Question: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Nulls, if used improperly, can create problems because they can represent ____. a. a default value b. a known, but missing,
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Nulls, if used improperly, can create problems because they can represent ____.
| a. | a default value |
| b. | a known, but missing, attribute value |
| c. | zero |
| d. | an unsortable value |
2 The referential integrity rule requires that ____.
| a. | every null foreign key value must reference an existing primary key value |
| b. | an attribute has a corresponding value |
| c. | every non-null foreign key value reference an existing primary key value |
| d. | you delete a row in one table whose primary key does not have a matching foreign key value in another table |
3. According to E.F. Codd, another word for the term “relation” is ____.
| a. | datafile |
| b. | data index |
| c. | table |
| d. | data query |
5. A table can be logically connected to another table by defining a ____.
| a. | hyperlink |
| b. | common attribute |
| c. | primary key |
| d. | logic key |
7. A primary key that consists of more than one field is called a ____ key.
| a. | composite |
| b. | secondary |
| c. | group |
| d. | foreign |
8. A field that consists of integer values is a ____ type field.
| a. | Date/Time |
| b. | Yes/No |
| c. | Memo |
| d. | Numeric |
9. In general terms, the ____ key is an attribute (or combination of attributes) that uniquely identifies any given entity.
| a. | indexed |
| b. | primary |
| c. | foreign |
| d. | redundant |
10. It might take more than a single attribute to define functional dependence; that is, a key may be composed of more than one attribute. A multi-attribute key is known as a ____ key.
| a. | primary |
| b. | super |
| c. | composite |
| d. | foreign |
11. A ____ key is defined as a key that is used strictly for data retrieval purposes.
| a. | primary |
| b. | foreign |
| c. | secondary |
| d. | data |
12. An attribute (or combination of attributes) that uniquely identifies each entity occurence in a
table is called a ____.
| a. | Superkey |
| b. | candidate key |
| c. | primary key |
| d. | secondary key |
13. An attribute (or combination of attributes) in one table whose values must either match
the primary key in another table or be null is called a ____ key.
| a. | Foreign |
| b. | Candidate |
| c. | Primary |
| d. | secondary |
14. A primary key ____.
| a. | consists of only one field |
| b. | has the same value for all records |
| c. | must contain a unique value for each record within the table |
| d. | is defined automatically |
15. Given its parent/child structure, the hierarchical model yields integrity and consistency; there cannot be
____________________.
| a. | a root |
| b. | a large amount of data |
| c. | a child without a parent |
| d. | many transactions |
16.A data model must represent the ____ world as closely as possible.
| a. | machine |
| b. | logical |
| c. | real |
| d. | abstract |
.17-Which of the following is not a degree of abstraction as defined by ANSI/SPARC?
| a. | Conceptual |
| b. | Physical |
| c. | Internal |
| d. | External |
18. The ____ model presents a global view of the database.
| a. | network |
| b. | physical |
| c. | conceptual |
| d. | logical |
Review Questions:
What two conditions must be met before an entity can be classified as a weak entity? Give an example of a weak entity.
What is a strong (or identifying) relationship, and how is it depicted in a Crow’s Foot ERD?
Given the business rule “an employee may have many degrees,” discuss its effect on attributes, entities, and relationships. (Hint: Remember what a multivalued attribute is and how it might be implemented.)
What is a composite entity, and when is it used?
Suppose you are working within the framework of the conceptual model in Figure Q4.5.
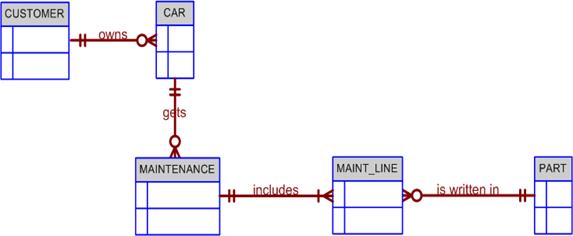
Figure Q4.5 The Conceptual Model for Question 5
Given the conceptual model in Figure Q4.5, answer the following:
Write the business rules that are reflected in it.
How would you (graphically) identify each of the following ERM components in a Crow’s Foot model?
- An entity
- The multiplicity (0:M)
- A week entity
- a strong relationship
Discuss the difference between a composite key and a composite attribute. How would each be indicated in an ERD?
What is a derived attribute? Give an example.
PROBLEMS
1. Given the following business rules, create the appropriate Crow’s Foot ERD.
- A company operates many departments.
- Each department employs one or more employees.
- Each of the employees might or might not have one or more dependents.
- Each employee might or might not have an employment history.
CUSTOMER CAR Owns gets MAINTENANCE MAINT LINE PART includes is written in
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (144 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 answer b 2 answer a 3 answer c 5 A table can be logically connected to another table by defining a ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


