Question: Ne saw in lecture the basic inductive proof structure for proving a itatement of the form nN,P(n) : - Prove P(0) and for all natural
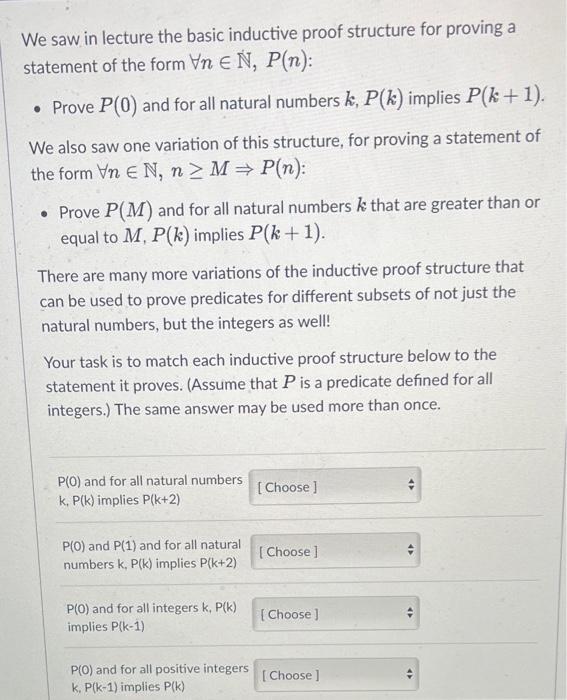
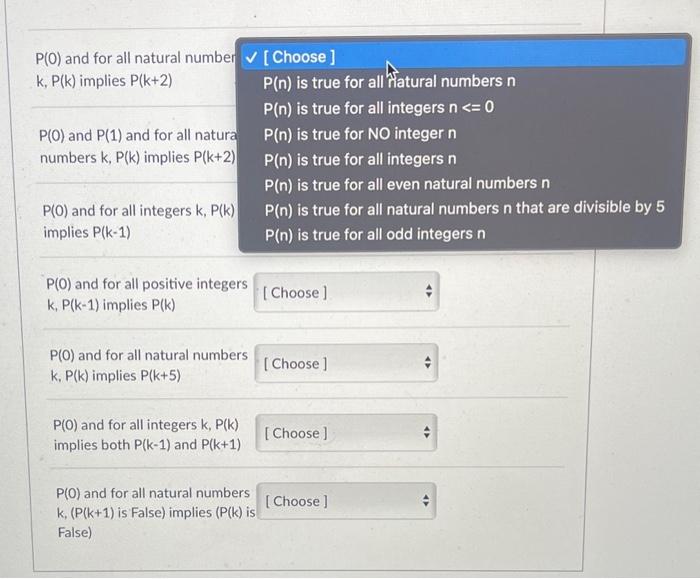
Ne saw in lecture the basic inductive proof structure for proving a itatement of the form nN,P(n) : - Prove P(0) and for all natural numbers k,P(k) implies P(k+1). We also saw one variation of this structure, for proving a statement of the form nN,nMP(n) : - Prove P(M) and for all natural numbers k that are greater than or equal to M,P(k) implies P(k+1). There are many more variations of the inductive proof structure that can be used to prove predicates for different subsets of not just the natural numbers, but the integers as well! Your task is to match each inductive proof structure below to the statement it proves. (Assume that P is a predicate defined for all integers.) The same answer may be used more than once. P(0) and for all natural numbers k, P(k) implies P(k+2) P(0) and P(1) and for all natural numbers k,P(k) implies P(k+2) P(0) and for all integers k,P(k) implies P(k1) P(0) and for all positive integers k. P(k1) implies P(k) P(0) and for all natural number k,P(k) implies P(k+2) P(0) and P(1) and for all natura numbers k,P(k) implies P(k+2) P(0) and for all integers k,P(k) implies P(k1) P(0) and for all positive integers k, P(k1) implies P(k) P(0) and for all natural numbers k. P(k) implies P(k+5) P(0) and for all integers k,P(k) implies both P(k1) and P(k+1) P(0) and for all natural numbers k, (P(k+1) is False) implies (P(k) is False)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


