Question: Need Help with the following.. /////////////////////// origional question //////////////// ////////////////////////// Returned comments //////////////////////////////////// The program submitted compiles and runs, but there are issues in the
Need Help with the following..
/////////////////////// origional question ////////////////

////////////////////////// Returned comments ////////////////////////////////////
The program submitted compiles and runs, but there are issues in the code that need to be addressed before moving ahead.
In the Course superclass, remember that attributes should always be declared with the most restrictive access that will work. In a Java class, private should always be the preferred level of access for non-constant attributes. You should use protected in those rare cases where private attributes and public accessor methods won't work (which is not the case here). The Course class should have public accessors so that the subclasses inherit these and don't have to implement access to the attributes in the superclass, should they be needed.
You have overridden the toString() method as the instructions specify. Using the @Override annotation is a good choice.
The two subclasses don't have the additional (private) attributes specified in the instructions.
__________________________________________CODE___________________________________________________
////////////////////////////////////////////////////course.java ////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package assignment.pkg1;
public class Course { protected String code; protected int creditHours; protected String title; protected String ClassType;
public Course(String CourseCode, int CourseHours, String CourseTitle, String classType) { code = CourseCode; creditHours = CourseHours; title = CourseTitle; ClassType = classType; }
@Override public String toString() { return "Java class name = '" +ClassType +"' " + "Course Code = " + code; } }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// FlexPathCourse.java /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package assignment.pkg1;
public class FlexPathCourse extends Course {
public FlexPathCourse(String FlexpathCode, int FlexpathHours, String FlexpathTitle, String ClassType) { super(FlexpathCode, FlexpathHours, FlexpathTitle, ClassType ); }
@Override public String toString() { return "Java class name = '" +ClassType +"' " + "Course Code = " + code; } }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// GuidedPathCourse.java //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package assignment.pkg1;
public class GuidedPathCourse extends Course {
public GuidedPathCourse(String GuidedpathCode, int GuidedpathHours, String GuidedpathTitle, String ClassType) { super(GuidedpathCode, GuidedpathHours, GuidedpathTitle, ClassType); }
@Override public String toString() { return "Java class name = '" +ClassType +"' " + "Course Code = " + code; } }
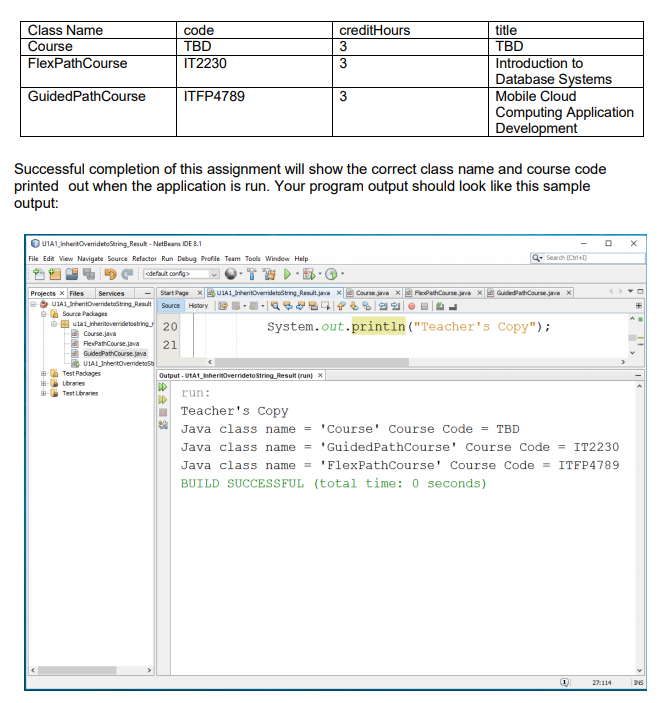
////////////////////////////////////////////// U1A1_InheritOverridetoString.java //////////////////////////////////////////////////
package assignment.pkg1;
public class U1A1_InheritOverridetoString {
public static void main(String[] args) { Course course = new Course("TBD", 3, "TBD","Course"); FlexPathCourse fp = new FlexPathCourse("IT2230", 3, "Introduction to Database Systems","FlexPathCourse"); GuidedPathCourse gp = new GuidedPathCourse("ITFP4789", 3, "Mobile Cloud Computing Application Development","GuidedPathCourse");
System.out.println(course); System.out.println(fp); System.out.println(gp);
}
}
Extending Java Classes and Overriding Their Methods In this assessment, you will design and code a Java console application that defines a class extends it into two other classes, overrides the toString) for all three classes, instantiates the classes into three objects, invokes the toString) on these objects, and prints out the return value of each toString) invocation. You can use either the Toolwire environment or your local Java development environment to complete this assignment. The requirements of this application are as follows. The application is to define a Java class called Course. The Course class has the following members 1. code attribute a string field to store the course code (e.g. IT4789) 2. creditHours attribute - an int field to store the credit hours of the course (e.g. 3) 3. title attribute a string field to store the title of the course (e.g. Mobile Cloud Computing Application Development) Parameterized constructor with the three parameters of code, creditHours, and title. The constructor simply assigns the received values to their corresponding attributes An overridden toString) method that returns the name of the Java class (i.e. Course) and the course code assigned to the class object 4. 5. The application need to extend the Course class into two other Java classes named 1. FlexPathCourse 2. GuidedPathCourse The FlexPathCourse class adds the following members 1. optionalResources attribute - a string field for the optional resources for a flexpath course Parameterized constructor with the three parameters of code, creditHours, and title The constructor simply assigns the received values to their corresponding attributes 2. 3. An overridden toString) method that returns the name of the Java class (i.e. FlexPathCourse) and the course code assigned to the class object The GuidedPathCourse class adds the following members 1. duration attribute an int field for the duration of a guidedpath course 2. requiredResources attribute - a string field for the required resources for a 3. Parameterized constructor with the three parameters of code, creditHours, and title 4. An overridden toString) method that returns the name of the Java class guidedpath course The constructor simply assigns the received values to their corresponding attributes (i.e. GuidedPathCourse) and the course code assigned to the class object The application will then instantiates three objects from the Course, FlexPathCourse, and GuidedPathCourse and invokes their corresponding toString) methods Use these attribute values when instantiating the three classes to test your application
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


