Question: n n E m Oi=1 II 1 + 0) nm i=1X1, X2, . . . ,Xn are independent random variables With the common probability density
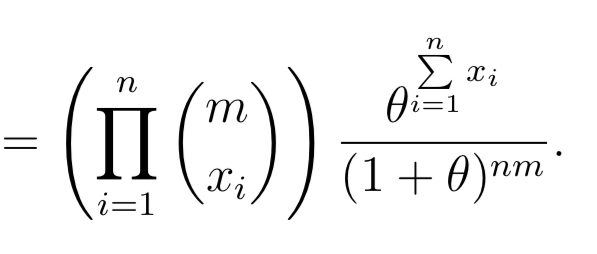
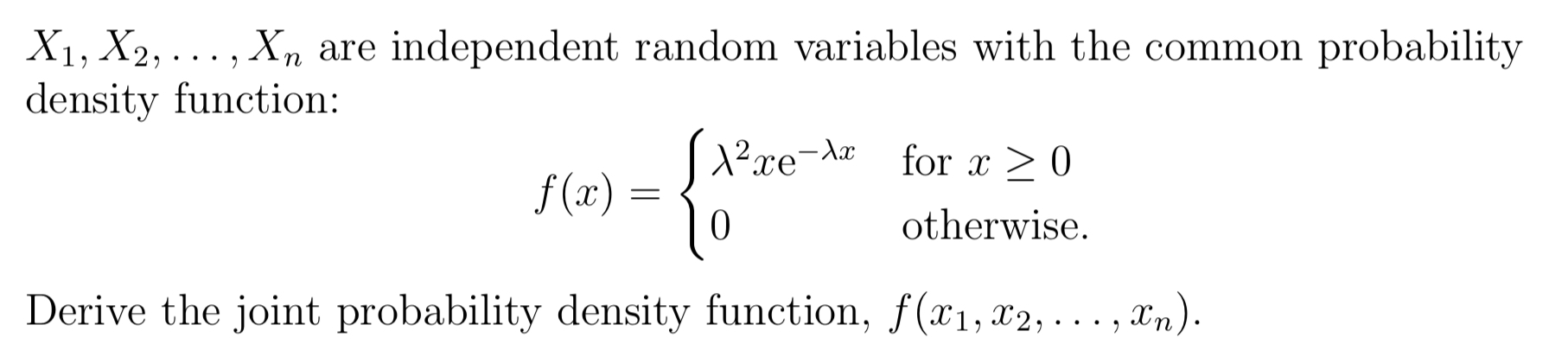
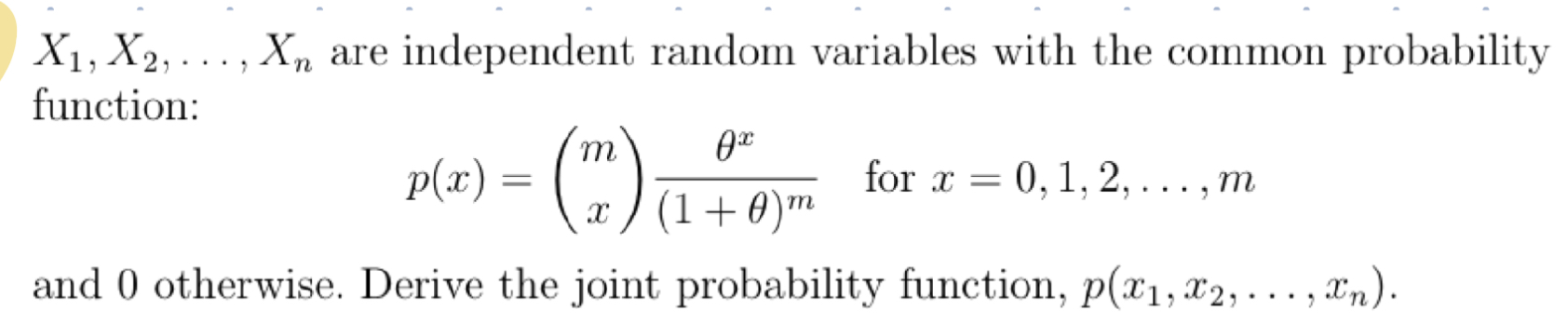
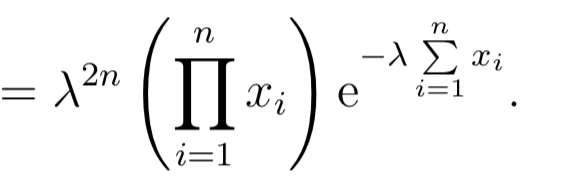
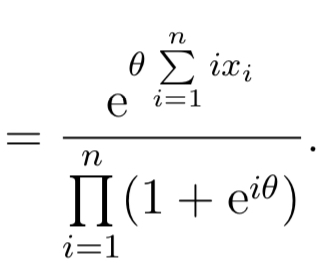
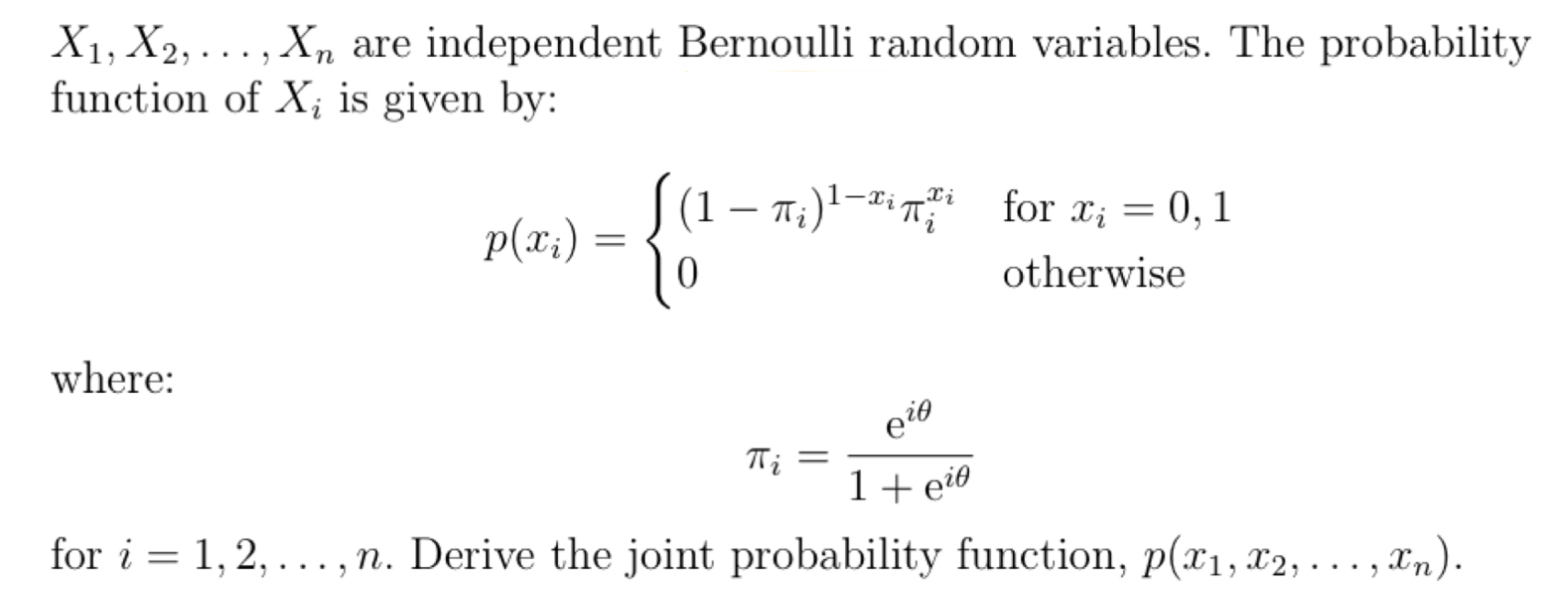
