Question: My Courses This Course Student Services HFC Online Video Tutorials line I BLW 253 Sections 90, 91, & 92 / My courses / 22/WI BLW-253-90
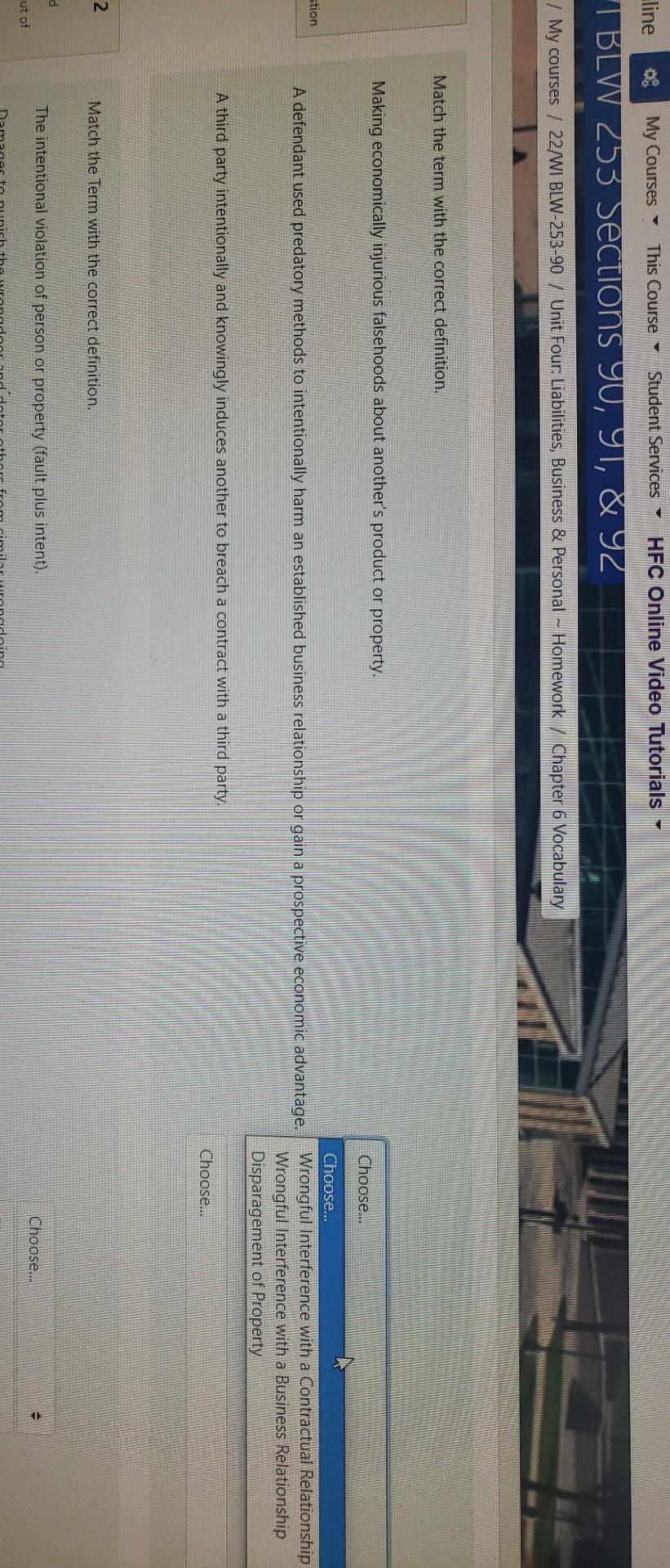
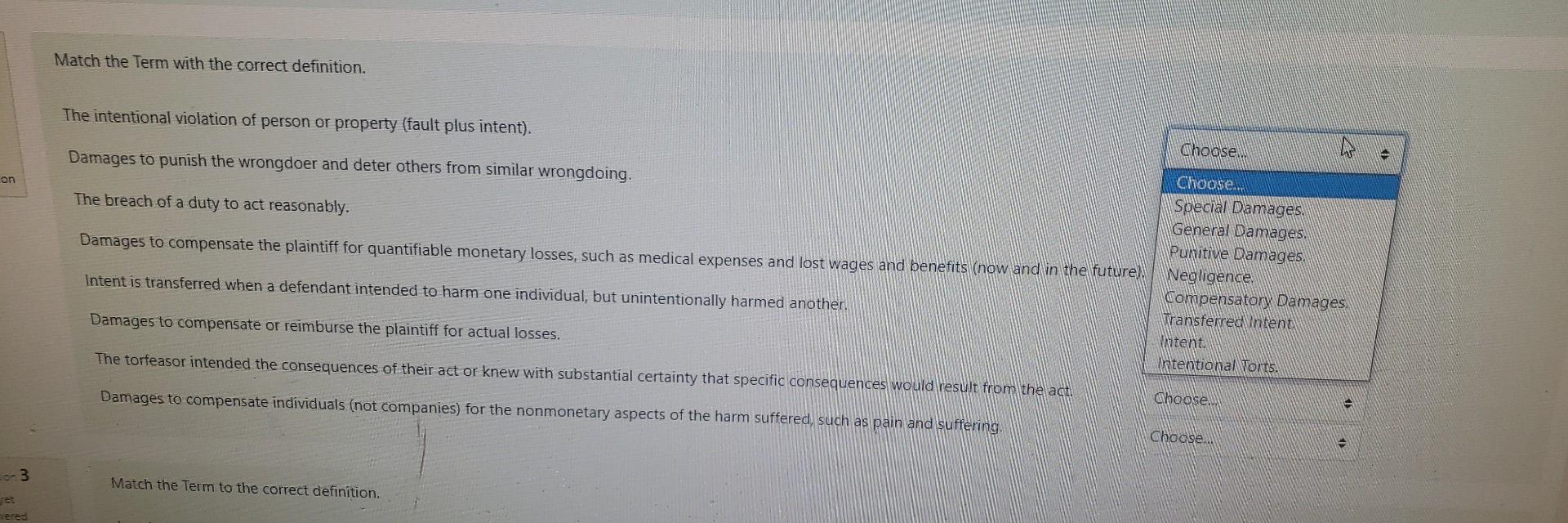

My Courses This Course Student Services HFC Online Video Tutorials line I BLW 253 Sections 90, 91, & 92 / My courses / 22/WI BLW-253-90 / Unit Four: Liabilities, Business & Personal - Homework Chapter 6 Vocabulary Match the term with the correct definition. Making economically injurious falsehoods about another's product or property. Choose... stion A defendant used predatory methods to intentionally harm an established business relationship or gain a prospective economic advantage. Choose... Wrongful Interference with a Contractual Relationship Wrongful Interference with a Business Relationship Disparagement of Property A third party intentionally and knowingly induces another to breach a contract with a third party. Choose... 2 Match the Term with the correct definition. d The intentional violation of person or property (fault plus intent). Choose... ut of Match the Term with the correct definition. The intentional violation of person or property (fault plus intent). Damages to punish the wrongdoer and deter others from similar wrongdoing. Choose on The breach of a duty to act reasonably. Damages to compensate the plaintiff for quantifiable monetary losses, such as medical expenses and lost wages and benefits (now and in the future) Intent is transferred when a defendant intended to harm one individual, but unintentionally harmed another. Choose. Special Damages General Damages Punitive Damages Wegligence Compensatory Damages. Wansferred intent Waitent. intentional Vorts. Damages to compensate or reimburse the plaintiff for actual losses. The torfeasor intended the consequences of their act or knew with substantial certainty that specific consequences would result from the act. Damages to compensate individuals (not companies) for the nonmonetary aspects of the harm suffered, such as pain and suffering. Choose. Choose. - 3 Match the Term to the correct definition. eres Match the Term to the correct definition. Legal cause for personal injury exists if the injury was foreseeable. Choose... A defense to