Question: Need help finding the correct answer to the data table calculations, please answer the the questions in a charitable format table. This is all this
Need help finding the correct answer to the data table calculations, please answer the the questions in a charitable format table. This is all this information I have regarding to data table number 2.
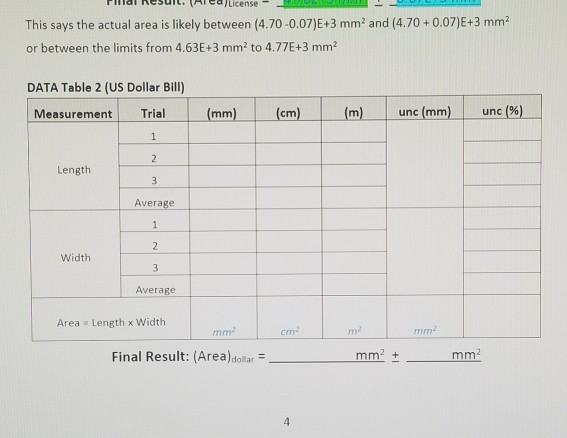
Here's the data I have regarding to the question.



I License This says the actual area is likely between (4.70 -0.07)E+3 mm and (4.70+ 0.07)E+3 mm or between the limits from 4.63E+3 mm2 to 4.77E+3 mm DATA Table 2 (US Dollar Bill) Measurement Trial (mm) (cm) (m) unc (mm) unc (%) 1 2 Length 3 Average 1 2 Width 3 Average Area Length x Width mm ! mm Final Result: (Area)dollar = mm+ mm 4 PHYS V01 Experiment Measurement EQUIPMENT NEEDED Metric ruler (or meter-stick) Dollar bill (good condition) 1 Sheet paper (printer or letter) 10 Pennies (post 1982 good condition) 1 1 1 Fine point Sharpie or ink pen Circular object (3 to 5 cm diameter) Circular object (6 to 9 cm diameter) 1 INTRODUCTION In this experiment you will measure the dimensions of several household items. Each measurement will be repeated multiple times following the accepted practices of data collection Measurements will be converted to other metric units and an average will be calculated for each. Absolute measurement uncertainty (unc) will be used to calculate relative or % uncertainty (%unc) for each measurement. The average measurement values will be used to calculate other derived values such as area, the constant pi (T), density of pennies, and their associated uncertainties. PROCEDURE-1 Determination of Rectangular Areas 1. Measure the length and width of the rectangular objects indicated in Tables 2 and 3 (in units of mm) with three trials for each measurement. a) Length: use top, middle, bottom. b) Width: use left, center, right. c) Record the results in the corresponding table. Note that these values will be similar for each measurement type and may even be the same. 2. Table 1 displays the results for a CA Driver License as an example object to show measurement data and the results of calculations to be performed later in the Analysis section. The absolute uncertainty (unc mm) has been assumed to be 0.5 mm for any measurements using the metric ruler. Consequently, all measurements must have the same number of decimal places and will end in either a 0 or 5 PROCEDURE-2 Determination of (pi) Select three round household objects covering a range of diameters. The first should be a dime (in good condition). The second should be between approximately 3 cm and 5 cm. The third between approximately 6 cm and 9 cm. It must be possible to measure both the diameter and circumference of each object. 2. Measure the diameter and circumference of the dime (already done) and the two circular objects that you have selected with three trials for each measurement, a) Diameter: take measurements through the center, but along three different angles such as 0". 60", and 120 for the different trials. 1. Page
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


