Question: Neutral Geometry: Which theorem, postulate, or definition describes each statement below? (This is a university-level advanced geometry proofing course that uses Gerard A Venema Foundations
Neutral Geometry: Which theorem, postulate, or definition describes each statement below? (This is a university-level advanced geometry proofing course that uses Gerard A Venema Foundations of Geometry 2nd Edition)
- This theorem is provable in neutral geometry, but its converse relies on the EPP. (more than one answer may be possible here)
- A statement equivalent to the EPP that allows for the existence of rectangles.
- Establishes that the angle sum of any triangle is no larger than 180 degrees.
- Establishes that the Elliptic Parallel Postulate is false in any model for neutral geometry.
- Tells us that in every triangle it is possible to drop a perpendicular from some vertex to the interior of the opposite side.
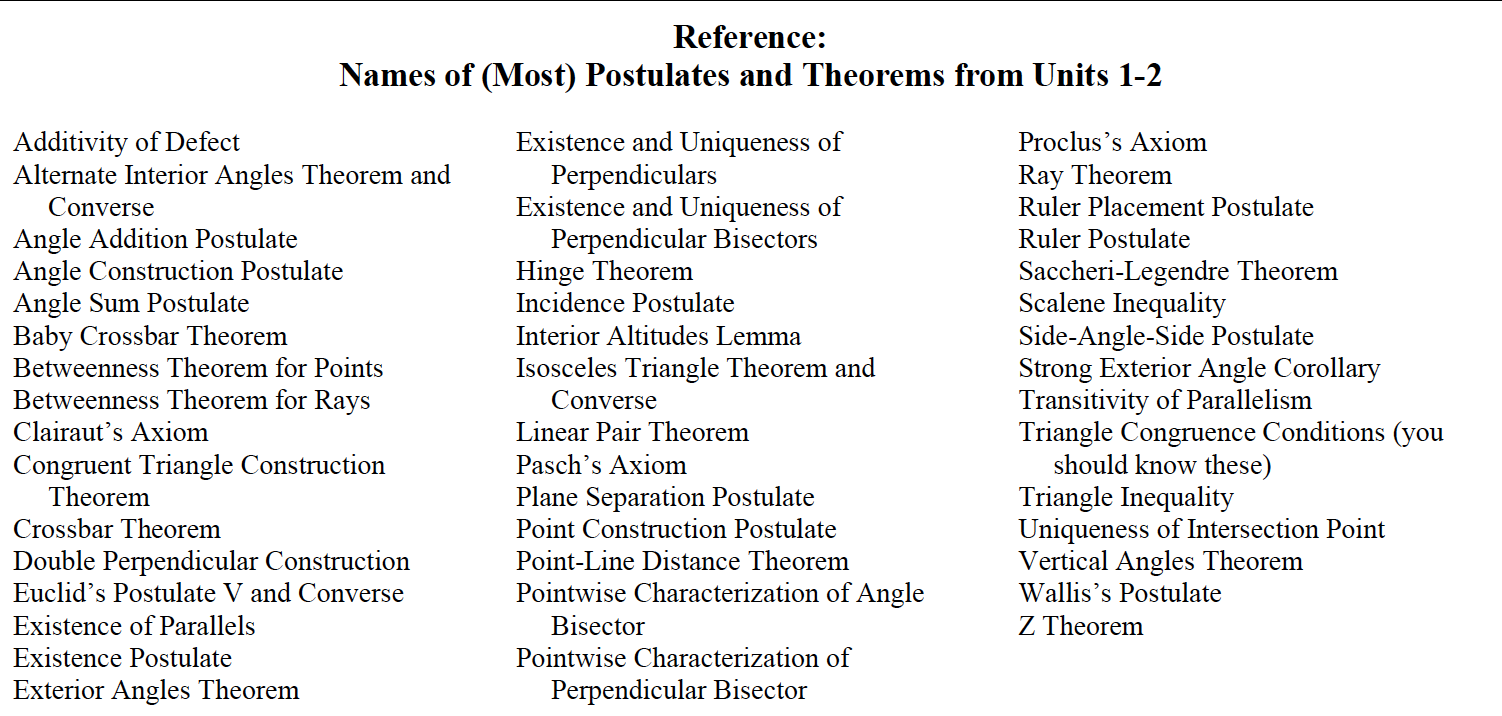
Reference: Names of (Most) Postulates and Theorems from Units 1-2 Additivity of Defect Alternate Interior Angles Theorem and Converse Angle Addition Postulate Angle Construction Postulate Angle Sum Postulate Baby Crossbar Theorem Betweenness Theorem for Points Betweenness Theorem for Rays Clairaut's Axiom Congruent Triangle Construction Theorem Crossbar Theorem Double Perpendicular Construction Euclid's Postulate V and Converse Existence of Parallels Existence Postulate Exterior Angles Theorem Existence and Uniqueness of Perpendiculars Existence and Uniqueness of Perpendicular Bisectors Hinge Theorem Incidence Postulate Interior Altitudes Lemma Isosceles Triangle Theorem and Converse Linear Pair Theorem Pasch's Axiom Plane Separation Postulate Point Construction Postulate Point-Line Distance Theorem Pointwise Characterization of Angle Bisector Pointwise Characterization of Perpendicular Bisector Proclus's Axiom Ray Theorem Ruler Placement Postulate Ruler Postulate Saccheri-Legendre Theorem Scalene Inequality Side-Angle-Side Postulate Strong Exterior Angle Corollary Transitivity of Parallelism Triangle Congruence Conditions (you should know these) Triangle Inequality Uniqueness of Intersection Point Vertical Angles Theorem Wallis's Postulate Z Theorem Reference: Names of (Most) Postulates and Theorems from Units 1-2 Additivity of Defect Alternate Interior Angles Theorem and Converse Angle Addition Postulate Angle Construction Postulate Angle Sum Postulate Baby Crossbar Theorem Betweenness Theorem for Points Betweenness Theorem for Rays Clairaut's Axiom Congruent Triangle Construction Theorem Crossbar Theorem Double Perpendicular Construction Euclid's Postulate V and Converse Existence of Parallels Existence Postulate Exterior Angles Theorem Existence and Uniqueness of Perpendiculars Existence and Uniqueness of Perpendicular Bisectors Hinge Theorem Incidence Postulate Interior Altitudes Lemma Isosceles Triangle Theorem and Converse Linear Pair Theorem Pasch's Axiom Plane Separation Postulate Point Construction Postulate Point-Line Distance Theorem Pointwise Characterization of Angle Bisector Pointwise Characterization of Perpendicular Bisector Proclus's Axiom Ray Theorem Ruler Placement Postulate Ruler Postulate Saccheri-Legendre Theorem Scalene Inequality Side-Angle-Side Postulate Strong Exterior Angle Corollary Transitivity of Parallelism Triangle Congruence Conditions (you should know these) Triangle Inequality Uniqueness of Intersection Point Vertical Angles Theorem Wallis's Postulate Z Theorem
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


