Question: 12. Domestic LPG cylinder has the following dimensions: height = 580 mm, diameter 318 mm. Assume there is only butane in the cylinder. Given

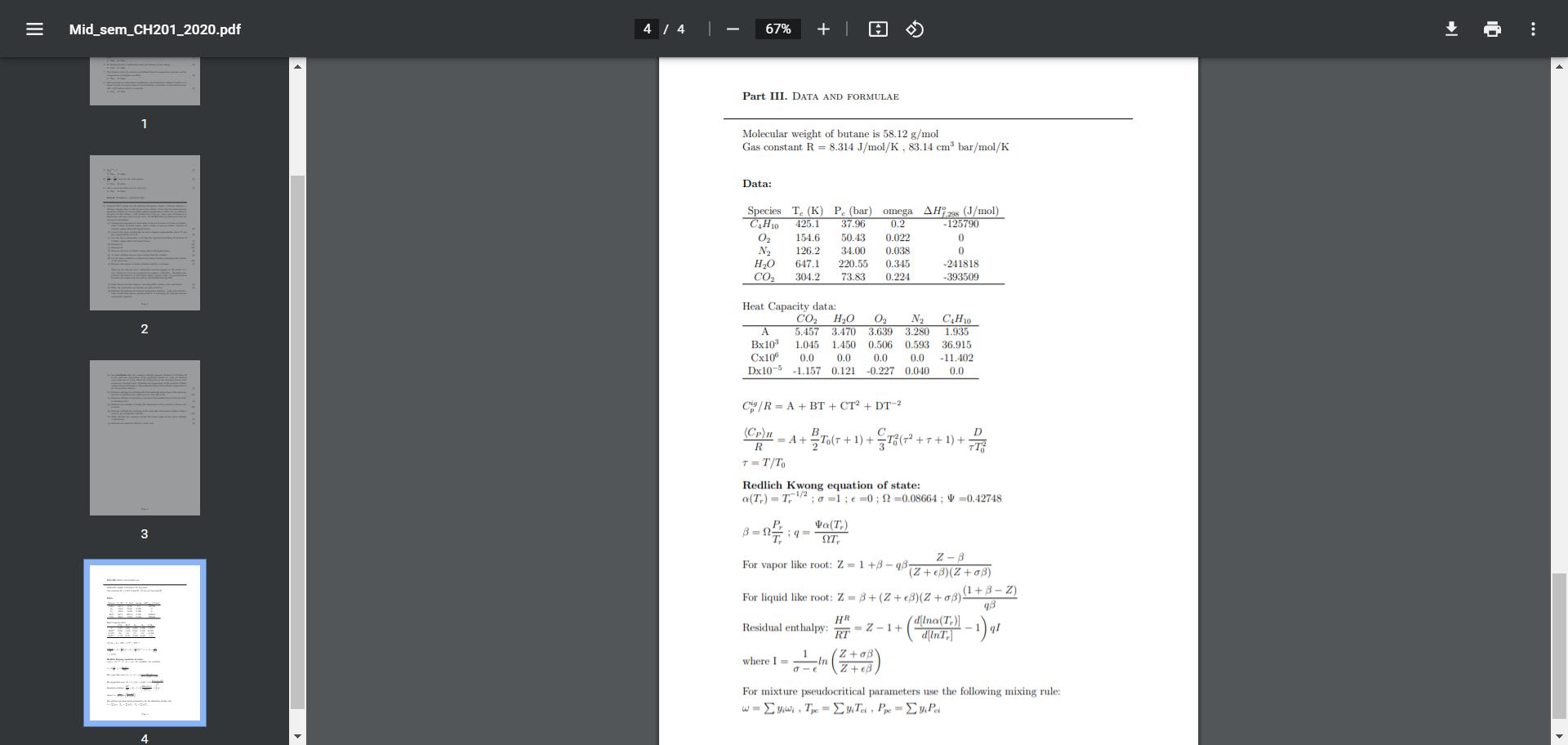
12. Domestic LPG cylinder has the following dimensions: height = 580 mm, diameter 318 mm. Assume there is only butane in the cylinder. Given that the initial pressure inside the cylinder is 2.5 bar and the ambient temperature is 298.15 K. According to the print on the cylinder, a full cylinder has 15 kg gas. Some part of butane is in liquid state and some part is in gas state. Use Redlich Kwong equation of state for all process calculations. = (a) Develop the expression for total moles of the gas in terms of volume of cylinder, molar volume of liquid butane, molar volume of gaseous butane, fraction of cylinder volume filled with liquid butane. (b) Convert the above relationship in terms of liquid compressibility factor Z and gas compressibility factor Zu (c) Use the above relationship to develop the equation for finding the fraction of cylinder volume filled with liquid butane. (d) Estimate Z (e) Estimate Z (f) Estimate fraction of cylinder volume filled with liquid butane. (g) At what condition the gas stops coming from the cylinder? (h) Use the above condition to estimate the moles of butane remaining in the cylinder at the end of use. (i) Estimate the number of moles of butane used by a customer When we use the gas stove, combustion reaction happens at the burner at 1 atm. 20 percent excess air is required for complete combustion. The flame tem- perature was found to be 870 Celsius using a thermocouple. Use pseudocritical pressure and temperature for mixture with Redlich Kwong EOS (j) Draw the process flow diagram containing LPG cylinder, valve and burner (k) Write the combustion reaction for one mole of butane. (1) Estimate the following for reactant and product mixtures: moles and mole frac- tions of individual species, pseudocritical T, P and omega for both the reactant and product mixtures. = Mid_sem_CH201_2020.pdf 1 2 4 / 4 67% + | Part III. DATA AND FORMULAE Molecular weight of butane is 58.12 g/mol Gas constant R = 8.314 J/mol/K, 83.14 cm bar/mol/K Data: Species T. (K) P. (bar) omega AH 298 (J/mol) CH10 425.1 37.96 0.2 0 154.6 50.43 0.022 N 126.2 34.00 0.038 HO 647.1 220.55 0.345 CO 304.2 73.83 0.224 -125790 0 0 -241818 -393509 Heat Capacity data: CO HO 0 N 5.457 3.470 3.639 3.280 C4H10 A 1.935 Bx10 1.045 1.450 0.506 0.593 36.915 Cx106 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -11.402 Dx10-5 -1.157 0.121 -0.227 0.040 0.0 C/R= A + BT + CT + DT-2 (Cp)u R T = T/To B +2T0(7 + 1) + 18 (7 +1 =A+ 8- =// 9 Va(T) , For vapor like root: Z=1+3-q8 where Im Redlich Kwong equation of state: a(T) = T/20=1; 0; 2-0.08664; V=0.42748 +T+1)+ -In -e D TT For liquid like root: Z=8+ (Z+8)(Z+08). HR dlna (T)] RT Residual enthalpy:
Step by Step Solution
3.61 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


