Question: Non-probability sampling: a. includes stratified sampling. b. denies the researcher the use of statistical theory to estimate the probability of correct inferences. c. always produces
Non-probability sampling:
a. includes stratified sampling.
b. denies the researcher the use of statistical theory to estimate the probability of correct inferences.
c. always produces samples that possess distorted characteristics relative to the population.
d. is always less desirable than probability sampling.
e. requires the manipulation of sampling frames.
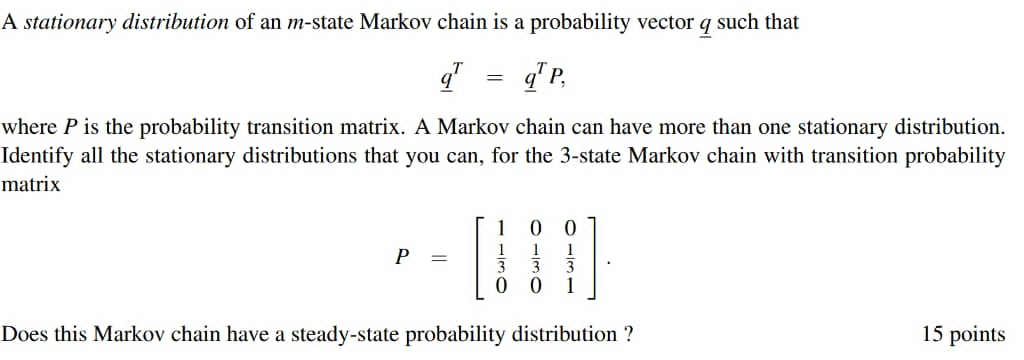
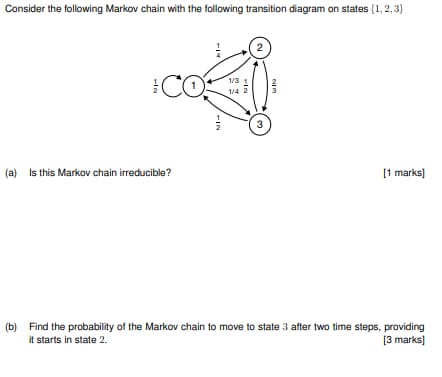
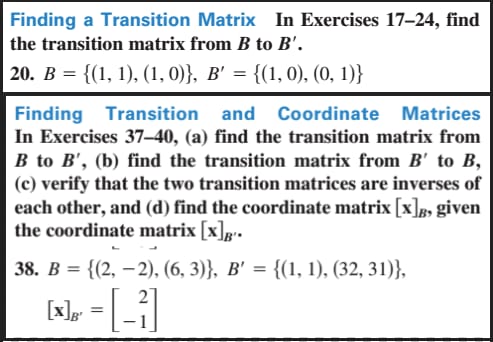
A stationary distribution of an m-state Markov chain is a probability vector q such that = q P, where P is the probability transition matrix. A Markov chain can have more than one stationary distribution. Identify all the stationary distributions that you can, for the 3-state Markov chain with transition probability matrix O P Does this Markov chain have a steady-state probability distribution ? 15 pointsConsider the following Markov chain with the following transition diagram on states {1, 2,3] al- 2 CO 1/3 NI - 3 (a) Is this Markov chain irreducible? [1 marks] (b) Find the probability of the Markov chain to move to state 3 after two time steps, providing it starts in state 2. [3 marks]Finding a Transition Matrix In Exercises 17-24, find the transition matrix from B to B'. 20. B = {(1, 1), (1, 0)}, B' = {(1, 0), (0, 1)} Finding Transition and Coordinate Matrices In Exercises 37-40, (a) find the transition matrix from B to B', (b) find the transition matrix from B' to B, (c) verify that the two transition matrices are inverses of each other, and (d) find the coordinate matrix [x]g, given the coordinate matrix [x]g- 38. B = {(2, -2), (6, 3)}, B' = {(1, 1), (32, 31)}, 2 [x ]B' =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


