Question: Need help with this Implementing a Loadable Kernel Module Summary: In this homework, you will be implement a loadable kernel module that uses Linux data

Need help with this
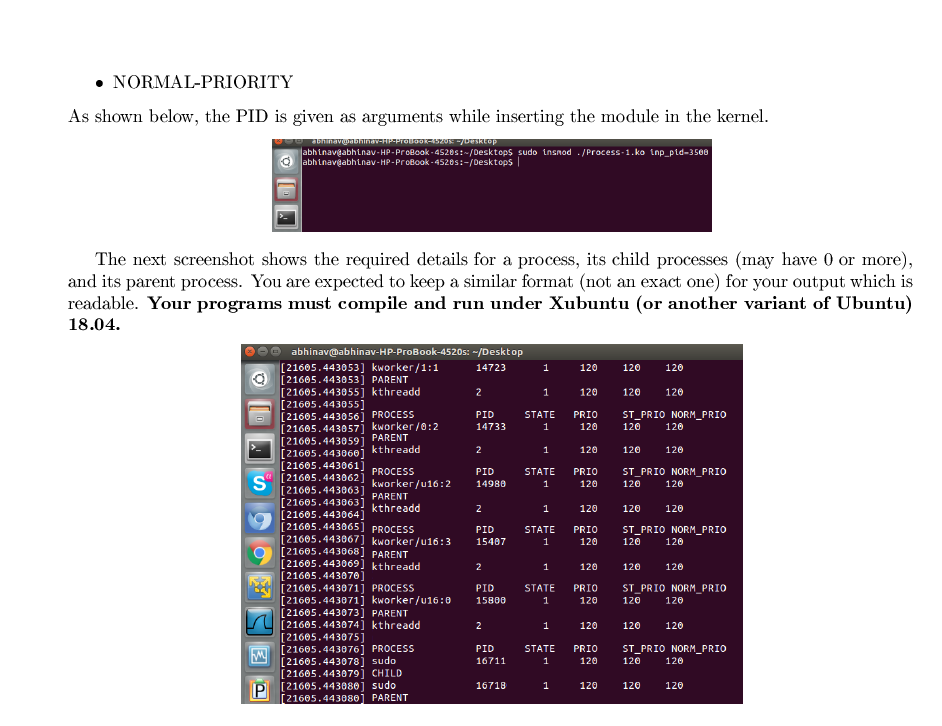
Implementing a Loadable Kernel Module Summary: In this homework, you will be implement a loadable kernel module that uses Linux data structures to display details about the processes executing in the kernel. 1 Background The kernel is a program that is the core of a computer's operating system, with complete control over everything in the system. It is the first program loaded on start-up. It performs tasks such as running processes, handling interrupts and all other handling that happens behind the scenes in kernel space whereas everything user does is executed in user-space. This separation prevents user data and kernel data from interfering with each other and causing instability and slowness. Kernel modules are pieces of code which provide functionality to the kernel. The word "Loadable" is prefixed to kernel module to show that it eases the process of integrating the module with the kernel. Generally, if any functionality is to be provided in the kernel, it has to incorporated by compiling the kernel with the proposed changes. Loadable Kernel Modules (LKM) ease that process by providing the facility to integrate itself within the kernel instead of requiring kernel re-compilation. For information on creating LKMs, see your textbook (Operating System Concepts 9th edition) page 96. You will need to use a so-called "makefile" to manage the compilation of your module. It will not be possible to use NetBeans or CLion to develop your code. The best way to start is with the sample LKM provided on the textbook's website In this assignment you will write a LKM for the Linux kernel that displays the certain details of the processes (along with its parent and child) executing in the kernel. As an important step to implementing the program, you should review the section on include files to get an idea of what functionality is available. From there, you may choose to outline your program in pseudocode, and then convert it into actual source code, while reading the documentation for any functions you used. Expect that a significant part of your time on this assignment will be spent reading researching understanding LKM documentation and reviewing kernel source code files (linux sched.h, and linux/list.h). The source code should be relatively short. For kernel source code, visit www.kernel.org/ Any lines numbers mentioned in this document refer to Linux 4.9.6; please reference that version as well. This document is separated into five sections: Background Reanirements. Makefiles, Include Files, and Submissipn. You have almost finished reading the I http://www.kernel.org/ Requirements, we will discuss what is expected of you in this homework. In Inciuue ries, we wiscuss several header files that include functionality related to file and directory manipulation. Lastly, Submission discusses how your source code should be submitted on Canvas. 2 Requirements (36 points total] In this assignment you will write a LKM for the Linux kernel that displays the following details for all the processes whose PID is greater than an integer given by the user as a module parameter: [26 points] PROCESS NAME PID STATE PRIORITY STATIC-PRIORITY 1 . NORMAL-PRIORITY As shown below, the PID is given as arguments while inserting the module in the kernel. wanaumann-HIPPOUDRISUS - USKLOP abhinaveabhinav-HP ProBook 4520:-/Desktops sudo insmod. /Process-1.ko inp_pid-3508 abhinaveabhinav-HP-Probook - 4520s:-/Desktops | 0 0 The next screenshot shows the required details for a process, its child processes (may have 0 or more), and its parent process. You are expected to keep a similar format (not an exact one) for your output which is readable. Your programs must compile and run under Xubuntu (or another variant of Ubuntu) 18.04. abhinav@abhinav-HP-ProBook 4520s: - /Desktop [21605.443053] kworker/1:1 14723 1 120 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 PID 14733 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 S PID 14986 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 N 1 120 120 120 [21605.443053] PARENT [21605.443055] kthreadd [21605.443855] [21605.443056 PROCESS [21605.443657 kworker/0:2 [21605.443859] PARENT [21605.443060] kthreadd [21605.443061] PROCESS [21605.443062] kworker/u16:2 [21605.443063] PARENT [21605.443063] [21605.443064] kthreadd [21665.443065] PROCESS [21605.443067] kworker/u16:3 [21605.443068] PARENT [21605.443069] kthreadd [21605.443070] [21605.443071] PROCESS [21605.443071] kworker/u16:0 [21605.443073] PARENT [21605.443074] kthreadd [21605.443075) [21605.443076] PROCESS [21605.443078 sudo [21605.443679] CHILD [21605.443880 sudo [21605.443880 PARENT PID 15467 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 N 1 120 120 120 PRIO PID 15800 STATE 1 STPRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 w PID 16711 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 16718 1 120 120 120 P Implementing a Loadable Kernel Module Summary: In this homework, you will be implement a loadable kernel module that uses Linux data structures to display details about the processes executing in the kernel. 