negligent claims wherein the plaintiff knew of the risk and voluntarily assumed it. lon An unforeseeable intervening event may break the causal connection between a wrongful act and an injury to another. In determining whether a duty of care has been breached, the courts ask how a reasonable person would have acted in the same circumstances. A doctrine which held that a plaintiff who was also negligent (who failed to exercise a reasonable degree of care) could not recover anything from the defendant. Choose... Comparative Negligence. Dram Shop Acts Proximate Cause. Good Samaritan Statute. Superseding Cause. Causation in Fact. Reasonable Person Standard. Contributory Negligence. Assumption of Risk. Choose... - "But for the wrongful act, the plaintiff would not have been injured. Someone who is aided voluntarily by another cannot turn around and sue the "Good Samaritan" for negligence. Modern doctrine which provides that both the plaintiff's and the defendant's negligence are computed, and the liability for damages is distributed accordingly. Choose... - A bar's owner or a bartender may be held liable for injuries caused by a person who became intoxicated while drinking at the bar. Choose... Finish attempt - My Courses This Course Student Services HFC Online Video Tutorials line I BLW 253 Sections 90, 91, & 92 / My courses / 22/WI BLW-253-90 / Unit Four: Liabilities, Business & Personal - Homework Chapter 6 Vocabulary Match the term with the correct definition. Making economically injurious falsehoods about another's product or property. Choose... stion A defendant used predatory methods to intentionally harm an established business relationship or gain a prospective economic advantage. Choose... Wrongful Interference with a Contractual Relationship Wrongful Interference with a Business Relationship Disparagement of Property A third party intentionally and knowingly induces another to breach a contract with a third party. Choose... 