Question: Need help implementing list for memory management. Create own version of malloc() and coalesc() functions in C program: - program should accept size of heap
Need help implementing list for memory management. Create own version of malloc() and coalesc() functions in C program:
- program should accept size of heap to be simulated as a commandline argument.
- malloc() function should allocate memory within the heap for N bytes. The size of the node_t struct will be 16 bytes. The size of the header_t struct will be 4 bytes.
- coalesc() function should detect and remove adjacent free regions. For coalesce:
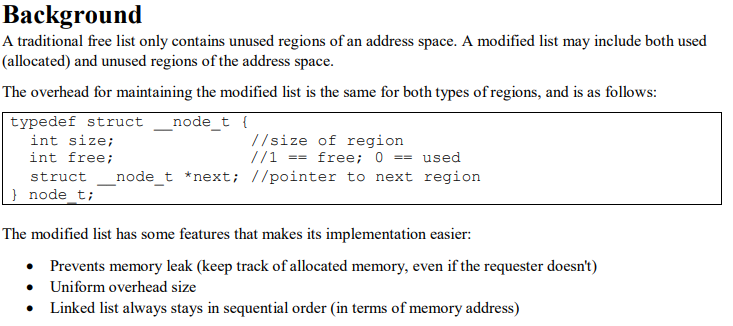
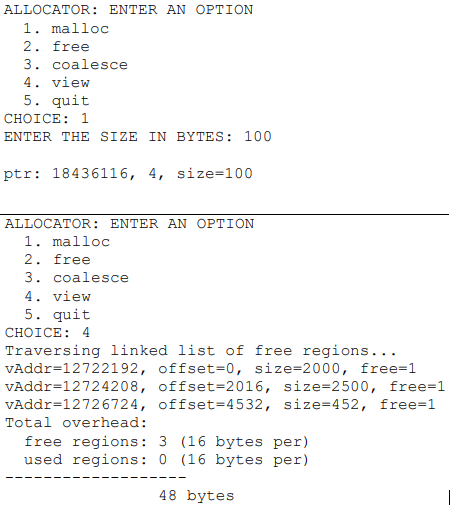
Background A traditional free list only contains unused regions of an address space. A modified list may include both used (allocated) and unused regions of the address space. The overhead for maintaining the modified list is the same for both types of regions, and is as follows: typedef structnodet { - - int size; int free; structnode_t *nexti //pointer to next region //size of regiorn //1 == free; 0 == used l nodet The modified list has some features that makes its implementation easier: Prevents memory leak (keep track of allocated memory, even ifthe requester doesn't) Uniform overhead size Linked list always stays in sequential order (in terms of memory address) ALLOCATOR: ENTER AN OPTION 1. malloc 2. Iree 3. coalesce 4. vieiw 5 quit CHOICE:1 ENTER THE SIZE IN BYTES: 100 ptr: 18436116, 4, size-100 ALLOCATOR: ENTER AN OPTION 1. malloc 2. Iree 3. Coalesce 4. view 5. quit CHOICE: 4 Traversing linked list of free regions. . . VAddr=12722192, offset=0, size=2000, free-1 VAddr-12724208, offset=2016, size=2500, free-1 vAddr-12726724, offset-4532, size-452, free-1 Total overhead: 3 (16 bytes per) free regions: used regions: 0 (16 bytes per) 48 bytes Background A traditional free list only contains unused regions of an address space. A modified list may include both used (allocated) and unused regions of the address space. The overhead for maintaining the modified list is the same for both types of regions, and is as follows: typedef structnodet { - - int size; int free; structnode_t *nexti //pointer to next region //size of regiorn //1 == free; 0 == used l nodet The modified list has some features that makes its implementation easier: Prevents memory leak (keep track of allocated memory, even ifthe requester doesn't) Uniform overhead size Linked list always stays in sequential order (in terms of memory address) ALLOCATOR: ENTER AN OPTION 1. malloc 2. Iree 3. coalesce 4. vieiw 5 quit CHOICE:1 ENTER THE SIZE IN BYTES: 100 ptr: 18436116, 4, size-100 ALLOCATOR: ENTER AN OPTION 1. malloc 2. Iree 3. Coalesce 4. view 5. quit CHOICE: 4 Traversing linked list of free regions. . . VAddr=12722192, offset=0, size=2000, free-1 VAddr-12724208, offset=2016, size=2500, free-1 vAddr-12726724, offset-4532, size-452, free-1 Total overhead: 3 (16 bytes per) free regions: used regions: 0 (16 bytes per) 48 bytes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


