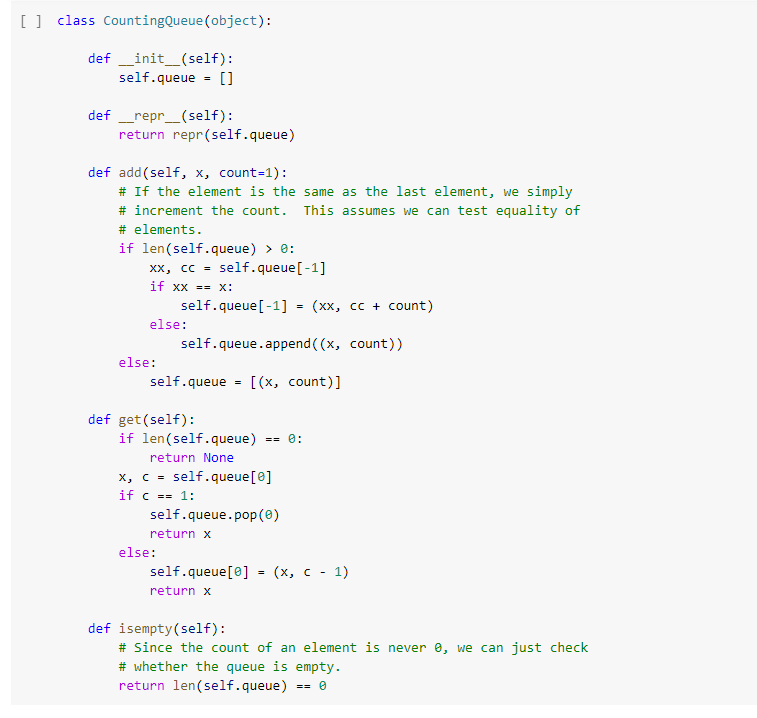
Question: Need some help with Python problem, fix bugs(in picture 2, the function countinuequeue_ier): class CountingQueue(object): def __init__(self): self.queue = [] def __repr__(self): return repr(self.queue) def
Need some help with Python problem, fix bugs(in picture 2, the function countinuequeue_ier):
class CountingQueue(object): def __init__(self): self.queue = [] def __repr__(self): return repr(self.queue) def add(self, x, count=1): # If the element is the same as the last element, we simply # increment the count. This assumes we can test equality of # elements. if len(self.queue) > 0: xx, cc = self.queue[-1] if xx == x: self.queue[-1] = (xx, cc + count) else: self.queue.append((x, count)) else: self.queue = [(x, count)] def get(self): if len(self.queue) == 0: return None x, c = self.queue[0] if c == 1: self.queue.pop(0) return x else: self.queue[0] = (x, c - 1) return x def isempty(self): # Since the count of an element is never 0, we can just check # whether the queue is empty. return len(self.queue) == 0
def countingqueue_iter(self):
"""Iterates through all the elements of the queue,
without removing them."""
for i in range(len(self.queue)):
yield self.queue[i]
# This is a way to add a method to a class once the class
# has already been defined.
CountingQueue.__iter__ = countingqueue_iter
CountingQueue.__len__=countingqueue_len
Testing:
try: from nose.tools import assert_equal, assert_almost_equal from nose.tools import assert_true, assert_false from nose.tools import assert_not_equal, assert_greater_equal except: !pip install nose from nose.tools import assert_equal, assert_almost_equal from nose.tools import assert_true, assert_false from nose.tools import assert_not_equal, assert_greater_equal
q = CountingQueue() for i in range(10): q.add('a') q.add('b') for i in range(3): q.add('c', count=2) l1 = [x for x in q] l2 = [] while not q.isempty(): l2.append(q.get()) assert_equal(l1, l2)
![countinuequeue_ier): class CountingQueue(object): def __init__(self): self.queue = [] def __repr__(self): return repr(self.queue)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f0320ce2b67_48466f0320c78bf0.jpg)
During lecture, we implemented an iterator for the Queue class using the generator technique. For this exercise, you will use that same technique to implement an iterator for CountingQueue. Note: this can be done elegantly in 3 lines of code. I def countingqueue_iter(self): *"Iterates through all the elements of the queue, without removing them. *** for i in range(len(self.queue)): yield self.queue[i] # This is a way to add a method to a class once the class # has already been defined. CountingQueue. _iter__ = countingqueue_iter CountingQueue. _len_=countingqueue_len All Tests for 'CountingQueue. _iter_ 9 = CountingQueue () for i in range(10): 4.add('a') 9.add('') 4.add('c', count=2) 11 = (x for x in 4] 12 = [] while not q. isempty(): 12.append(9.get() assert_equal(11, 12) AssertionError Traceback (most recent call last)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


