Question: Objectives 1. Learn to create network packets. 2. Learn how packets can be sent over the network. 3. Familiarize you with the concept of sockets.

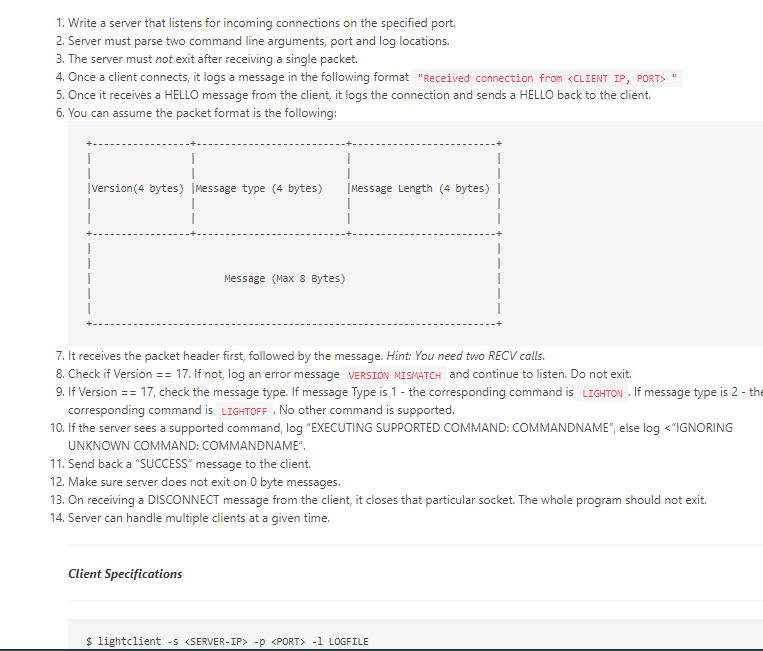
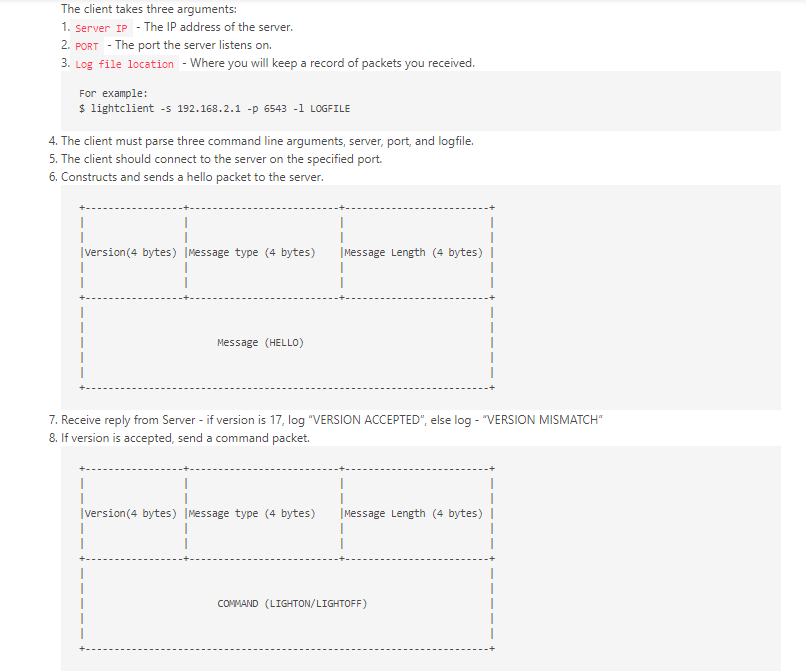
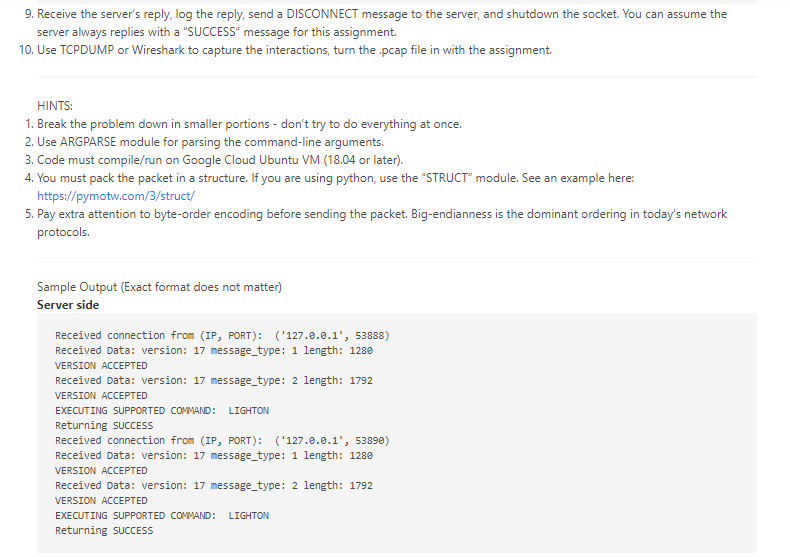
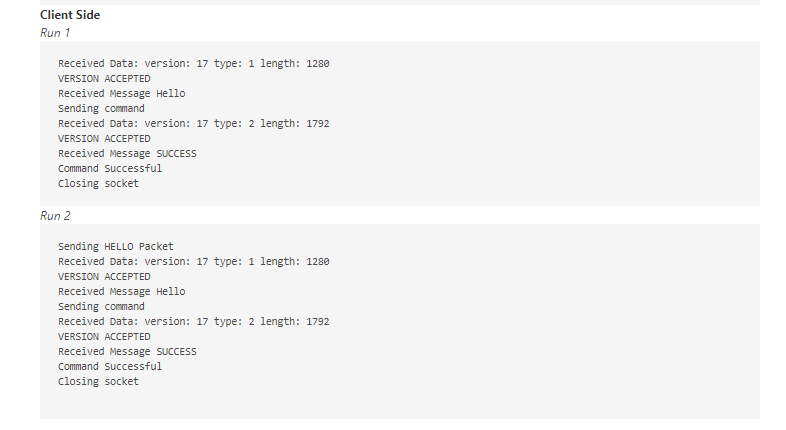
Objectives 1. Learn to create network packets. 2. Learn how packets can be sent over the network. 3. Familiarize you with the concept of sockets. 4. Learn packing structures, endianness, unpacking, and interpreting network data. 5. Learn how to use actual data from a packet. 6. Use packet capture to visually inspect protocols. Overview HINT: Look at python argparse" module for this portion. $ lightserver -p -1 1. PORT - The port server listens on. 2. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of actions. For example: $ lightserver -p 30000 -1 /tmp/logfile Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments, port and log locations. 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON. If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF . No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME", else log -D -1 LOGFILE The client takes three arguments: 1. Server IP - The IP address of the server. 2. PORT - The port the server listens on. 3. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of packets you received. For example: $ lightclient -5 192.168.2.1 -p 6543 -1 LOGFILE 4. The client must parse three command line arguments, server, port, and logfile. 5. The client should connect to the server on the specified port. 6. Constructs and sends a hello packet to the server. 1 version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | Message (HELLO) 7. Receive reply from Server - if version is 17, log "VERSION ACCEPTED", else log - "VERSION MISMATCH" 8. If version is accepted, send a command packet. version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 COMMAND (LIGHTON/LIGHTOFF) 9. Receive the server's reply, log the reply, send a DISCONNECT message to the server, and shutdown the socket. You can assume the server always replies with a "SUCCESS" message for this assignment 10. Use TCPDUMP or Wireshark to capture the interactions, turn the .pcap file in with the assignment. HINTS: 1. Break the problem down in smaller portions - don't try to do everything at once. 2. Use ARGPARSE module for parsing the command-line arguments. 3. Code must compile/run on Google Cloud Ubuntu VM (18.04 or later). 