are in backlog). Show any shortfall as (positive) backlog, not as negative inventory (e.g. short by 200 units: on-hand inventory = 0, backlog = 200, [inventory-backlog] =-200). Show backlog as a cumulative total (e.g., if in the following month, you are again short an additional 300 units, backlog would be 500 units in total, and [inventory - backlog] would be -500. Ship whatever backlog you have as SOON as possible; otherwise, you lose the orders forever. Materials Units = Regular Production Units (show # of units, not $ in this column). That is, the two columns contain basically the same information. Materials Units column is added here at the end of this table only to facilitate the cost calculations (Total cost = staffing cost + hire cost + fire cost + OH inventory cost + backlog cost + material cost) Show all of the respective cost calculations in the bottom row ("Total Cost row), and show the (real) total cost (for this entire plan) in the upper right corner of the spreadsheet. Part 1 Grading: The maximum possible points on this assignment is 30. Grading criteria include proper applications of the planning methods (as consistent with their concepts), following all directions/constraints, and professional appearance. Use the Excel file: "Class Mini Project - Part 1 Student S2021 vl for the approved forecasts and the spreadsheet in the required format *The portion you need to work on (by filling in and making notes etc.) and submit should look like below. Hire Total Cost $ Fire On-Hand Inventory 8,400 Backlog Materials Units Title (description of plan, either Chase or Mixed) Forecast Shipments Regular Staffing Demand Production DEC 2020 6,000 50 JAN 3000 FEB 4000 MAR 13900 APR 25200 MAY 26200 JUN 6200 JUL 3500 AUG 6400 SEP 12200 OCT 3600 NOV 4000 DEC 3800 Total Qty Total Cost Total Cost: Hire Materials Units Staffing 50 Fire On-Hand Inventory 8400 Backlog 4000 13900 Plan: (note either "Chase" or "Mixed" strategy) Forecasted Monthly Regular Demand Shipments Production Dec-20 6000 JAN 3000 FEB MAR APR 25200 MAY 26200 JUN 6200 JUL 3500 AUG 6400 SEP 12200 OCT NOV 4000 DEC 3800 Total Qty Total Cost 3600 Operations and Cost Data - Do not include this in your submission Demand, shipments, production rates, staffing levels, etc are to be in whole numbers (no decimal values) Cost calculations, of course, will need to retain (in Excel sheet) at least 2 decimal points (cents) but report ONLY whole number $. Assume 20 production days per month (4 weeks of 5 days each) The production level seen in December 2020 was 6000 units per month The staffing level at the end of December 2020 was 50 people The ending inventory level for December 2020 (8400 units) is the beginning inventory for January 2021 Desired safety stock inventory level is 1000 units for each month, but this level is subject to the other operating constraints Desired inventory level at the end of the year (after December 2021 demand is satisfied) is 2000 units, subject to the other operating constraints The maximum level of inventory that the firm can store at one time is 19,500 units The maximum level of production in the facility in any month is 24,000 units. You should try the best to use whole people (i.e., FTE) only, but part time employees (i.e., less than regular work hours) may be allowed only when the production level/rate requires Note that employees do not produce in every month) more than is required by the plan. Both the Chase and Mixed (level production with inventory) plans are to consider only regular production (ie, working 40 hours per week at the maximum with "NO" overtime). Cost Information: Inventory holding cost Backorder cost Average pay rate Hiring cost Firing cost Labor time / unit Material cost / unit Previous production rate Staffing Plan beginning inventory Production capacity Inventory capacity (Desired) Safety stock level Planned ending inventory $7 per unit per month based on ending inventory for the month $9 per unit per month based on ending backorder level in a month $8 per hour ($1,280 per employee per month) $4,000 per employee hired $2,500 per employee fired 80 minutes/unit (one employee can produce 120 units per month) calculate $ (Avg. of the last two digits of the members' OSU IDs + 20) 6,000 units in December 2020 50 people at the end of December 2020 8,400 units 24,000 units per month maximum 19,500 units maximum 1,000 units, but subject to the other operating constraints 2,000 units, but subject to the other operating constraintsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


