Question: Please help with this Assignment in Java language. All the files need to be copied below. Point.java public class Point { /** * The x-coordinate
Please help with this Assignment in Java language. All the files need to be copied below.

Point.java
public class Point { /** * The x-coordinate of the point. */ private int myX; /** * The y-coordinate of the point. */ private int myY; /** * The constructor defines the point without argument */ public Point() { this.myX = 0; this.myY = 0; } /** * The constructor defines the point with arguments * * @param theX the x-coordinate of the point. * @param theY the y-coordinate of the point. */ public Point(int theX, int theY) { this.myX = theX; this.myY = theY; } /** * The method return the value of x-coordinate of the point. * * @return the value of x-coordinate of the point. */ public int getX() // getter method { return myX; } /** * The method sets new value of x-coordinate of the point. * * @param theX the new value of x-coordinate of the point. */ public void setX(int theX) // setter method { this.myX = theX; } /** * The method return the value of y-coordinate of the point. * * @return the value of y-coordinate of the point. */ public int getY() { return myY; } /** * The method sets new value of y-coordinate of the point. * * @param theX the new value of y-coordinate of the point. */ public void setY(int theY) { this.myY = theY; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("[Point X=" + this.myX + ", Y=" + this.myY + "]"); } /** * The method calculates the distance between two points * * @param p1 the first point * @param p2 the second point * @return the distance between two points */ public static double calculateDistance(Point p1, Point p2) { int deltaX = p1.myX - p2.myX; int deltaY = p1.myY - p2.myY; double squareOfDeltaX = Math.pow(deltaX, 2); double squareOfDeltaY = Math.pow(deltaY, 2); return Math.sqrt(squareOfDeltaX + squareOfDeltaY); } }Shape.java
public interface Shape extends Comparable{ /** * The method return the type of shape * @return the type of shape in string format */ public String getType(); /** * The method returns the perimeter of the shape * @return the perimeter of the shape */ public double getPerimeter(); /** * The method returns the area of the shape * @return the area of the shape */ public double getArea(); }
ShapeMain.java
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; public class ShapeMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { List shapes = new ArrayList(); Scanner console = new Scanner(new File("shapes.txt")); while (console.hasNext()) { String shapeType = console.next(); if (shapeType.equals(TRIANGLE)) { Point point1 = new Point(); point1.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); point1.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); Point point2 = new Point(); point2.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); point2.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); Point point3 = new Point(); point3.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); point3.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); shapes.add(new Triangle(point1, point2, point3)); } else if (shapeType.equals(RECTANGLE)) { Point topLeft = new Point(); topLeft.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); topLeft.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); Point bottomRight = new Point(); bottomRight.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); bottomRight.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); shapes.add(new Rectangle(topLeft, bottomRight)); } else if (shapeType.equals(SQUARE)) { Point topLeft = new Point(); topLeft.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); topLeft.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); int length = Integer.parseInt(console.next()); shapes.add(new Square(topLeft, length)); } else if (shapeType.equals(CIRCLE)) { Point center = new Point(); center.setX(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); center.setY(Integer.parseInt(console.next())); int radius = Integer.parseInt(console.next()); shapes.add(new Circle(center, radius)); } else { System.err.println("There is something wrong with the inputs"); console.close(); System.exit(1); } } console.close(); Collections.sort(shapes); System.out.println("Print shapes in ascending order:"); Iterator iterator = shapes.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Shape shape = iterator.next(); System.out.println(String.format("%s => Perimeter=%.3f and Area=%.3f", shape, shape.getPerimeter(), shape.getArea())); } } public static final String TRIANGLE = "t"; public static final String RECTANGLE = "r"; public static final String SQUARE = "s"; public static final String CIRCLE = "c"; } shapes.txt
s 6 9 1 c 8 6 6 s 3 -9 9 s -8 -8 6 s 8 -1 8 r -1 -2 8 8 t -5 -3 4 -5 -7 -1 r -5 -3 2 7 r -9 -1 5 -9 s -9 5 8 s -2 7 1 s 9 8 7 s -5 2 8 s -9 8 2 r -2 -9 -7 1 r 0 8 -3 5 c -7 4 9 c 3 3 4 r -2 3 9 -2 t 7 -3 7 -7 8 -4
shapes_output.txt
