Question: Matlab GUI for pressure vessel optimisation Pressure vessel design summary In design of pressure vessels to operate at an internal pressure of P (in Pa)
Matlab GUI for pressure vessel optimisation
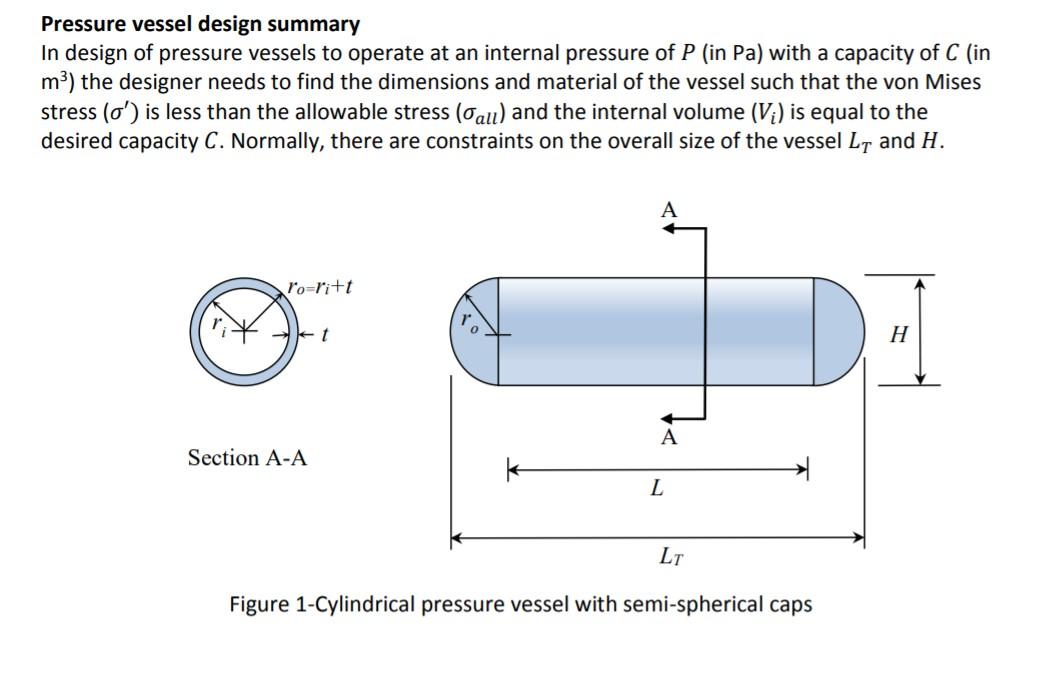

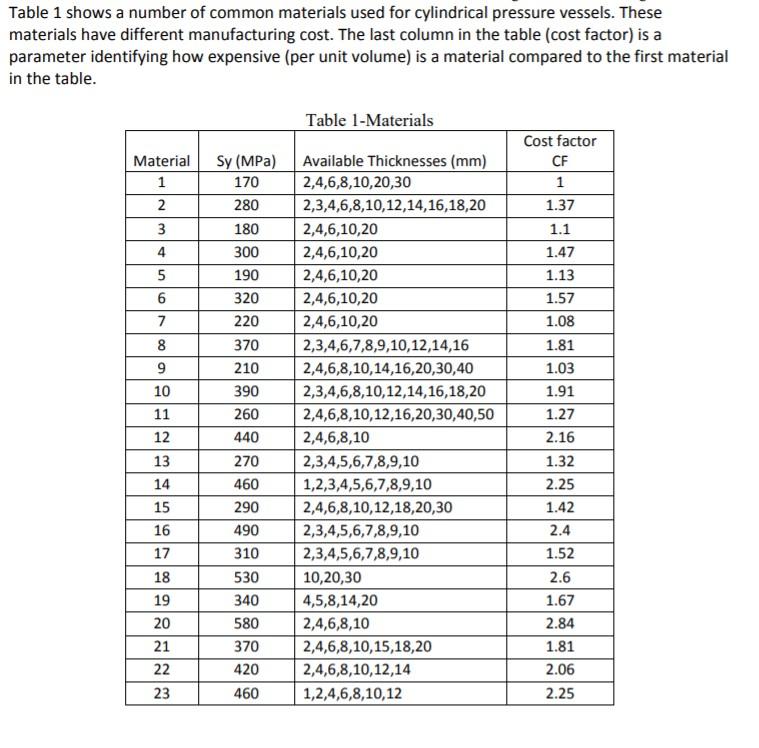

Pressure vessel design summary In design of pressure vessels to operate at an internal pressure of P (in Pa) with a capacity of C (in m?) the designer needs to find the dimensions and material of the vessel such that the von Mises stress (o') is less than the allowable stress (all) and the internal volume (Vi) is equal to the desired capacity C. Normally, there are constraints on the overall size of the vessel L7 and H. l'orrit H A Section A-A L LT Figure 1-Cylindrical pressure vessel with semi-spherical caps Design model summary Allowable stress (based on a desired factor of safety of nd): Call (1) ) nd (2) Vessel internal volume (capacity): Vi = nerL + 4ntry/3 von Mises stress: O'=(0-0-)2+(G-0)2+(01-05)2 (3) The stress components which are used to calculate the von Mises stress are different in thin-walled and thick-walled pressure vessels as shown below: Case thin-walled: t/r 0.0 0 = 73-7 (5.a) (1 + (1- (5.b) rip (5.c) (6) Vessel material volume: Vmat = 2nentL +4rert Vessel cost index: CI = Vmat X CF; CF from Table 1 (7) Overall size: LT = L + 2r. H = 2r. (8) (9) Table 1 shows a number of common materials used for cylindrical pressure vessels. These materials have different manufacturing cost. The last column in the table (cost factor) is a parameter identifying how expensive (per unit volume) is a material compared to the first material in the table. Table 1-Materials Material 1 2 3 4 Cost factor CF 1 1.37 1.1 1.47 1.13 1.57 1.08 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 WINO Sy (MPa) 170 280 180 300 190 320 220 370 210 390 