Question: Objective: Experiment with Lists, Stacks, and Queues: Simulate an OS task manager Assignment: Using the startup code, implement the following: 1-Create List L1 of 10
Objective: Experiment with Lists, Stacks, and Queues:
Simulate an OS task manager
Assignment:
Using the startup code, implement the following:
1-Create List L1 of 10 elements (task IDs), e.g. L1 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10;
2-Insert a new list element in between (at every other element), such as: 1,100, 2,200, 3,300, 4,400, ... 10,1000;
Simulate a new CPU core assignment:
3-Create another List L2, and extract the newly inserted elements into this new list L2
i.e. L1 should go back to the original list: L1 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
L2 should be: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000
Start executing:
4-Create a Queue Q1 by extracting L1, and inserting L2 elements: i.e. Q should start with: 1,2,3, ... 10, and (10, 20 ... 100) will be inserted
Q1=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000
Label tasks as finished with the possibility of revisiting a task, such as:
5-Create a Stack S1 which by deleting the elements of Q1 and inserting them in L1
6-Pop out all elements of the Stack, i.e. should end up with an empty stack
Extra credit: Simulate a re-executed task, i.e. Pop out a task out of the Stack and reinsert, this simulate a failed task.
7-Verify the functionality and capture the results in a report form.
#include "List.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template typename Object>
class Stack
{
public:
bool isEmpty() const
{
return theList.empty();
}
const Object& top() const
{
return theList.front();
}
void push(const Object& x)
{
theList.push_front(x);
}
void pop(Object& x)
{
x = theList.front(); theList.pop_front();
}
private:
List
};
template typename Object>
class Queue
{
public:
bool isEmpty() const
{
return theList.empty();
}
const Object& getFront() const
{
return theList.front();
}
void enqueue(const Object& x)
{
theList.push_back(x);
}
void dequeue(Object& x)
