Question: Module 4. Student Ch04 P24 Build a Model 6 A 20-year, 8% semiannual coupon bond with a par value of $1,000 may be called in
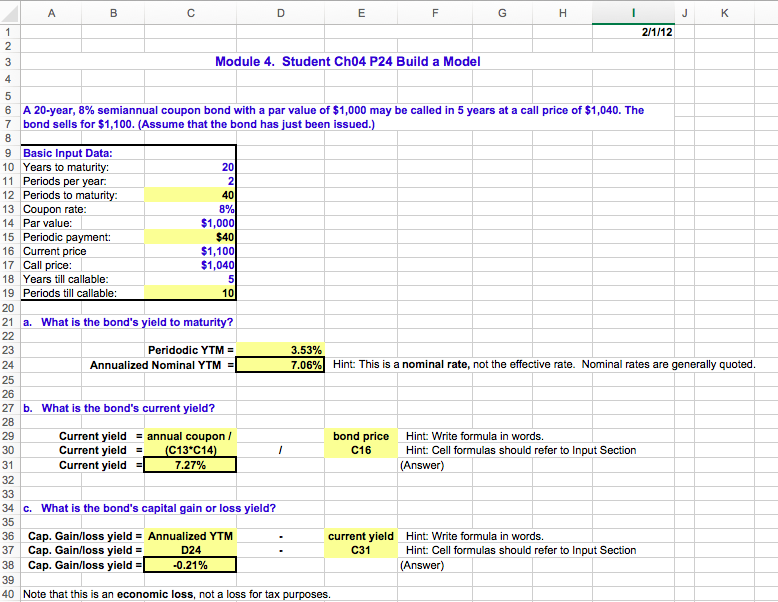
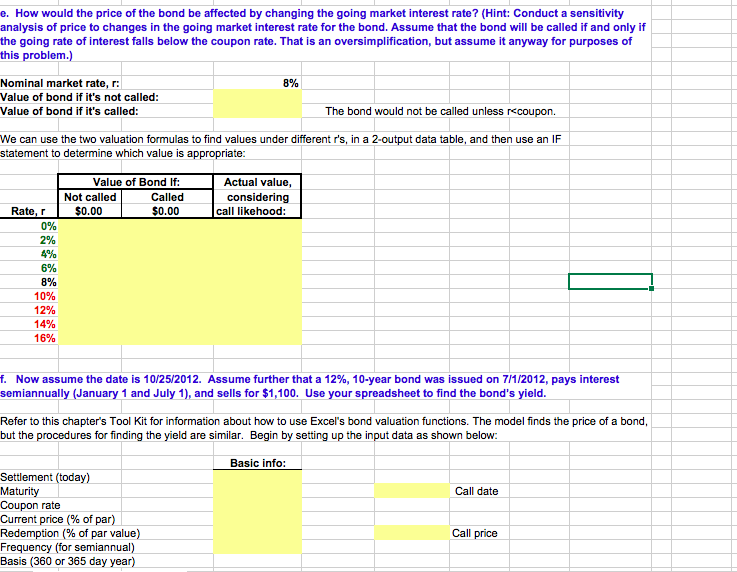
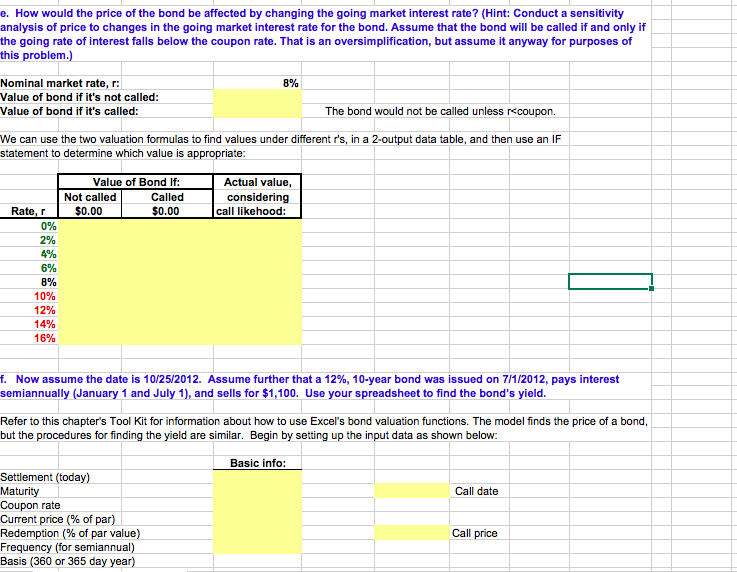
Module 4. Student Ch04 P24 Build a Model 6 A 20-year, 8% semiannual coupon bond with a par value of $1,000 may be called in 5 years at a call price of $1,040. The 7 bond sells for $1,100. (Assume that the bond has just been issued.) 9 Basic Input Data: 10 Years to maturity: 11 Periods per year 12 Periods to maturity 13 Coupon rate 14 Par value: $1,000 15 Periodic payment: 16 Current price 17 Call price $1,100 $1,040 18 Years till callable 19 Periods till callable: 10 20 21 a. What is the bond's yield to maturity? Peridodic YTM 3.53% 7.06%) Hint This is a nominal rate, not the effective rate. Nominal rates are generally quoted 24 Annualized Nominal YTM 25 27 b. What is the bond's current yield? Current yieldannual coupon / Current yield- (C13*C14) Current yield bond price Hint: Write formula in words. C16 Hint: Cell formulas should refer to Input Section 34 c. What is the bond's capital gain or loss yield? 36 Cap. Gain/loss yield Annualized YTM 37 Cap. Gain/loss yield 38 Cap. Gain/loss yield current yield C31 Hint: Write formula in words D24 Hint: Cell formulas should refer to Input Section -0.21% 40 Note that this is an economic loss, not a loss for tax purposes e. How would the price of the bond be affected by changing the going market interest rate? (Hint: Conduct a sensitivity analysis of price to changes in the going market interest rate for the bond. Assume that the bond will be called if and only if the going rate of interest falls below the coupon rate. That is an oversimplification, but assume it anyway for purposes of this problem.) Nominal market rate, r: 8% Value of bond if it's not called: Value of bond if it's called: The bond would not be called unless rccoupon. We can use the two valuation formulas to find values under different r's, in a 2-output data table, and then use an IF statement to determine which value is appropriate: Value of Bond If: Actual value Not called Called considering Rate, r$0.00 $0.00 call likehood: 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% f. Now, assume the date is 10/25/2012. Assume further that a 12%, 10-year bond was issued on 7/1/2012, pays interest semiannually (January 1 and July 1), and sells for $1,100. Use your spreadsheet to find the bond's yield Refer to this chapter's Tool Kit for information about how to use Excel's bond valuation functions. The model finds the price of a bond, but the procedures for finding the yield are similar. Begin by setting up the input data as shown below: Basic info: Settlement (today) Maturity Coupon rate Current price (% of par) Redemption (% of par value) Frequency (for semiannual) Basis (360 or 365 day year) Call date Call price e. How would the price of the bond be affected by changing the going market interest rate? (Hint: Conduct a sensitivity analysis of price to changes in the going market interest rate for the bond. Assume that the bond will be called if and only if the going rate of interest falls below the coupon rate. That is an oversimplification, but assume it anyway for purposes of this problem.) Nominal market rate, r: 8% Value of bond if it's not called: Value of bond if it's called: The bond would not be called unless rccoupon. We can use the two valuation formulas to find values under different r's, in a 2-output data table, and then use an IF statement to determine which value is appropriate: Value of Bond If: Actual value Not called Called considering Rate, r$0.00 $0.00 call likehood: 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% f. Now, assume the date is 10/25/2012. Assume further that a 12%, 10-year bond was issued on 7/1/2012, pays interest semiannually (January 1 and July 1), and sells for $1,100. Use your spreadsheet to find the bond's yield Refer to this chapter's Tool Kit for information about how to use Excel's bond valuation functions. The model finds the price of a bond, but the procedures for finding the yield are similar. Begin by setting up the input data as shown below: Basic info: Settlement (today) Maturity Coupon rate Current price (% of par) Redemption (% of par value) Frequency (for semiannual) Basis (360 or 365 day year) Call date Call price Module 4. Student Ch04 P24 Build a Model 6 A 20-year, 8% semiannual coupon bond with a par value of $1,000 may be called in 5 years at a call price of $1,040. The 7 bond sells for $1,100. (Assume that the bond has just been issued.) 9 Basic Input Data: 10 Years to maturity: 11 Periods per year 12 Periods to maturity 13 Coupon rate 14 Par value: $1,000 15 Periodic payment: 16 Current price 17 Call price $1,100 $1,040 18 Years till callable 19 Periods till callable: 10 20 21 a. What is the bond's yield to maturity? Peridodic YTM 3.53% 7.06%) Hint This is a nominal rate, not the effective rate. Nominal rates are generally quoted 24 Annualized Nominal YTM 25 27 b. What is the bond's current yield? Current yieldannual coupon / Current yield- (C13*C14) Current yield bond price Hint: Write formula in words. C16 Hint: Cell formulas should refer to Input Section 34 c. What is the bond's capital gain or loss yield? 