2 Match the Term with the correct definition. d The intentional violation of person or property (fault plus intent). Choose... ut of Match the Term with the correct definition. The intentional violation of person or property (fault plus intent). Damages to punish the wrongdoer and deter others from similar wrongdoing. Choose on The breach of a duty to act reasonably. Damages to compensate the plaintiff for quantifiable monetary losses, such as medical expenses and lost wages and benefits (now and in the future) Intent is transferred when a defendant intended to harm one individual, but unintentionally harmed another. Choose. Special Damages General Damages Punitive Damages Wegligence Compensatory Damages. Wansferred intent Waitent. intentional Vorts. Damages to compensate or reimburse the plaintiff for actual losses. The torfeasor intended the consequences of their act or knew with substantial certainty that specific consequences would result from the act. Damages to compensate individuals (not companies) for the nonmonetary aspects of the harm suffered, such as pain and suffering. Choose. Choose. - 3 Match the Term to the correct definition. eres Match the Term to the correct definition. Legal cause for personal injury exists if the injury was foreseeable. Choose... A defense to negligent claims wherein the plaintiff knew of the risk and voluntarily assumed it. lon An unforeseeable intervening event may break the causal connection between a wrongful act and an injury to another. In determining whether a duty of care has been breached, the courts ask how a reasonable person would have acted in the same circumstances. A doctrine which held that a plaintiff who was also negligent (who failed to exercise a reasonable degree of care) could not recover anything from the defendant. Choose... Comparative Negligence. Dram Shop Acts Proximate Cause. Good Samaritan Statute. Superseding Cause. Causation in Fact. Reasonable Person Standard. Contributory Negligence. Assumption of Risk. Choose... - "But for the wrongful act, the plaintiff would not have been injured. Someone who is aided voluntarily by another cannot turn around and sue the "Good Samaritan" for negligence. Modern doctrine which provides that both the plaintiff's and the defendant's negligence are computed, and the liability for damages is distributed accordingly. Choose... - A bar's owner or a bartender may be held liable for injuries caused by a person who became intoxicated while drinking at the bar. Choose... Finish attempt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


