Question: Need help with a, b, c and d 2. Marine microbes have evolved mechanisms to utilize a range of oxidizing agents to extract the energy
Need help with a, b, c and d

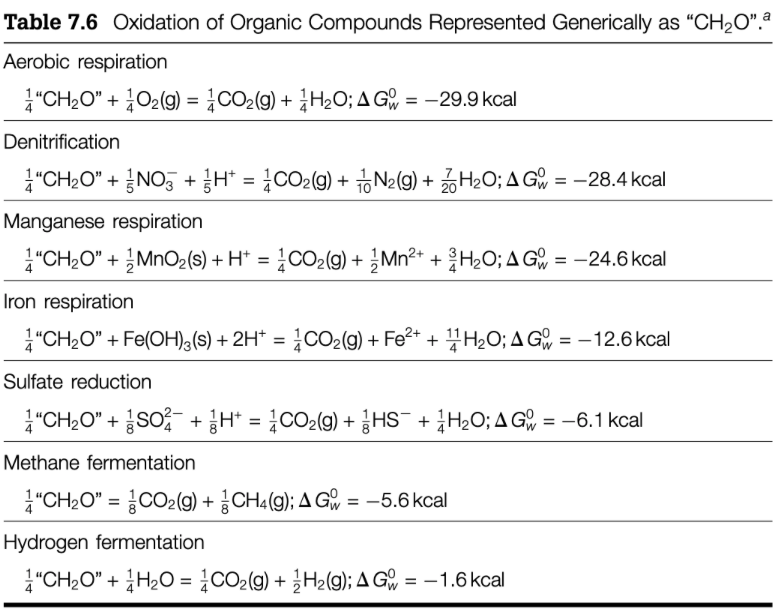
2. Marine microbes have evolved mechanisms to utilize a range of oxidizing agents to extract the energy stored in organic matter. For example: i. 14 CH2O + 1/5 NO3-+ 1/5 H+ = 14 CO2(g) + 1/10 N2(g)+ 7/20 H20; = ii. 44 CH20 + 1/8 SO42- + 1/8 H+ = 14 CO2(g) + 1/8 HS + 144 H20; iii. 14 CH2O + Fe(OH)3(s) + 2H+ = 14 CO2(g) + Fe2+ + 11/4 H20; Based on the data in Table 7.6 in Libes Ch. 7, for each of reactions i, ii, and iii, please indicate: (10 p) a) What is the free energy yield in seawater for the reaction? b) Is the reaction spontaneous? If so, why? c) In what order do you expect the reactions to occur in the marine environment and why? d) If aerobic oxidation of organic matter, denitrification and sulfate reduction were the only processes occurring in ocean sediments, what would a qualitative vertical sediment profile of O2, NO3-, SO42- and H2S look like? Please illustrate your answer in the space below: = = = Table 7.6 Oxidation of Organic Compounds Represented Generically as CH2O. a Aerobic respiration A "CH20" + 2O2(g) = CO2() + 3H2O; A G= 29.9 kcal Denitrification * CH20 + 2NO3 + 3H* = 4CO2(g) + + N2(g) + 2 H20; A G r = -28.4 kcal Manganese respiration CH2O" + 2 MnO2(s) + H+ = 4CO2(g) + 2 Mn2+ + H2O; A G = -24.6 kcal Iron respiration A "CH2O" + Fe(OH)3(s) + 2H+ = 4CO2(g) + Fe2+ + 4H2O; A G - (+ + = -12.6kcal Sulfate reduction A 4 "CH2O + SO2 + 2H+ = 4CO2(g) + 3HS- + 4H20; A G r = -6.1 kcal Methane fermentation A "CH20" = CO2(g) + CH4 (9); A G` = -5.6 kcal Hydrogen fermentation CH2O" + 4H2O = 4CO2(g) + 2 H2(g); A G = -1.6 kcal = = 2. Marine microbes have evolved mechanisms to utilize a range of oxidizing agents to extract the energy stored in organic matter. For example: i. 14 CH2O + 1/5 NO3-+ 1/5 H+ = 14 CO2(g) + 1/10 N2(g)+ 7/20 H20; = ii. 44 CH20 + 1/8 SO42- + 1/8 H+ = 14 CO2(g) + 1/8 HS + 144 H20; iii. 14 CH2O + Fe(OH)3(s) + 2H+ = 14 CO2(g) + Fe2+ + 11/4 H20; Based on the data in Table 7.6 in Libes Ch. 7, for each of reactions i, ii, and iii, please indicate: (10 p) a) What is the free energy yield in seawater for the reaction? b) Is the reaction spontaneous? If so, why? c) In what order do you expect the reactions to occur in the marine environment and why? d) If aerobic oxidation of organic matter, denitrification and sulfate reduction were the only processes occurring in ocean sediments, what would a qualitative vertical sediment profile of O2, NO3-, SO42- and H2S look like? Please illustrate your answer in the space below: = = = Table 7.6 Oxidation of Organic Compounds Represented Generically as CH2O. a Aerobic respiration A "CH20" + 2O2(g) = CO2() + 3H2O; A G= 29.9 kcal Denitrification * CH20 + 2NO3 + 3H* = 4CO2(g) + + N2(g) + 2 H20; A G r = -28.4 kcal Manganese respiration CH2O" + 2 MnO2(s) + H+ = 4CO2(g) + 2 Mn2+ + H2O; A G = -24.6 kcal Iron respiration A "CH2O" + Fe(OH)3(s) + 2H+ = 4CO2(g) + Fe2+ + 4H2O; A G - (+ + = -12.6kcal Sulfate reduction A 4 "CH2O + SO2 + 2H+ = 4CO2(g) + 3HS- + 4H20; A G r = -6.1 kcal Methane fermentation A "CH20" = CO2(g) + CH4 (9); A G` = -5.6 kcal Hydrogen fermentation CH2O" + 4H2O = 4CO2(g) + 2 H2(g); A G = -1.6 kcal = =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


