Question: Moon Tech (MT) Inc. produces an innovative high-tech device called Yuebing at a variable cost of $60 per unit. Cha Tech (CT) Inc. produces a
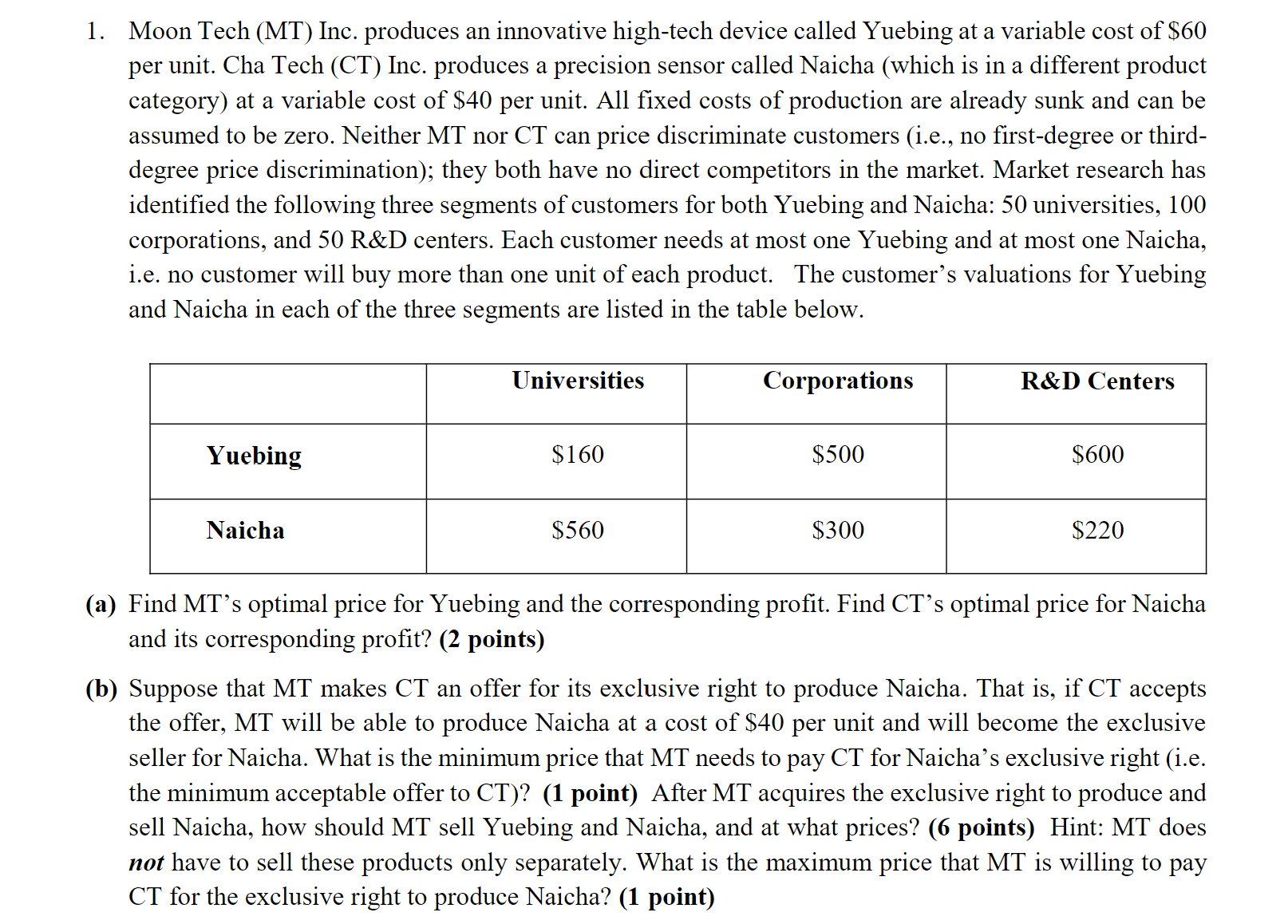
Moon Tech (MT) Inc. produces an innovative high-tech device called Yuebing at a variable cost of $60 per unit. Cha Tech (CT) Inc. produces a precision sensor called Naicha (which is in a different product category) at a variable cost of $40 per unit. All fixed costs of production are already sunk and can be assumed to be zero. Neither MT nor CT can price discriminate customers (i.e., no first-degree or thirddegree price discrimination); they both have no direct competitors in the market. Market research has identified the following three segments of customers for both Yuebing and Naicha: 50 universities, 100 corporations, and 50 R\&D centers. Each customer needs at most one Yuebing and at most one Naicha, i.e. no customer will buy more than one unit of each product. The customer's valuations for Yuebing and Naicha in each of the three segments are listed in the table below. a) Find MT's optimal price for Yuebing and the corresponding profit. Find CT's optimal price for Naicha and its corresponding profit? (2 points) b) Suppose that MT makes CT an offer for its exclusive right to produce Naicha. That is, if CT accepts the offer, MT will be able to produce Naicha at a cost of $40 per unit and will become the exclusive seller for Naicha. What is the minimum price that MT needs to pay CT for Naicha's exclusive right (i.e. the minimum acceptable offer to CT )? (1 point) After MT acquires the exclusive right to produce and sell Naicha, how should MT sell Yuebing and Naicha, and at what prices? (6 points) Hint: MT does not have to sell these products only separately. What is the maximum price that MT is willing to pay CT for the exclusive right to produce Naicha? (1 point)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