4. You must pack the packet in a structure. If you are using python, use the "STRUCT module. See an example here: https://pymotw.com/3/struct/ 5. Pay extra attention to byte-order encoding before sending the packet. Big-endianness is the dominant ordering in today's network protocols. Sample Output (Exact format does not matter) Server side Received connection from (IP, PORT): ('127.0.0.1', 53888) Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: LIGHTON Returning SUCCESS Received connection from (IP, PORT): ('127.0.0.1', 53890) Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: LIGHTON Returning SUCCESS Client Side Run 1 Received Data: version: 17 type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message Hello Sending command Received Data: version: 17 type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message SUCCESS Command Successful Closing socket Run 2 Sending HELLO Packet Received Data: version: 17 type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message Hello Sending command Received Data: version: 17 type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message SUCCESS Command Successful Closing socket Objectives 1. Learn to create network packets. 2. Learn how packets can be sent over the network. 3. Familiarize you with the concept of sockets. 4. Learn packing structures, endianness, unpacking, and interpreting network data. 5. Learn how to use actual data from a packet. 6. Use packet capture to visually inspect protocols. Overview HINT: Look at python argparse" module for this portion. $ lightserver -p -1 1. PORT - The port server listens on. 2. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of actions. For example: $ lightserver -p 30000 -1 /tmp/logfile Deliverables (each worth 5 points) 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 1. Write a server that listens for incoming connections on the specified port. 2. Server must parse two command line arguments, port and log locations. 3. The server must not exit after receiving a single packet. 4. Once a client connects it logs a message in the following format "Received connection from 5. Once it receives a HELLO message from the client, it logs the connection and sends a HELLO back to the client. 6. You can assume the packet format is the following: version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 Message (Max 8 Bytes) 7. It receives the packet header first, followed by the message. Hint: You need two RECV calls. 8. Check if Version == 17. If not, log an error message VERSION MISMATCH and continue to listen. Do not exit. 9. If Version == 17, check the message type. If message Type is 1- the corresponding command is LIGHTON. If message type is 2 - the corresponding command is LIGHTOFF . No other command is supported. 