Question: NOTE: NEED CODE USING NUMPY Referring to Example 6.6, simulate and plot the bivariate normal distribution with the shown parameters using the Cholesky factorization for
NOTE: NEED CODE USING NUMPY
Referring to Example 6.6, simulate and plot the bivariate normal distribution with the shown parameters using the Cholesky factorization for the simulation.
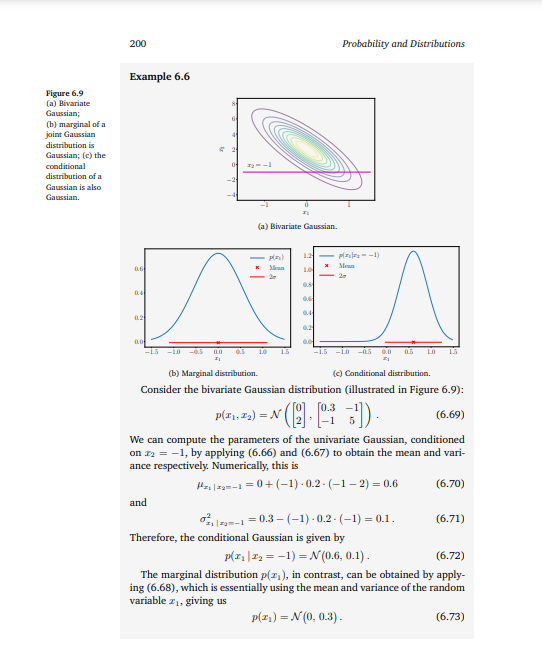
200 Probability and Distributions Example 6.6 Figure 6.9 (a) Bivariate Gaussian; (b) marginal of a jaint Gaussian distribution is Gaussian; (c) the conditional distribution of a Gaussian is also Gaussian. (b) Marginal distribution. (c) Conditional distribution. Consider the bivariate Gaussian distribution (illustrated in Figure 6.9): p(x1,x2)=N([02],[0.3115]). We can compute the parameters of the univariate Gaussian, conditioned on x2=1, by applying (6.66) and (6.67) to obtain the mean and variance respectively. Numerically, this is x1x2=1=0+(1)0.2(12)=0.6 and x1x2=12=0.3(1)0.2(1)=0.1. Therefore, the conditional Gaussian is given by p(x1x2=1)=N(0.6,0.1). The marginal distribution p(x1), in contrast, can be obtained by applying (6.68), which is essentially using the mean and variance of the random variable x1, giving us p(x1)=N(0,0.3)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