Print shapes in ascending order: {Type=Triangle, Point1=[Point X=7, Y=-3], Point2=[Point X=7, Y=-7], Point3=[Point X=8, Y=-4]} => Perimeter=8.576 and Area=2.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=-2, Y=7], BottomRight=[Point X=-1, Y=8]} => Perimeter=4.000 and Area=1.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=6, Y=9], BottomRight=[Point X=7, Y=10]} => Perimeter=4.000 and Area=1.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=-9, Y=8], BottomRight=[Point X=-7, Y=10]} => Perimeter=8.000 and Area=4.000 {Type=Triangle, Point1=[Point X=-5, Y=-3], Point2=[Point X=4, Y=-5], Point3=[Point X=-7, Y=-1]} => Perimeter=23.753 and Area=7.000 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=0, Y=8], BottomRight=[Point X=-3, Y=5]} => Perimeter=12.000 and Area=9.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=-8, Y=-8], BottomRight=[Point X=-2, Y=-2]} => Perimeter=24.000 and Area=36.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=9, Y=8], BottomRight=[Point X=16, Y=15]} => Perimeter=28.000 and Area=49.000 {Type=Circle, Center=[Point X=3, Y=3], Radius=4} => Perimeter=25.133 and Area=50.265 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=-2, Y=-9], BottomRight=[Point X=-7, Y=1]} => Perimeter=30.000 and Area=50.000 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=-2, Y=3], BottomRight=[Point X=9, Y=-2]} => Perimeter=32.000 and Area=55.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=-5, Y=2], BottomRight=[Point X=3, Y=10]} => Perimeter=32.000 and Area=64.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=-9, Y=5], BottomRight=[Point X=-1, Y=13]} => Perimeter=32.000 and Area=64.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=8, Y=-1], BottomRight=[Point X=16, Y=7]} => Perimeter=32.000 and Area=64.000 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=-5, Y=-3], BottomRight=[Point X=2, Y=7]} => Perimeter=34.000 and Area=70.000 {Type=Square, TopLeft=[Point X=3, Y=-9], BottomRight=[Point X=12, Y=0]} => Perimeter=36.000 and Area=81.000 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=-1, Y=-2], BottomRight=[Point X=8, Y=8]} => Perimeter=38.000 and Area=90.000 {Type=Rectangle, TopLeft=[Point X=-9, Y=-1], BottomRight=[Point X=5, Y=-9]} => Perimeter=44.000 and Area=112.000 {Type=Circle, Center=[Point X=8, Y=6], Radius=6} => Perimeter=37.699 and Area=113.097 {Type=Circle, Center=[Point X=-7, Y=4], Radius=9} => Perimeter=56.549 and Area=254.469

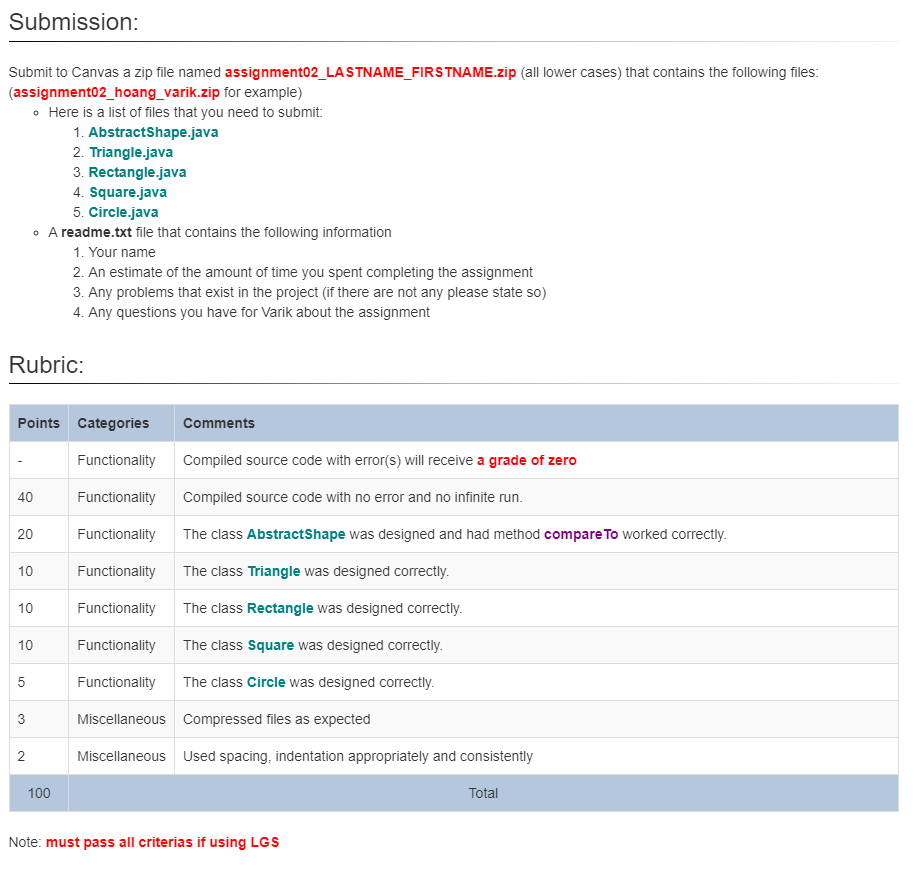
In this assignment, we only focus on 2D shapes. Create an interface named Shape with prototypes: (The Shape interface must be extended from another interface Comparable) Create an abstract class named AbstractShape that implements the interface Shape. The only method that we need to implement in this class is to compare two Shape objects. The method signature must be public int compare To(Shape other). The method will determine conditions as follow: 1. Area (please use Heron's formula for triangle) 2. Perimeter 3. Type of shape For example, if a square has the area 4.0 and the rectangle has the area 8.0 then the square should go before the rectangle. For another example, if a square and a rectangle have the same area and perimeter, the rectangle should go before the square because when we compare the name, rectangle starts with the letter ' r ' and square starts with the letter 's', so the letter 'r' goes before 's'. String class also provides compare To method, so we can rely on the result of this one. For each concrete class below, we should have one constructor that has noparameterpassed in and one constructor that allows user to accept all values from parameters and assign them to the attributes of the class. (We can assume that the point inputs will form valid shapes) 1. Create a concrete class named Triangle with three attributes point1, point2, and point 3 . Those three points will form a triangle. The data type of those points will be the provided Point class. The class Triangle should extend the abstract class AbstractShape. The to String() method should follow the format: {Type=Triangle,Point=[PointX=0,Y=0],Point=[PointX=0,Y=0],Point3=[PointX=0,Y=0]} 2. Create a concrete class named Rectangle with two attributes topLeft and bottomRight. Those two points will form a rectangle. The data type of those points will be the provided Point class. The class Rectangle should extend the abstract class AbstractShape. The to String() method should follow the format: \{Type=Rectangle, Topleft=[Point X=0,Y=0], BottomRight=[Point X=0,Y=0]} 3. Create a concrete class named Square with no attribute because it will use attributes from the class Rectangle which it inherited from. In the constructor that accepts no parameter, use only one statement to initiate the attributes of the Square class (super keyword). The second constructor accept the top left point and the length of the side (int primitive data type). Based on those two parameters, create the bottom right point and call