Question: Model Selection (if multiple predictor variables) Consider all the predictor variables simultaneously. Based on the p-values of the slope coefficients, are any of these much
Model Selection (if multiple predictor variables)
- Consider all the predictor variables simultaneously. Based on the p-values of the slope coefficients, are any of these much less useful predictor variables for predicting the response variable (target)? Why or why not?
- Based on the best subset analysis, which model do you recommend? Why?
- Any collinearity problems? Why or why not?
- What decision do you recommend to management based on these findings?
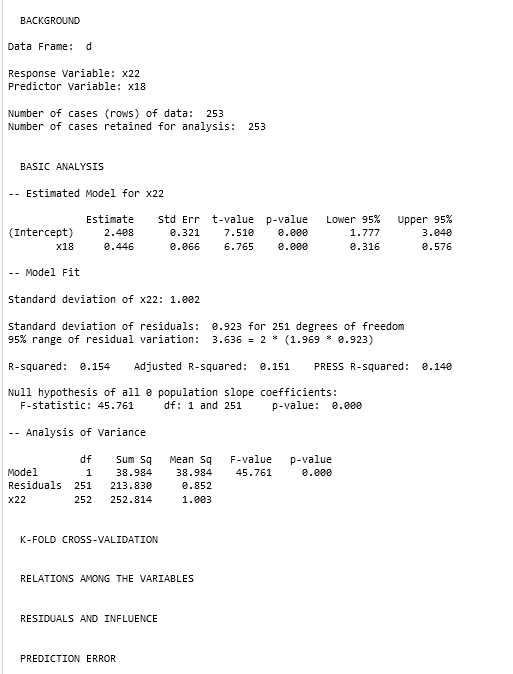
BACKGROUND Data Frame: d Response Variable: x22 Predictor Variable: x18 Number of cases (rows) of data: 253 Number of cases retained for analysis: 253 BASIC ANALYSIS Estimated Model for x22 Estimate Std Err t-value p-value Lower 95% Upper 95% (Intercept) 2.408 0. 321 7.510 1.777 3.840 x18 8.446 3.866 6.765 3. 316 8. 576 - - Model Fit Standard deviation of x22: 1.802 Standard deviation of residuals: @.923 for 251 degrees of freedom 95% range of residual variation: 3.636 = 2 $ (1.969 $ 0.923) R-squared: 0.154 Adjusted R-squared: 0.151 PRESS R-squared: 0.140 Null hypothesis of all @ population slope coefficients: F-statistic: 45.761 df: 1 and 251 p-value: 0.080 -- Analysis of Variance df sum 5q Mean 5q F-value p-value Model 38.984 38.984 45.761 0. 080 Residuals 251 213 . 838 8. 852 *22 252 252 . 814 1. 803 K-FOLD CROSS-VALIDATION RELATIONS AMONG THE VARIABLES RESIDUALS AND INFLUENCE PREDICTION ERROR
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


