Question: Need help please! class HashTable def init_(self, s-13): self.size = s self.slots ,. [None] * self.size self.data = [None] * self.size def put(self,key,data): hashvalue self.hashfunctionkey,len(self.slots))
Need help please!
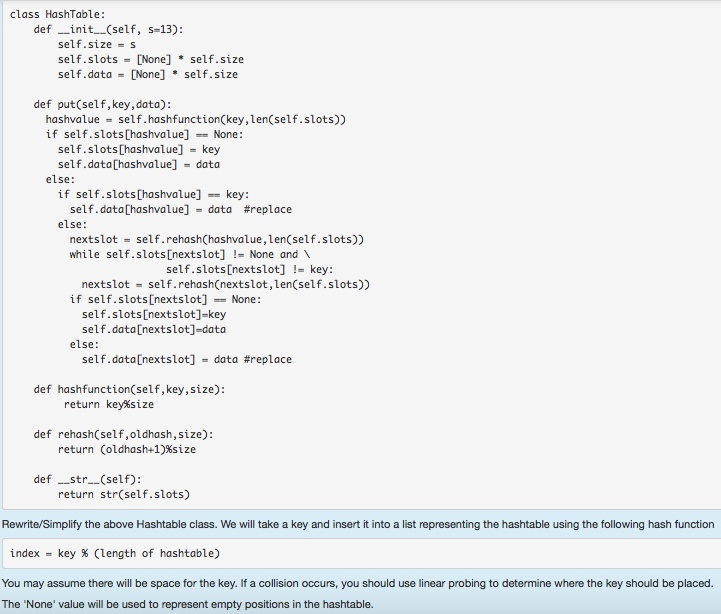
class HashTable def init_(self, s-13): self.size = s self.slots ,. [None] * self.size self.data = [None] * self.size def put(self,key,data): hashvalue self.hashfunctionkey,len(self.slots)) if self.slots [hashvalue]None: self.slots [hashvalue] key self.data[hashvalue] = data else: if self.slots [hashvalue]key: self.data[hashvalue]=data #replace else: nextslot self.rehash(hashvalue,len(self.slots)) while self.slots [nextslot]None and self.slots[nextslot]key: nextslot = self.rehash(nextslot , 1en(self.slots)) if self.slots [nextslot]None self.slots [nextslot]-key self.data[nextslot]-data else: se1f.data[nextslot]-data #replace def hashfunction self, key,size): key%size return def rehash(self,oldhash,size): return (oldhash+1)%size def str_(self) return str(self.slots) Rewrite/Simplify the above Hashtable class. We will take a key and insert it into a list representing the hashtable using the following hash function index key % (length of hashtable) You may assume there will be space for the key. If a collision occurs, you should use linear probing to determine where the key should be placed. The 'None' value will be used to represent empty positions in the hashtable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


