Question: my homework please use JAVA Exercise 1 Consider the 7 classes provided with this exercise which are: Shape, TwoDimensionalShape, Circle, Rectangle, Square, Triangle, and Point.
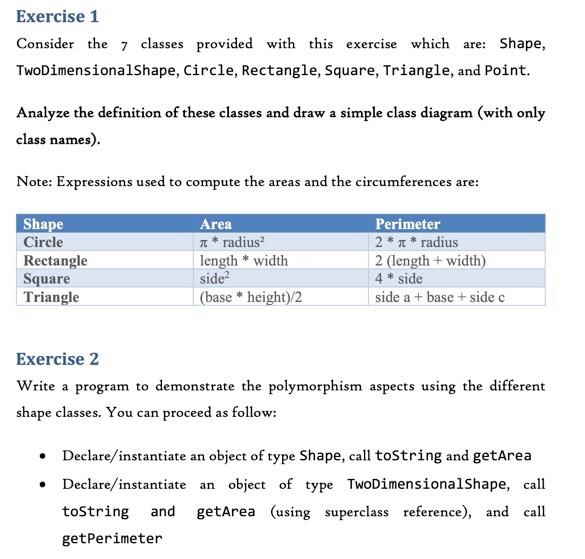





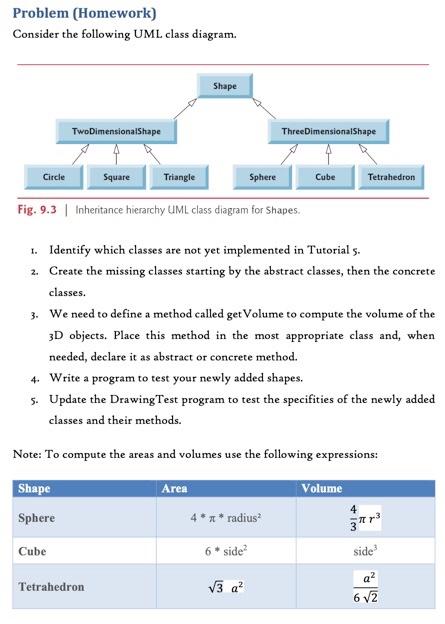
Exercise 1 Consider the 7 classes provided with this exercise which are: Shape, TwoDimensionalShape, Circle, Rectangle, Square, Triangle, and Point. Analyze the definition of these classes and draw a simple class diagram (with only class names). Note: Expressions used to compute the areas and the circumferences are: Shape Circle Rectangle Square Triangle Area 1* radius length * width side? (base * height)/2 Perimeter 2* * * radius 2 (length + width) 4* side side a + base + side c Exercise 2 Write a program to demonstrate the polymorphism aspects using the different shape classes. You can proceed as follow: Declare/instantiate an object of type Shape, call toString and getArea Declare/instantiate an object of type TwoDimensionalShape, call toString and getArea (using superclass reference), and call getPerimeter Declare/instantiate an object of type Rectangle, and call toString, getArea, and getPerimeter (using superclass reference only) Declare/instantiate objects of type Circle, Sqaure, and Triangle, call toString and getArea (using indirect superclass reference), and call getPerimeter (using direct superclass reference) Exercise 3 Create a class called Drawing. This class contains a set (array) of shapes which initialized using its unique constructor. In addition, define the following methods: getShapes: returns the reference to the array of shapes. updateShape: takes a Shape object and an index, put the object in the array at the specified index, returns true if the index is correct, or false otherwise. shapeAt: takes an index, returns the Shape object from the array at the specified index if the index is correct, or null otherwise. getShapeArea: takes an index, returns the Shape object's area from the array at the specified index if the index is correct, or 0.8 otherwise. Exercise 4 Write a program to demonstrate the polymorphism aspects using the different shape classes and Drawing. You can proceed as follow: Declare/instantiate an array of 4 Shapes. Create one object from each of the following types: Shape, TwoDimensionalShape, Circle, and Triangle. Insert the created objects into the array. . Declare/instantiate an object of type Drawing using the previously defined array. Get the list of shapes from the Drawing object using getShapes and print their information (by calling toString and getArea) Using updateShape, create/put new object of type Rectangle in the position 0, and another of type Square in the position 1. Find the newly inserted objects using shapeAt and print their info Exercise 5 Answer the following questions: . Why we cannot call the getPerimeter method? If we change the array type will solve the problem completely? Is there any other way to solve the problem without any modification? Exercise 1 The abstract class is the class which we never intend (or it is not useful) to create objects of this class. Considering the shape classes of the Tutorial os, which are the classes that you qualified to be abstract? Justify your answer. Exercise 2 Declare the classes Shape and TwoDimentionalShape as abstract classes and compile/execute the test programs (Shape Test and Drawing Test). Identify the eventual compile-time errors (if any) and try to resolve them. Exercise 3 An abstract class normally contains one or more abstract methods. The abstract method is a method that do not provide implementation Focus the classes Shape and TwoDimentionalShape, and try to identify which methods that you qualified to be abstract? Justify your answer. Exercise 4 Declare the get Area() from Shape and get Perimeter() from TwoDimentionalShape as abstract methods and compile/execute the test programs (Shape Test and Drawing Test). Identify the eventual compile-time errors (if any) and try to resolve them. Exercise 5 Update the Drawing Test program in order to print the perimeter by downcasting the Shape's instance. Declare the getArea() from Shape and get Perimeter() from TwoDimentionalShape as abstract methods and compile/execute the test programs (Shape Test and Drawing Test). Identify the eventual compile-time errors (if any) and try to resolve them. Problem (Homework) Consider the following UML class diagram. Shape TwoDimensionalShape Three DimensionalShape Circle Square Triangle Sphere Cube Tetrahedron Fig. 9.3 Inheritance hierarchy UML class diagram for Shapes. 1. Identify which classes are not yet implemented in Tutorial s. 2. Create the missing classes starting by the abstract classes, then the concrete classes. 3. We need to define a method called get Volume to compute the volume of the 3D objects. Place this method in the most appropriate class and, when needed, declare it as abstract or concrete method. 4. Write a program to test your newly added shapes. s. Update the Drawing Test program to test the specifities of the newly added classes and their methods. Note: To compute the areas and volumes use the following expressions: Shape Area Volume 4 Sphere 4** radius 3 Cube 6* side? side Tetrahedron V3 a? 6 V2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