10. If the server sees a supported command, log "EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: COMMANDNAME", else log -D -1 LOGFILE The client takes three arguments: 1. Server IP - The IP address of the server. 2. PORT - The port the server listens on. 3. Log file location - Where you will keep a record of packets you received. For example: $ lightclient -5 192.168.2.1 -p 6543 -1 LOGFILE 4. The client must parse three command line arguments, server, port, and logfile. 5. The client should connect to the server on the specified port. 6. Constructs and sends a hello packet to the server. 1 version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | Message (HELLO) 7. Receive reply from Server - if version is 17, log "VERSION ACCEPTED", else log - "VERSION MISMATCH" 8. If version is accepted, send a command packet. version (4 bytes) |Message type (4 bytes) Message Length (4 bytes) | 1 1 COMMAND (LIGHTON/LIGHTOFF) 9. Receive the server's reply, log the reply, send a DISCONNECT message to the server, and shutdown the socket. You can assume the server always replies with a "SUCCESS" message for this assignment 10. Use TCPDUMP or Wireshark to capture the interactions, turn the .pcap file in with the assignment. HINTS: 1. Break the problem down in smaller portions - don't try to do everything at once. 2. Use ARGPARSE module for parsing the command-line arguments. 3. Code must compile/run on Google Cloud Ubuntu VM (18.04 or later). 4. You must pack the packet in a structure. If you are using python, use the "STRUCT module. See an example here: https://pymotw.com/3/struct/ 5. Pay extra attention to byte-order encoding before sending the packet. Big-endianness is the dominant ordering in today's network protocols. Sample Output (Exact format does not matter) Server side Received connection from (IP, PORT): ('127.0.0.1', 53888) Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: LIGHTON Returning SUCCESS Received connection from (IP, PORT): ('127.0.0.1', 53890) Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Data: version: 17 message_type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED EXECUTING SUPPORTED COMMAND: LIGHTON Returning SUCCESS Client Side Run 1 Received Data: version: 17 type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message Hello Sending command Received Data: version: 17 type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message SUCCESS Command Successful Closing socket Run 2 Sending HELLO Packet Received Data: version: 17 type: 1 length: 1280 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message Hello Sending command Received Data: version: 17 type: 2 length: 1792 VERSION ACCEPTED Received Message SUCCESS Command Successful Closing socket