260 440 270 460 290 490 310 530 340 580 370 420 460 Available Thicknesses (mm) 2,4,6,8,10,20,30 2,3,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20 2,4,6,10,20 2,4,6,10,20 2,4,6,10,20 2,4,6,10,20 2,4,6,10,20 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,12,14,16 2,4,6,8,10,14,16,20,30,40 2,3,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20 2,4,6,8,10,12,16,20,30,40,50 2,4,6,8,10 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 2,4,6,8,10,12,18,20,30 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 10,20,30 4,5,8,14,20 2,4,6,8,10 2,4,6,8,10,15,18,20 2,4,6,8,10,12,14 1,2,4,6,8,10,12 14 15 16 1.81 1.03 1.91 1.27 2.16 1.32 2.25 1.42 2.4 1.52 2.6 1.67 2.84 1.81 2.06 2.25 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Task 2 [70%] Write an optimisation programme with a graphical user interface that gets the following inputs: internal pressure P (in bars), capacity C (in litres), a desired factor of safety na and the constrained values for Lt,c and H. (in metres) search parameter(s) and then finds and shows: the optimal size (ri, L and t), the index of the optimum material (from Table 1 above), and the type of the optimal solution (thin-walled or thick-walled), as well as allowable stress, von Mises stress, volume of the material, cost index, the overall dimensions Ls and H, OR a suitable message in case no feasible solutions is found. Note: Marks will be deducted if the programme does not find or show the right results, if GUI does not show all requested parameters, if outputs are not rounded to a reasonable engineering precision, if there is missing parameter name or unit on the GUI or unit in the optimiser, if there is missing definition/ necessary comment in the optimiser, for unclear programme structure, and for uncaptured output error
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


