Question: M/M/1 queue Make de next solved model in R studio and answer the following: 1. Description of the case study 2. Definition of the model
M/M/1 queue
Make de next solved model in R studio and answer the following:
1. Description of the case study 2. Definition of the model and the parameters to be used 3. Presentation of results 4. Conclusions and recommendations
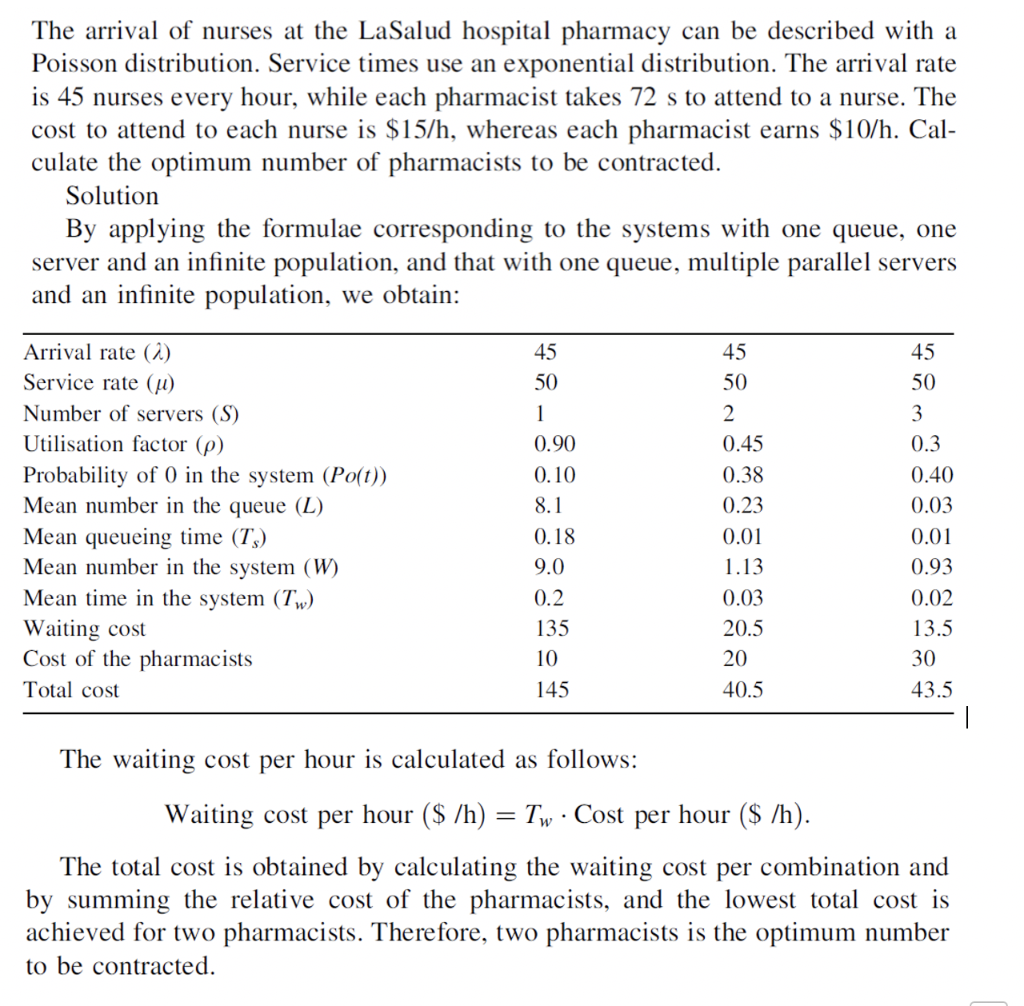
The arrival of nurses at the LaSalud hospital pharmacy can be described with a Poisson distribution. Service times use an exponential distribution. The arrival rate is 45 nurses every hour, while each pharmacist takes 72 s to attend to a nurse. The cost to attend to each nurse is $15/h, whereas each pharmacist earns $10/h. Cal- culate the optimum number of pharmacists to be contracted. Solution By applying the formulae corresponding to the systems with one queue, one server and an infinite population, and that with one queue, multiple parallel servers and an infinite population, we obtain: Arrival rate (2) Service rate (1) Number of servers (S) Utilisation factor (p) Probability of 0 in the system (Po(t)) Mean number in the queue (L) Mean queueing time (T) Mean number in the system (W) Mean time in the system (Tw) Waiting cost Cost of the pharmacists Total cost 45 50 1 0.90 0.10 8.1 0.18 9.0 0.2 135 10 145 45 50 2 0.45 0.38 0.23 0.01 1.13 0.03 20.5 20 40.5 45 50 3 0.3 0.40 0.03 0.01 0.93 0.02 13.5 30 43.5 1 The waiting cost per hour is calculated as follows: Waiting cost per hour ($ /h) = Tw Cost per hour ($ /h). The total cost is obtained by calculating the waiting cost per combination and by summing the relative cost of the pharmacists, and the lowest total cost is achieved for two pharmacists. Therefore, two pharmacists is the optimum number to be contracted. The arrival of nurses at the LaSalud hospital pharmacy can be described with a Poisson distribution. Service times use an exponential distribution. The arrival rate is 45 nurses every hour, while each pharmacist takes 72 s to attend to a nurse. The cost to attend to each nurse is $15/h, whereas each pharmacist earns $10/h. Cal- culate the optimum number of pharmacists to be contracted. Solution By applying the formulae corresponding to the systems with one queue, one server and an infinite population, and that with one queue, multiple parallel servers and an infinite population, we obtain: Arrival rate (2) Service rate (1) Number of servers (S) Utilisation factor (p) Probability of 0 in the system (Po(t)) Mean number in the queue (L) Mean queueing time (T) Mean number in the system (W) Mean time in the system (Tw) Waiting cost Cost of the pharmacists Total cost 45 50 1 0.90 0.10 8.1 0.18 9.0 0.2 135 10 145 45 50 2 0.45 0.38 0.23 0.01 1.13 0.03 20.5 20 40.5 45 50 3 0.3 0.40 0.03 0.01 0.93 0.02 13.5 30 43.5 1 The waiting cost per hour is calculated as follows: Waiting cost per hour ($ /h) = Tw Cost per hour ($ /h). The total cost is obtained by calculating the waiting cost per combination and by summing the relative cost of the pharmacists, and the lowest total cost is achieved for two pharmacists. Therefore, two pharmacists is the optimum number to be contracted
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