the corresponding constructor in the super class that passes in the top left and bottom right points. The to String() method should follow the format: \{Type=Square, Topleft=[Point X=0,Y=0], BottomRight= [Point X=0,Y=0]} 4. Create a concrete class named Circle with one attribute center (Point class) and radius (int primitive data type). The class Circle should extend the abstract class AbstractShape. The to String() method should follow the format: {Type=Circle,Center=[PointX=0,Y=0],Radius=0} In this assignment, there is a test file provided for sanity check called ShapeMain.java Assignment \#2 - Shapes Background: In geometry, a shape can be defined as the form of an object or its outline, outer boundary or outer surface. Everything we see in the world around us has a shape. We can find different basic shapes such as the two-dimensional square, rectangle, and oval or the three-dimensional rectangular prism, cylinder, and sphere in the objects we see around us. These geometric shapes appear in objects we see as credit cards, bills and coins, finger rings, photo frames, dart boards, huts, windows, magician's wands, tall buildings, flower pots, toy trains, and balloons. Shapes can be classified into open and closed shapes. Closed geometric shapes can further be put into two broad categories, namely two-dimensional and threedimensional shapes. The color, overall size, and orientation called the non-defining attributes of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional shape do not define or affect the shape in any way. These attributes can change without any effect on the shape. On the other hand, defining attributes such as the number of sides (parallel or nonparallel, straight or curved), vertices, edges, and faces of a shape, whether the shape is open or closed, and the angle measures determine the shape of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional object. Any change in these defining attributes will change the shape. Objectives: This assignment will assess your mastery of the following objectives: - To design interface, abstract class, and concrete classes. - To design condition for the comparable class. Extra credit is only considered if the assignment submit (and complete) on-time according to original due date on syllabus. The due date is extended will not count. Implementation Guidelines: The program does not compile will receive grade of zero. Place your code in a class named AbstractShape, Triangle, Rectangle, Square, and Circle. - The instructions include: 1. Create an abstract class AbstractShape that implements the interface Shape. There is only one method compare To need to be implemented in this class. The purpose of this method is to determine if the shape goes before another by comparing the area, perimenter, and the name/type of the shape. 2. Create a concrete class Triangle that only extends the abstract class AbstractShape then implement required methods. 3. Create a concrete class Rectangle that only extends the abstract class AbstractShape then implement required methods. 4. Create a concrete class Square that only extends the concrete class Rectangle then implement required methods. The class should not need to have any extra field because it can rely on the fields of the parent class. 5. Create a concrete class Circle that only extends the abstract class AbstractShape then implement required methods. - Be sure your code follows the naming and coding conventions for the class: 1. Instance fields of a class should be named starting with 'my' 2. Parameters to methods should be named starting with 'the' 3. Parameters to methods should be specified as final 4. Javadoc comments should be used for the class as well as the methods of the class 5. You will lose points for each of these things on every assignment if you do not adhere to the rules. 6. See this document for specifics (as well as an example): https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/codeconventionsintroduction.html Download: - Point.java (do not modify the content of this file) - Shape.java (do not modify the content of this file) - ShapeMain.java (only use this file for sanity check when everything is complete) - shapes.txt (the input test file for ShapeMain.java) - shapes_output.txt (the output test file for ShapeMain.java) - readme.txt (example) Submit to Canvas a zip file named assignment02_LASTNAME_FIRSTNAME.zip (all lower cases) that contains the following files: (assignment02_hoang_varik.zip for example) - Here is a list of files that you need to submit: 1. AbstractShape.java 2. Triangle.java 3. Rectangle.java 4. Square.java 5. Circle.java - A readme.txt file that contains the following information 1. Your name 2. An estimate of the amount of time you spent completing the assignment 3. Any problems that exist in the project (if there are not any please state so) 4. Any questions you have for Varik about the assignment Rubric
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


