Question: monte carlo sumulation queneing problem Problem #1 (25 points) - A Simulation Done By Hand Consider a single-channel queueing system with customer interarrival-times (in minutes)
monte carlo sumulation queneing problem
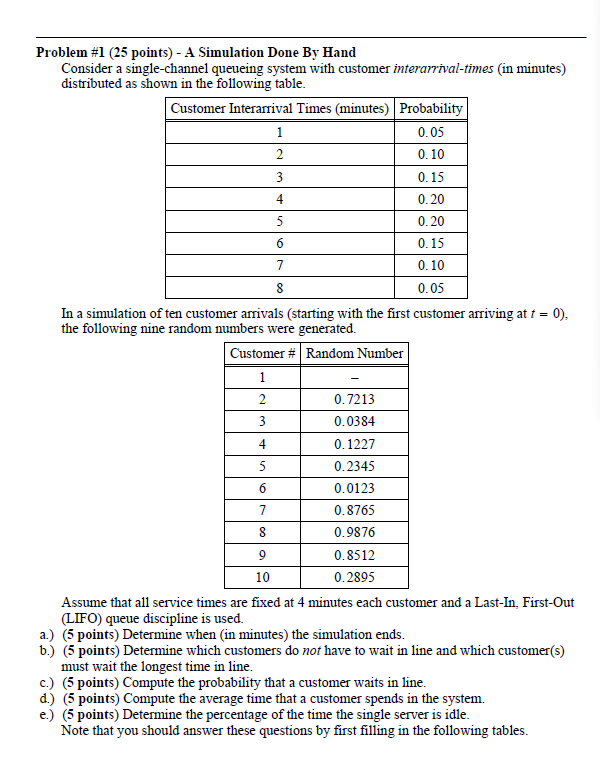
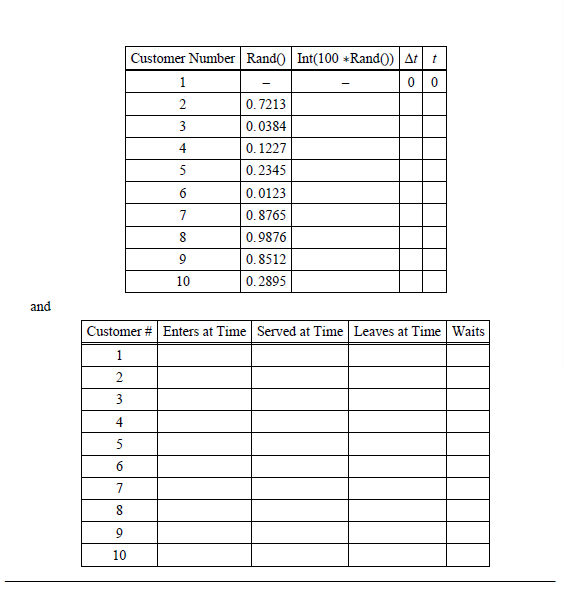
Problem #1 (25 points) - A Simulation Done By Hand Consider a single-channel queueing system with customer interarrival-times (in minutes) distributed as shown in the following table Customer Interarrival Times (minutes) Probability 0. 05 0. 10 0. 15 0. 20 5 0.20 6 0. 15 0. 10 8 0. 05 In a simulation of ten customer arrivals (starting with the first customer arriving at f = 0), the following nine random numbers were generated Customer #| Random Number 1 0. 7213 0. 0384 0. 1227 0.2345 6 0.0123 7 0. 8765 0.9876 9 0. 8512 10 0.2895 Assume that all service times are fixed at 4 minutes each customer and a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) queue discipline is used. a.) (5 points) Determine when (in minutes) the simulation ends. b.) (5 points) Determine which customers do not have to wait in line and which customer(s) must wait the longest time in line c.) (5 points) Compute the probability that a customer waits in line. d.) (5 points) Compute the average time that a customer spends in the system. e.) (5 points) Determine the percentage of the time the single server is idle. Note that you should answer these questions by first filling in the following tables.Customer Number | Rand()| Int(100 *Rand()) 0 0 0. 7213 3 0. 0384 4 0. 1227 0.2345 0. 0123 0. 8765 0.9876 9 0. 8512 10 0.2895 and Customer # Enters at Time Served at Time | Leaves at Time | Waits w 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