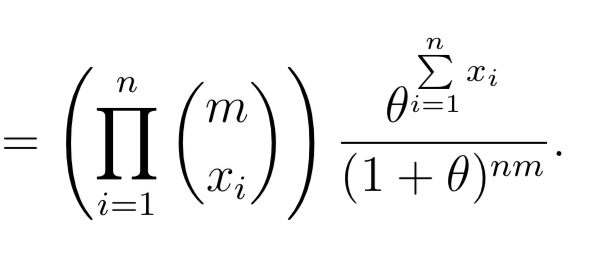
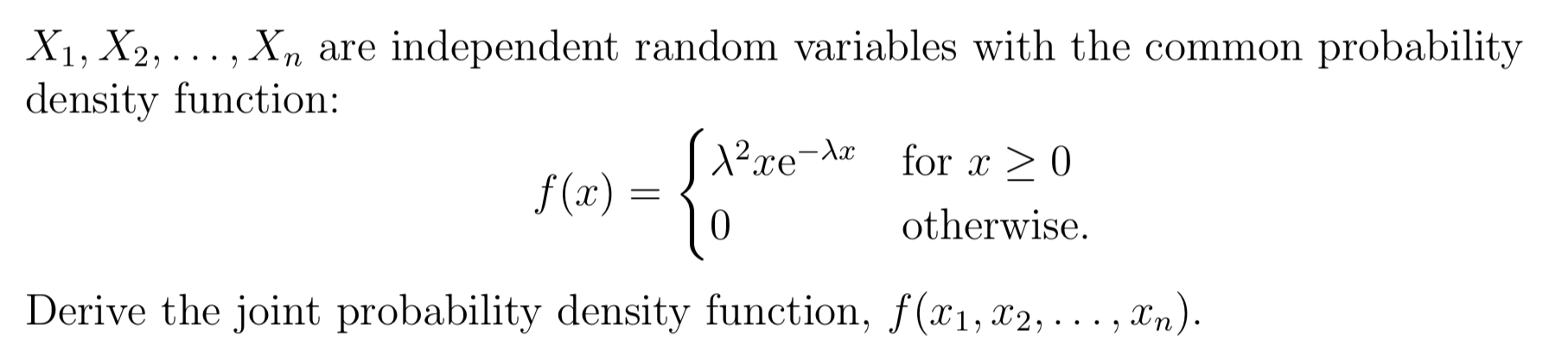
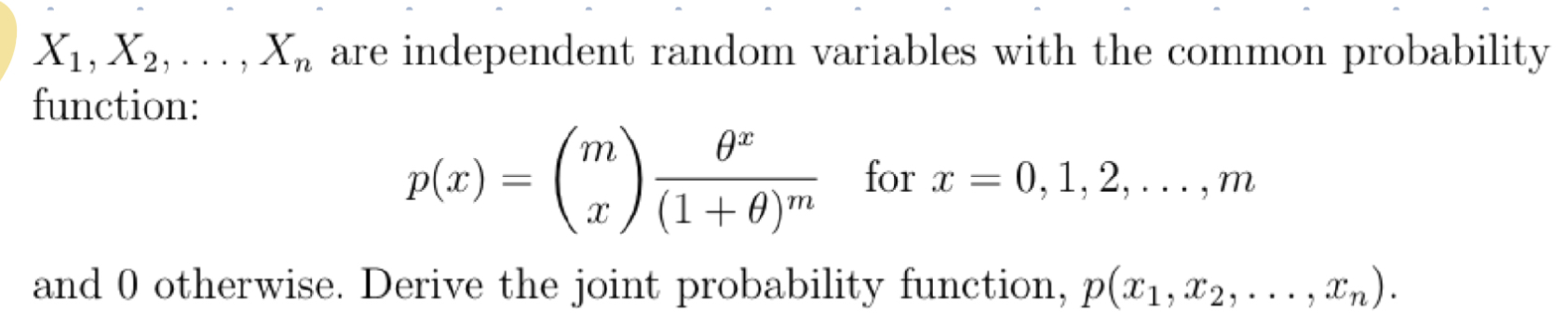
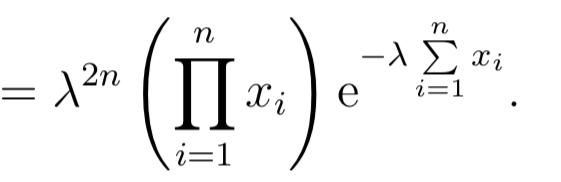
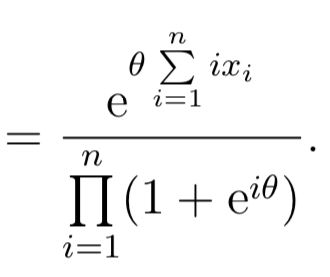
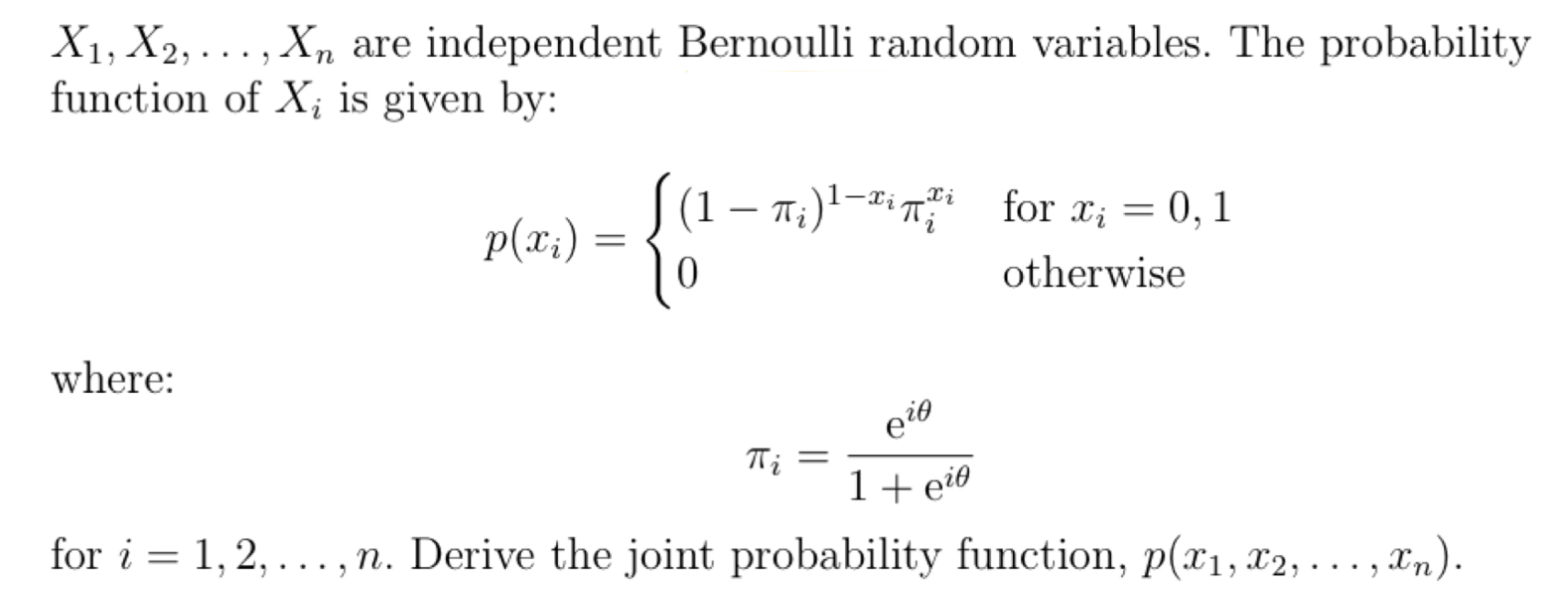
n n E m Oi=1 II 1 + 0) nm i=1X1, X2, . . . ,Xn are independent random variables With the common probability density function: VaseM3 for a" 2 0 m = { 0 otherwise. Derive the joint probability density function, f (11:1, x2, . . . ,xn). X 1, X 2,. . . ,X.n are independent random variables with the (10111111011 probability function: 711 9\": = f = .1.2,..., p(:1:) (3:) (1 + 9)?\" or :1: 0.4 , m and 0 otherwise. Derive the joint probability function, p(z1,m2, . . . ,SCn). n n 2n Exi e i=1 i=1\fX1, X2, . .., Xn are independent Bernoulli random variables. The probability function of X; is given by: (1 - 7Al-in; for xi = 0, 1 p(xi) = 0 otherwise where: Thi 1 + eie for i = 1, 2, ..., n. Derive the joint probability function, p(x1, x2, . . ., In)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