36 Cap. Gain/loss yield Annualized YTM 37 Cap. Gain/loss yield 38 Cap. Gain/loss yield current yield C31 Hint: Write formula in words D24 Hint: Cell formulas should refer to Input Section -0.21% 40 Note that this is an economic loss, not a loss for tax purposes e. How would the price of the bond be affected by changing the going market interest rate? (Hint: Conduct a sensitivity analysis of price to changes in the going market interest rate for the bond. Assume that the bond will be called if and only if the going rate of interest falls below the coupon rate. That is an oversimplification, but assume it anyway for purposes of this problem.) Nominal market rate, r: 8% Value of bond if it's not called: Value of bond if it's called: The bond would not be called unless rccoupon. We can use the two valuation formulas to find values under different r's, in a 2-output data table, and then use an IF statement to determine which value is appropriate: Value of Bond If: Actual value Not called Called considering Rate, r$0.00 $0.00 call likehood: 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% f. Now, assume the date is 10/25/2012. Assume further that a 12%, 10-year bond was issued on 7/1/2012, pays interest semiannually (January 1 and July 1), and sells for $1,100. Use your spreadsheet to find the bond's yield Refer to this chapter's Tool Kit for information about how to use Excel's bond valuation functions. The model finds the price of a bond, but the procedures for finding the yield are similar. Begin by setting up the input data as shown below: Basic info: Settlement (today) Maturity Coupon rate Current price (% of par) Redemption (% of par value) Frequency (for semiannual) Basis (360 or 365 day year) Call date Call price e. How would the price of the bond be affected by changing the going market interest rate? (Hint: Conduct a sensitivity analysis of price to changes in the going market interest rate for the bond. Assume that the bond will be called if and only if the going rate of interest falls below the coupon rate. That is an oversimplification, but assume it anyway for purposes of this problem.) Nominal market rate, r: 8% Value of bond if it's not called: Value of bond if it's called: The bond would not be called unless rccoupon. We can use the two valuation formulas to find values under different r's, in a 2-output data table, and then use an IF statement to determine which value is appropriate: Value of Bond If: Actual value Not called Called considering Rate, r$0.00 $0.00 call likehood: 0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16% f. Now, assume the date is 10/25/2012. Assume further that a 12%, 10-year bond was issued on 7/1/2012, pays interest semiannually (January 1 and July 1), and sells for $1,100. Use your spreadsheet to find the bond's yield Refer to this chapter's Tool Kit for information about how to use Excel's bond valuation functions. The model finds the price of a bond, but the procedures for finding the yield are similar. Begin by setting up the input data as shown below: Basic info: Settlement (today) Maturity Coupon rate Current price (% of par) Redemption (% of par value) Frequency (for semiannual) Basis (360 or 365 day year) Call date Call price
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