{
x = theList.front(); theList.pop_front();
}
private:
List
};
int main()
{
int i;
const int N = 10;
Listint> L1;
Stackint> S1;
Queueint> Q1;
Listint>::iterator node; //Variable to keep track of the position as we traverse
// List Section example:
//Q1: Create List L1 of 10 elements, e.g. L1 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10;
// create the list array as a starting point:
for (i = N; i > 0; --i)
{
L1.push_front(i);
}
// show L1 with an iterator
cout
for (auto it = L1.begin(); it != L1.end(); ++it)
{
cout
}
// Stack Section example:
//
// Stack to be created per the above assignment requirment
cout
for (i = N - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
S1.push(i);
cout
}
while (!S1.isEmpty())
{
cout
S1.pop(i);
}
// Queue section, to be created per the above assignment requirment
//
//
return 0;
}
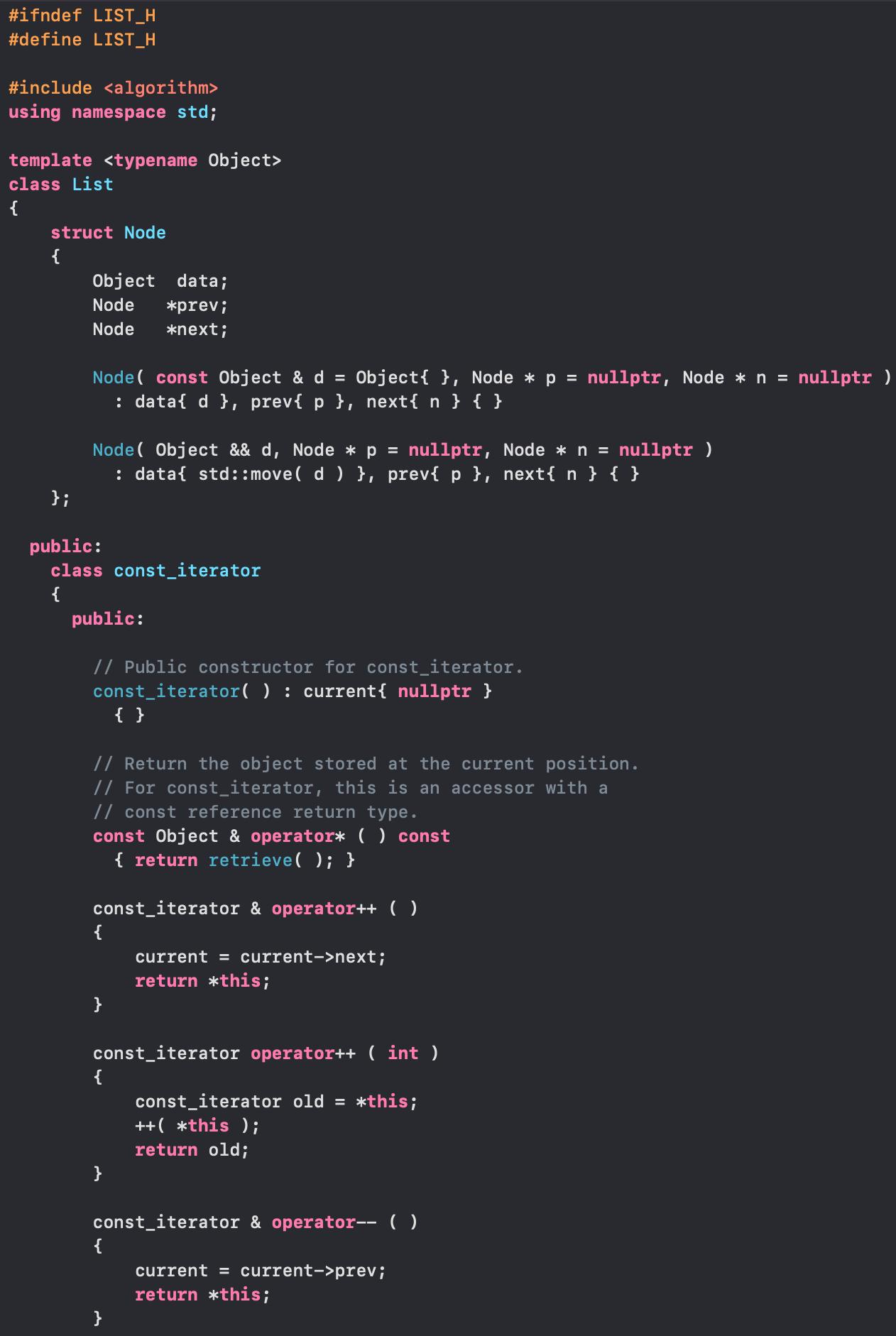
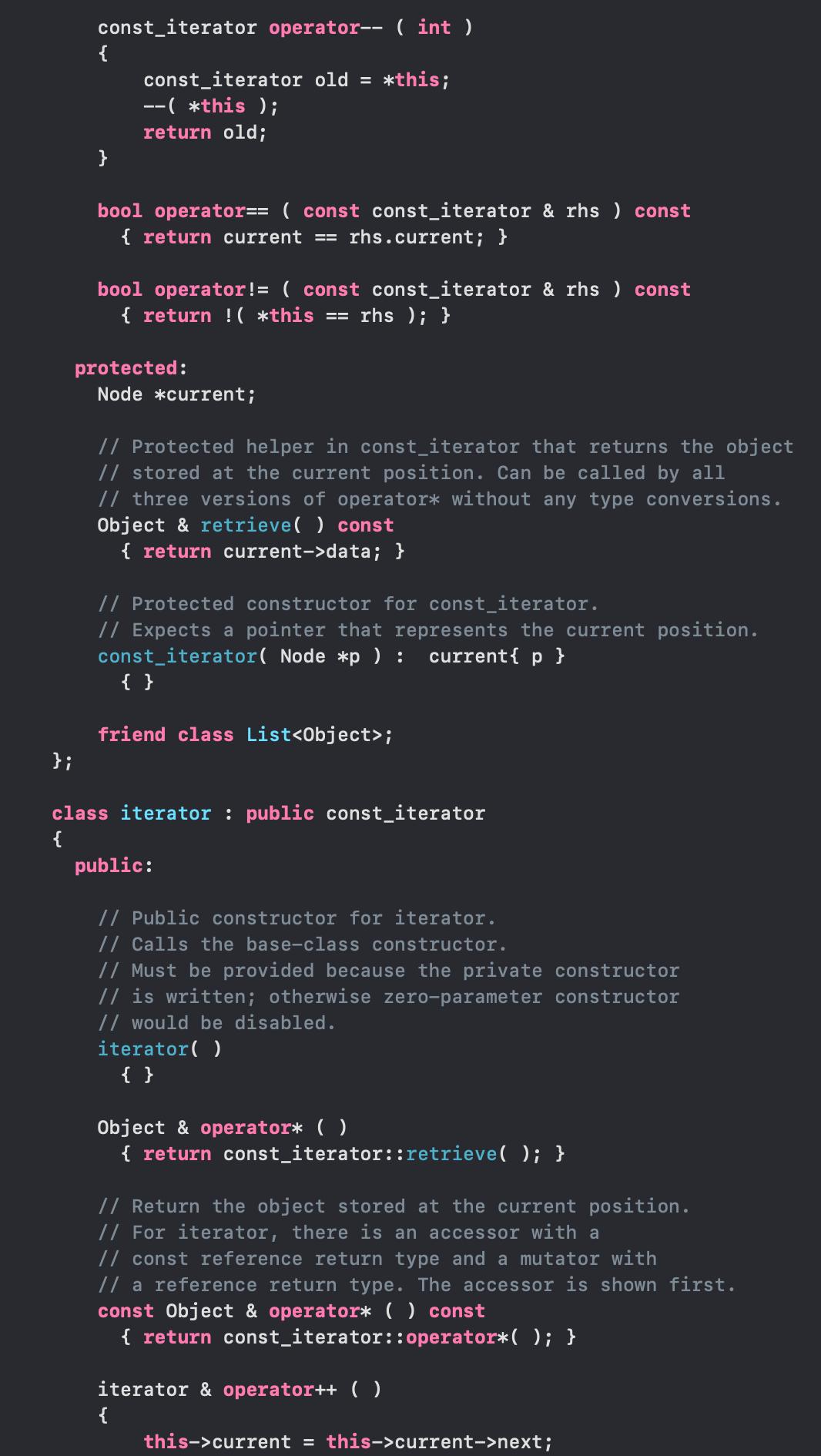
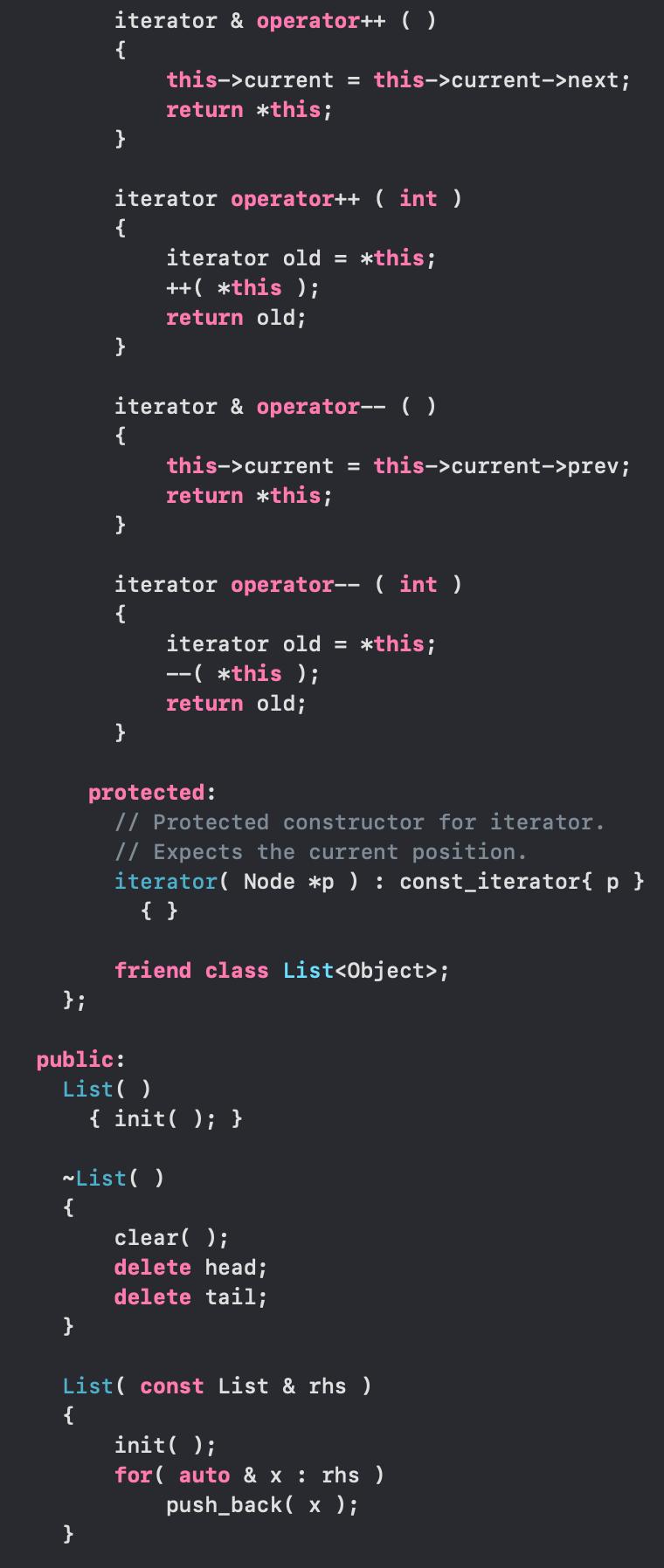
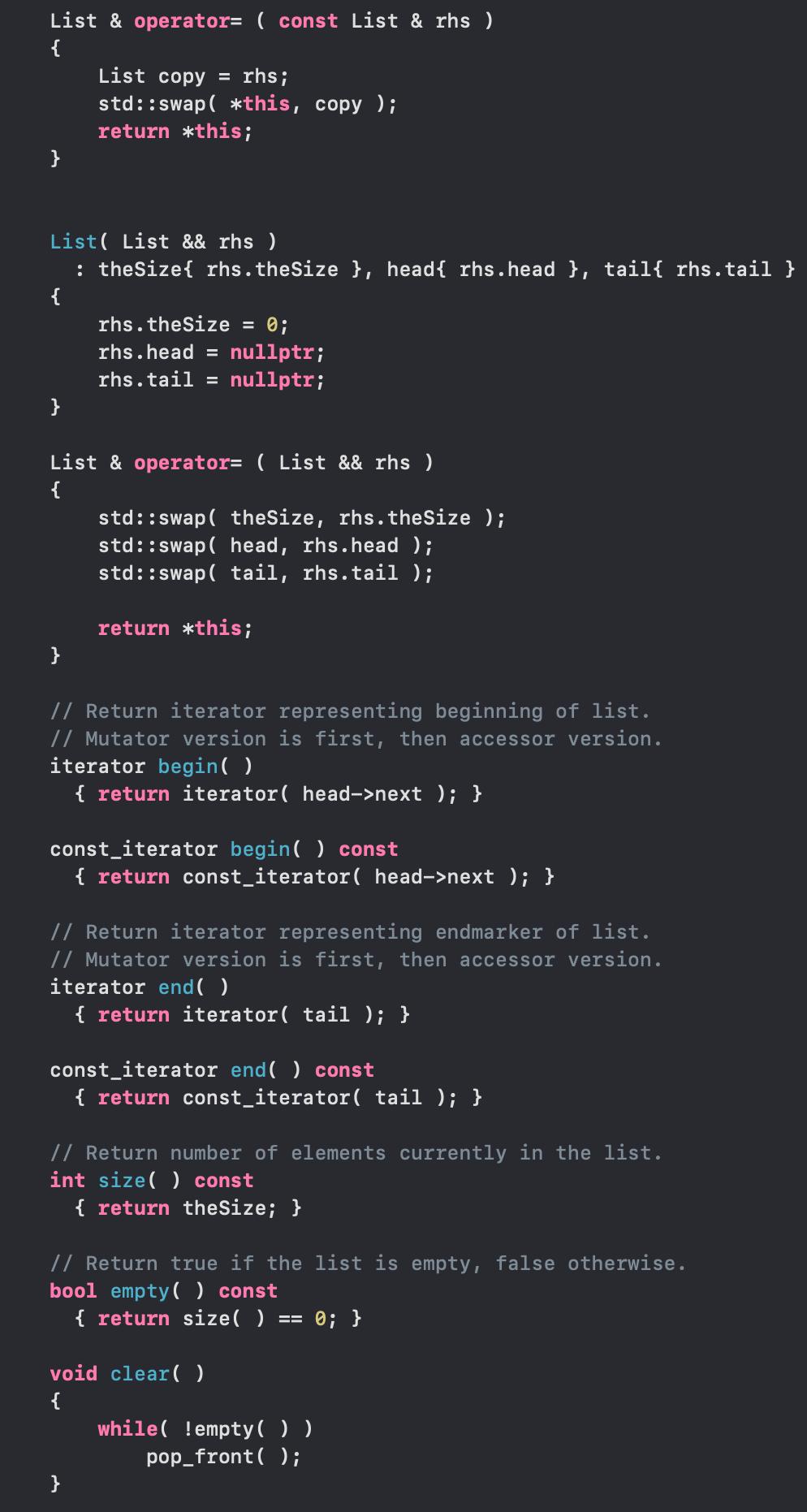
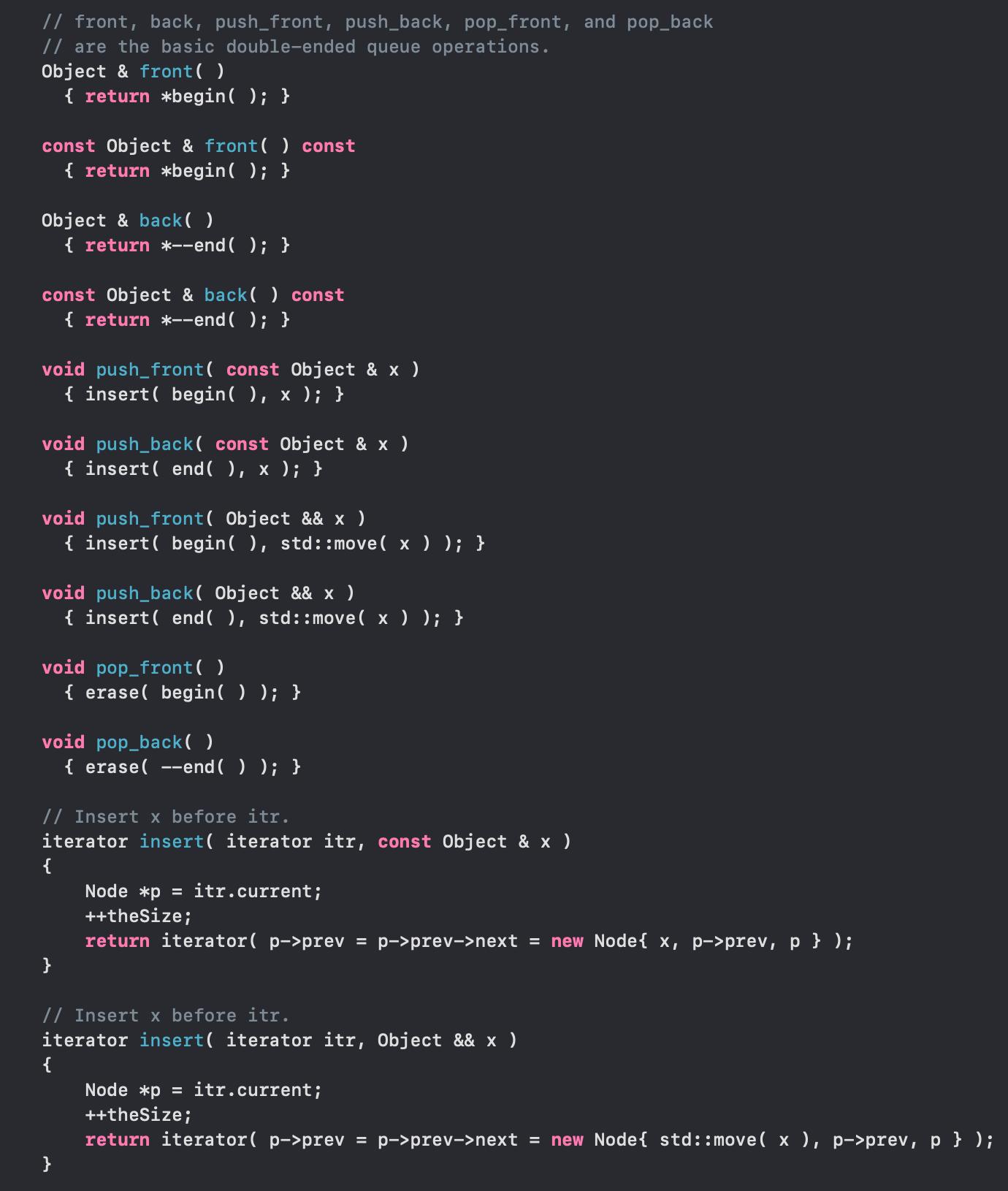
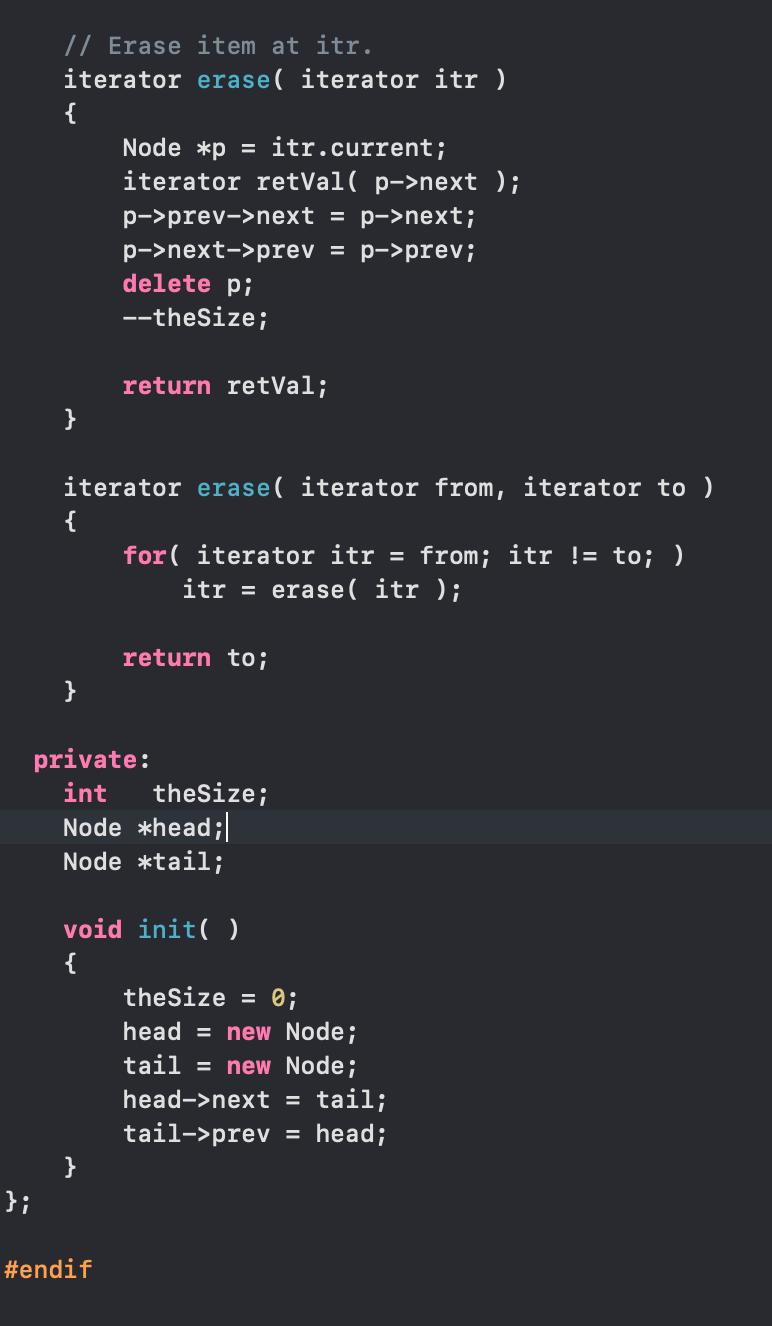
#ifndef LIST_H #define LIST_H #include using namespace std; template class List struct Node { { Object data; Node *prev; }; Node *next; Node(const Object & d = Object { }, Node * p = nullptr, Node * n = nullptr ) : data{ d }, prev{ p }, next{ n } { } Node(Object && d, Node * p = nullptr, Node * n = nullptr ) public: : data{ std::move( d ) }, prev{ p }, next{ n } { } class const_iterator { public: // Public constructor for const_iterator. const_iterator( ) : current{ nullptr } { } // Return the object stored at the current position. // For const_iterator, this is an accessor with a // const reference return type. const Object & operator* ( ) const { return retrieve ( ); } const_iterator & operator++ ( ) { current = current->next; return *this; } const_iterator operator++ ( int ) { const_iterator old = *this; ++( this ); return old; } const_iterator & operator-- ( ) { current = current->prev; } return *this;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