1 Background The kernel is a program that is the core of a computer's operating system, with complete control over everything in the system. It is the first program loaded on start-up. It performs tasks such as running processes, handling interrupts and all other handling that happens behind the scenes in kernel space whereas everything user does is executed in user-space. This separation prevents user data and kernel data from interfering with each other and causing instability and slowness. Kernel modules are pieces of code which provide functionality to the kernel. The word "Loadable" is prefixed to kernel module to show that it eases the process of integrating the module with the kernel. Generally, if any functionality is to be provided in the kernel, it has to incorporated by compiling the kernel with the proposed changes. Loadable Kernel Modules (LKM) ease that process by providing the facility to integrate itself within the kernel instead of requiring kernel re-compilation. For information on creating LKMs, see your textbook (Operating System Concepts 9th edition) page 96. You will need to use a so-called "makefile" to manage the compilation of your module. It will not be possible to use NetBeans or CLion to develop your code. The best way to start is with the sample LKM provided on the textbook's website In this assignment you will write a LKM for the Linux kernel that displays the certain details of the processes (along with its parent and child) executing in the kernel. As an important step to implementing the program, you should review the section on include files to get an idea of what functionality is available. From there, you may choose to outline your program in pseudocode, and then convert it into actual source code, while reading the documentation for any functions you used. Expect that a significant part of your time on this assignment will be spent reading researching understanding LKM documentation and reviewing kernel source code files (linux sched.h, and linux/list.h). The source code should be relatively short. For kernel source code, visit www.kernel.org/ Any lines numbers mentioned in this document refer to Linux 4.9.6; please reference that version as well. This document is separated into five sections: Background Reanirements. Makefiles, Include Files, and Submissipn. You have almost finished reading the I http://www.kernel.org/ Requirements, we will discuss what is expected of you in this homework. In Inciuue ries, we wiscuss several header files that include functionality related to file and directory manipulation. Lastly, Submission discusses how your source code should be submitted on Canvas. 2 Requirements (36 points total] In this assignment you will write a LKM for the Linux kernel that displays the following details for all the processes whose PID is greater than an integer given by the user as a module parameter: [26 points] PROCESS NAME PID STATE PRIORITY STATIC-PRIORITY 1 . NORMAL-PRIORITY As shown below, the PID is given as arguments while inserting the module in the kernel. wanaumann-HIPPOUDRISUS - USKLOP abhinaveabhinav-HP ProBook 4520:-/Desktops sudo insmod. /Process-1.ko inp_pid-3508 abhinaveabhinav-HP-Probook - 4520s:-/Desktops | 0 0 The next screenshot shows the required details for a process, its child processes (may have 0 or more), and its parent process. You are expected to keep a similar format (not an exact one) for your output which is readable. Your programs must compile and run under Xubuntu (or another variant of Ubuntu) 18.04. abhinav@abhinav-HP-ProBook 4520s: - /Desktop [21605.443053] kworker/1:1 14723 1 120 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 PID 14733 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 S PID 14986 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 N 1 120 120 120 [21605.443053] PARENT [21605.443055] kthreadd [21605.443855] [21605.443056 PROCESS [21605.443657 kworker/0:2 [21605.443859] PARENT [21605.443060] kthreadd [21605.443061] PROCESS [21605.443062] kworker/u16:2 [21605.443063] PARENT [21605.443063] [21605.443064] kthreadd [21665.443065] PROCESS [21605.443067] kworker/u16:3 [21605.443068] PARENT [21605.443069] kthreadd [21605.443070] [21605.443071] PROCESS [21605.443071] kworker/u16:0 [21605.443073] PARENT [21605.443074] kthreadd [21605.443075) [21605.443076] PROCESS [21605.443078 sudo [21605.443679] CHILD [21605.443880 sudo [21605.443880 PARENT PID 15467 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 N 1 120 120 120 PRIO PID 15800 STATE 1 STPRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 120 2 1 120 120 120 w PID 16711 STATE 1 PRIO 120 ST_PRIO NORM_PRIO 120 120 16718 1 120 120 120 P
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


